13-07-2024 - Energy systems - The 2T Otto cycle [EN]-[IT]

~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
13-07-2024 - Energy systems - The 2T Otto cycle [EN]-[IT]
The 2T Otto cycle
The two-stroke Otto cycle offers a synthesis between power and construction simplicity. This characteristic makes it suitable for a wide range of applications where low weight and high specific power are essential. However, its inefficiencies in terms of fuel consumption and polluting emissions must be considered. These two negative aspects significantly restrict the use of two-stroke engines.
Two-stroke engine
Two-stroke engines are, as the name suggests, engines that complete the thermodynamic cycle in 2 strokes or 2 phases.
Description of the two times
-During the first time the washing ports (openings from which the fluid enters and exits the cylinder) are closed, the piston generates depression in the crankcase, attracting fresh charge. In this phase the compression and ignition transformations take place directly in the cylinder.
-In the second half the piston compresses the fresh charge in the crankcase during its downward stroke and transfers the charge into the cylinder. These are the combustion and expansion phases.
In a two-stroke engine the intake, compression, combustion and expansion, and exhaust phases overlap.
The two-stroke engine has no mechanically controlled valves.
Difference between 4T and 2T
Below are the main differences between a 2T and a 4T spark ignition engine.
Working cycle
The main difference between a two-stroke engine and a 4-stroke engine is in the duty cycle. In a 2-stroke engine, a work cycle is completed in two piston movements, while a 4-stroke engine: completes a work cycle in four piston movements.
Number of Phases
-The 2T engine has two main phases. One phase is that of Suction-compression and the other that of Ignition-expansion and Exhaust.
-The 4T engine has four distinct phases, intake, compression, combustion and expansion with exhaust.
Valves and Lights
The two-stroke engine uses ports, or openings in the cylinder, to transfer the air-fuel mixture and to exhaust the burnt gases.
Instead, the four-stroke engine uses valves mechanically controlled by a camshaft to control the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust ports.
Wash
At a certain point in operation, in the two-stroke engine, a port opens in the cylinder which discharges the gas spontaneously. Consequently there will be an immediate drop in pressure until a port (wash) opens from where fresh mixture is introduced.
Basically, washing is that phase in which the fresh charge introduced into the cylinder contributes to expelling the burnt gases.
Diagram
Below is the distribution diagram
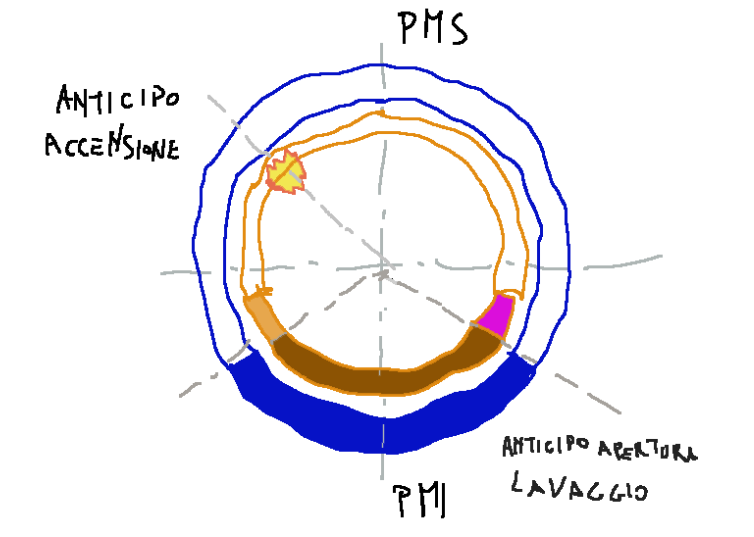
Conclusions
We can say that two-stroke (2T) and four-stroke (4T) engines have distinct advantages and disadvantages that make them suitable for different applications, but 2-stroke engines have negative characteristics that today are not in line with the modern challenges related to pollution.
Request
In your youth, did you ever ride a moped with a 2-stroke engine?

ITALIAN
13-07-2024 - Sistemi energetici - Il ciclo Otto a 2T [EN]-[IT]
Il ciclo Otto a 2T
Il ciclo Otto a due tempi offre una sintesi tra potenza e semplicità costruttiva. Questa sua caratteristica lo rende adatto per una vasta gamma di applicazioni dove il peso ridotto e l'alta potenza specifica sono essenziali. Bisogna però considerare le sue inefficienze in termini di consumo di carburante e di emissioni inquinanti. Questi due aspetti negativi restringono notevolmente l'impiego dei motori a due tempi.
Motore a due tempi
I motori a due tempi sono, come suggerisce il nome, motori che compiono il ciclo termodinamico in 2 tempi o 2 fasi.
Descrizione dei due tempi
-Durante il primo tempo vengono chiuse le luci di lavaggio (aperture dalle quali il fluido entra ed esce nel cilindro), il pistone genera depressione nel basamento richiamando carica fresca.In questa fase avvengono le trasformazioni di compressione ed accensione direttamente nel cilindro.
-Nel secondo tempo il pistone comprime la carica fresca nel basamento durante la sua corsa di discesa e trasferisce la carica nel cilindro. Queste sono le fasi di combustione ed espansione.
In un motore a due tempi le fasi di aspirazione, compressione, combustione ed espansione, e scarico si sovrappongono.
Il motore a due tempi non ha valvole comandate meccanicamente.
Differenza tra 4T e 2T
Qui di seguito sono le principali differenze tra un motore ad accensione comandata 2T e uno 4T.
Ciclo di lavoro
La differenza principale tra un motore a due tempi ed uno a 4 tempi è nel ciclo di lavoro. Nel motore 2T viene completato un ciclo di lavoro in due movimenti del pistone, mentre un Motore 4T: completa un ciclo di lavoro in quattro movimenti del pistone.
Numero di Fasi
-Il motore 2T ha due fasi principali. Una fase è quella di Aspira-compressione e l’altra quella di Accensione-espansione e Scarico.
- Il motore 4T ha quattro fasi ben distinte, aspirazione, compressione, combustione ed espansione con scarico.
Valvole e Luci
Il motore a due tempi utilizza luci, ovvero delle aperture nel cilindro, per il trasferimento della miscela aria-carburante e per lo scarico dei gas combusti.
Invece, il motore a quattro tempi utilizza valvole comandate meccanicamente da un albero a camme per controllare l'apertura e la chiusura delle porte di aspirazione e scarico.
Lavaggio
Ad un certo punto del funzionamento, nel motore a due tempi, si apre una luce nel cilindro che scarica il gas spontaneamente. Conseguentemente si avrà un immediato calo della pressione fino a quando si aprirà anche una luce (lavaggio) da dove viene introdotta miscela fresca.
Sostanzialmente il lavaggio è quella fase in cui la carica fresca che si immette nel cilindro contribuisce ad espellere i gas combusti.
Diagramma
Qui di seguito il diagramma della distribuzione

Conclusioni
Possiamo dire che i motori a due tempi (2T) e a quattro tempi (4T) presentano vantaggi e svantaggi distinti che li rendono adatti a diverse applicazioni, ma i motori a 2 tempi hanno caratteristiche negative che oggi non sono in linea con le sfide moderne relative all'inquinamento.
Domanda
Nella vostra giovinezza avete mai guidato anche voi un ciclomotore con motore a 2tempi?
THE END
These types of circles is really needed to understand in depth what is needed to be understood
Thanks for leaving a comment. One thing that is often forgotten is that in a 2-stroke engine the wash port is closed and the exhaust port remains open for a short distance contributing to the release of gas and fresh mixture, while it is not correct to think that in a 2-stroke engine the absence of valves allows a more efficient charge replacement process than that of a 4-stroke engine.
I think adding a big of colors to your diagrams will make us understand it better
This is easy
Thanks for commenting. In this article I tried to draw the circular diagram in color. I too noticed that colors help to understand concepts better. In this article I have described some things, in my opinion one of the important things to know regarding the 2T Otto cycle is that in a 2T engine during the washing phase the fresh charge that is introduced into the cylinder contributes to expelling the burnt gases.
The circle was very easy for me to understand this time
I think you should keep adding colors
Thanks for being here. In this article I also wanted to draw the diagram. In my opinion, an important thing in this article is to remember that in a two-stroke engine, during the first time the piston closes the wash ports and the pressure difference draws the fresh charge into the crankcase
Great breakdown of the 2T cycle vs. 4T engines brother. The differences are clear and pretty informative. Nice one as always 💯
Thank you for leaving a few words in this article. I'll try to give a technical contribution. These contents are always difficult to understand and explain and I try to continuously improve, that is, to make them as understandable as I can, but I understand that I have to improve. In the 2 stroke Otto cycle I believe that one thing to keep in mind is the fact that in this cycle during the first half the piston closes the washing ports and the pressure difference draws the fresh charge into the crankcase
Thank you brother because it's no doubt a pretty technical one. You're actually doing great making it as understandable as can be. Some of the people don't really have much physics and engineering experience so to be able to get them to at least get an idea of what you're saying is great. Perfect job man