16-03-2024 - Economy - Businesses and objectives [EN]-[IT]

~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
16-03-2024 - Economy - Businesses and objectives [EN]-[IT]
Achievements and objectives
Businesses have the objective of maximizing profit, but this is not always the case as there are types of businesses that sell private or public goods.
In the context of public goods, the objectives are not always of a financial nature.
However, in a business it is important to understand well what the financial objectives are and these are essentially 4. They are listed below.
-Maximization of profit
-Break-even point
-Maximization of revenue
-Cost minimization
Business activities can operate in both the public and private sectors. Below are some examples.
Public parks, Police and Justice operate in the public sector
Healthcare, waste collection, dental services can operate in both the public and private sectors.
NOTE: In a State a certain percentage of the gross domestic product is allocated to public spending.
Profit Maximization
To calculate profit maximization we will need the following data: quantity, price, total revenue, average revenue, marginal revenue.
Consumer preferences
We can construct graphs in which to highlight the point at which the company maximizes profit by producing the quantity for which marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue.
We may have areas in the graphs that tell us that marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost, so an increase in production increases profit.
Or, still in the graphs, we can have areas in which the marginal cost is greater than the marginal revenue, so the reduction in production increases profit.
Marginal cost
Marginal cost is the cost of an additional unit produced, i.e. it corresponds to the change in total production costs that occurs when the quantity produced is changed by one unit.
Mathematically it is the derivative of the total cost (C) with respect to the quantity produced (q).
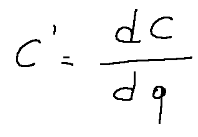
Marginal Revenue
Marginal revenue is the derivative of the total revenue of a commodity (the turnover of a company) with respect to the quantity of goods sold (which coincides with that produced if there is no stock of that commodity). Marginal revenue shows the impact of changes in sales of a commodity in overall revenue
Mathematically it is expressed like this
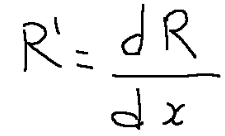
Break-even point
The break-even point is the production level at which the total cost equals the total revenue obtained from sales.
Revenue Maximization
Revenue maximization is aiming to have as much revenue as possible and this can be achieved by acting in three ways:
1-By acting on the price
2-Acting on the quantity
3-Acting on both price and quantity
Cost minimization
This activity aims to lower the cost of the product, but it is important to understand when this action must be implemented. Let's explain better. All products have their own life cycle based on: launch, growth, maturity and decline. We cannot apply the minimization strategy at any stage, it is important to apply it when the market is mature.
IMPORTANT NOTE: in a mature market, increasing the price as well as the quantity are two ineffective options.
Company objectives
In addition to good revenues, the company can also have as its objective the valorization of the company towards the shareholders.
As non-purely financial objectives, the company can have the following objectives:
-Social objectives
-Acquire market power
- Increase brand recognition
-Ethical and environmental objectives
-Objectives linked to image reputation.
Example of data table for profit monitoring
Below is a table showing the useful data to understand the profit and the change in profit.
The formulas for obtaining the data are indicated at the top of the table
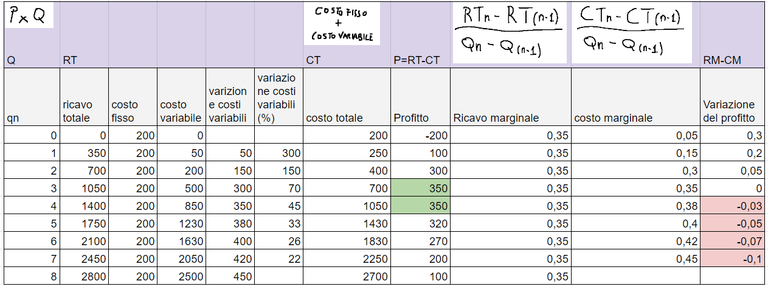
From this table we understand that the greatest profit stands at 350 in value and occurs when the quantities are 3 and 4, furthermore we see that the change in profit becomes negative when the quantities range from 4 to 7
Conclusions
Profit maximization is the main objective of a company, but it is not necessarily the only one. Each company can calculate the highest profit point.
Request
Have you ever seen a company's top profit calculations? Or have you seen these calculations performed?

ITALIAN
16-03-2024 - Economia -Imprese e obiettivi [EN]-[IT]
Imprese e obiettivi
Le imprese hanno come obiettivo la massimizzazione del profitto, ma non sempre è così in quanto ci sono tipologie di imprese che vendono beni privati o pubblici.
Nell’ambito dei beni pubblici gli obiettivi non sono sempre di carattere finanziario.
In un'impresa è comunque importante capire bene quali sono gli obiettivi finanziari e questi sono sostanzialmente 4. Sono elencati qui di seguito.
-Massimizzazione del profitto
-Punto di pareggio
-Massimizzazione del ricavo
-Minimizzazione dei costi
Le attività di impresa possono agire sia nel settore pubblico che nel settore privato. Qui di seguito ci sono degli esempi.
Parchi pubblici, Polizia e Giustizia agiscono nel settore pubblico
L’Assistenza sanitaria, la raccolta dei rifiuti, servizi odontoiatrici possono agire sia nel settore pubblico che in quello privato.
NOTA: In uno Stato una certa percentuale del prodotto interno lordo viene destinata alla spesa pubblica.
Massimizzazione del profitto
Per calcolare la massimizzazione del profitto avremo bisogno dei seguenti dati: quantità, prezzo, ricavo totale, ricavo medio, ricavo marginale.
Le preferenze del consumatore
Possiamo costruire grafici in cui evidenziare il punto in cui l’impresa massimizza il profitto producendo la quantità per la quale il costo marginale è uguale al ricavo marginale.
Possiamo avere delle zone nei grafici che ci indicano che il ricavo marginale è maggiore del costo marginale, quindi un aumento della produzione accresce il profitto.
Oppure, sempre nei grafici, possiamo avere delle zone in cui il costo marginale è maggiore del ricavo marginale, quindi la riduzione della produzione fa aumentare il profitto.
Costo marginale
Il costo marginale è il costo di un'unità aggiuntiva prodotta, cioè corrisponde alla variazione nei costi totali di produzione che si verifica quando si varia di un'unità la quantità prodotta.
Matematicamente è la derivata del costo totale (C) rispetto alla quantità prodotta (q).
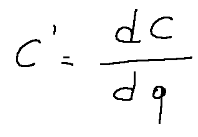
Ricavo marginale
Il ricavo marginale è la derivata del ricavo totale di una merce (il fatturato di un'impresa) rispetto alla quantità di merce venduta (che coincide con quella prodotta se siamo in assenza di scorte di quella merce). Il ricavo marginale mostra l'incidenza di variazioni delle vendite di una merce nel fatturato complessivo
Matematicamente si esprime così
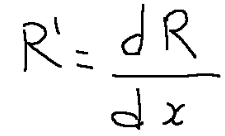
Punto di pareggio
Il punto di pareggio è il livello di produzione in corrispondenza del quale il costo totale è uguale al ricavo totale ottenuto dalle vendite.
Massimizzazione del ricavo
La massimizzazione del ricavo è puntare ad avere il maggior ricavo possibile e questo si può ottenere agendo in tre modi:
1-Agendo sul prezzo
2-Agendo sulla quantità
3-Agendo sia sul prezzo che sulla quantità
Minimizzazione dei costi
Questa attività mira ad abbassare il costo del prodotto, ma è importante bene capire quando questa azione deve essere messa in atto. Spieghiamo meglio. Tutti i prodotti hanno un proprio ciclo di vita basato su: lancio, crescita, maturità e declino. Non possiamo applicare la strategia di minimizzazione in qualsiasi fase, è importante applicarla quando il mercato è maturo.
NOTA IMPORTANTE: in un mercato maturo, l’aumento del prezzo così come della quantità sono due opzioni poco efficaci.
Obiettivi dell’impresa
Oltre a dei buoni ricavi, l’impresa può avere come obiettivo anche la valorizzazione dell’impresa nei confronti degli azionisti.
Come obiettivi non prettamente finanziari l’impresa può avere i seguenti obietti:
-Obiettivi sociali
-Acquisire potere di mercato
-Accrescere il riconoscimento della marca
-Obiettivi etici e ambientali
-Obiettivi legati alla reputazione di immagine.
Esempio di tabella dati per monitoraggio profitti
Qui di seguito una tabella in cui sono rappresentati i dati utili per comprendere il profitto e la variazione del profitto.
Nella parte alta della tabella sono indicate le formule per ricavare i dati

Da questa tabella comprendiamo che il maggior profitto si attesta su 350 di valore e avviene quando le quantità sono 3 e 4, inoltre vediamo che la variazione del profitto diventa negativa quando le quantità vanno da 4 a 7
Conclusioni
La massimizzazione del profitto è l'obiettivo principale di un'impresa, ma non è detto che sia l'unico. Ogni impresa può calcolare il punto di maggior profitto.
Domanda
Avete mai visto i calcoli di maggior profitto di un'impresa? Oppure avete visto eseguire questi calcoli?
THE END
Non li ho visti, ma so che è un argomento su cui si concentrano.
In effetti è difficile vedere i calcoli di maggior profitto di un'impresa per due motivi, sono documenti e calcoli che potrebbero avere un certo grado di riservatezza, l'altro motivo è che le piccole e medie imprese molto spesso non fanno questi calcoli... preferiscono guadagnare quando c'è da guadagnare e chiudere quando arrivano i problemi, senza dover far tanta fatica a far calcoli e a cercare di sistemare la situazione quando diventa difficile.
Don’t you think we also need to calculate our profit when we want to calculate profit maximization so when we remove our capital and other things, we’d know how much we’ve got left
Hi @rafzat , it's exactly as you say. The important thing is to establish how many differences there must be between the cost and the price. This will be important to stay on the market.
I am able to lead a lot from this lecture and the truth is we can still combine both to push one business forward
Thanks for being here. The main concept of this article can be summarized very briefly in the following sentence. The company can act in 3 ways: on price, on quantity or on both.
This lecture is very useful even to those who are not economic oriented. It makes me understand business prospects
Hi @christybliss , For a business it is important to always seek profit maximization. Once the right strategy to maximize profit has been found, it is not certain that it will be valid over time, because factors can change. Therefore profit maximization is something that must always be sought and adapted. When companies are no longer able to maximize profit they begin to have inefficiencies and have problems because they begin to earn less and less.
Sometimes I always find it hard to differentiate between economics and business education.
Hi @precab Sometimes it is difficult to distinguish the two things, business management merges with the principles of economics. I would say that very often there are two topics that are related to each other.