11-07-2024 - Energy systems - internal combustion engines [EN]-[IT]

~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
11-07-2024 - Energy systems - internal combustion engines [EN]-[IT]
internal combustion engines
Internal combustion engines are volumetric endothermic machines operating in an open circuit. In internal combustion engines the various thermodynamic transformations of the reference cycles occur in temporal succession in the same place. Gas turbines have a similar thermodynamic cycle, but perform the thermodynamic transformations in different parts of the machine, not in the same place as in internal combustion engines.
Below is a sketch of an internal combustion engine
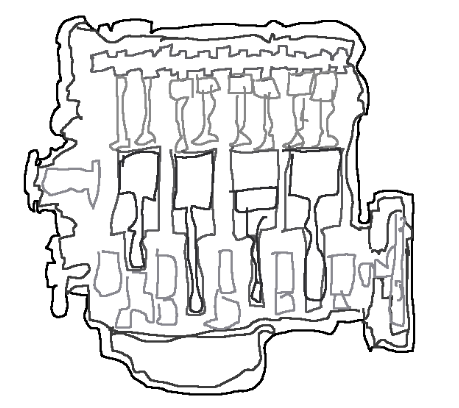
Classification
Internal combustion engines are classified based on different reasoning, below are some of these classifications:
-Based on the operating cycle
-Depending on the ignition method
-Depending on the type of fuel
-Depending on the cylinder configuration
-Depending on the air supply system
-Based on the arrangement of the cylinders
-Depending on the application
-Depending on the crankshaft arrangement
In particular we can describe the following particular distinctions:
-Classification based on ignition:
spark ignition engines (petrol engines, LPG)
Compression ignition engines (Diesel engines)
-Classification based on the cycle period:
four-stroke engines (4T)
two-stroke engines (2T)
-Classification based on nutrition
aspirated engines
supercharged engines
Application fields
Internal combustion engines have a wide field of application because these engines have excellent modularity of the construction architecture.
Below is a list of some application fields:
Automotive
Aeronautics
Naval
Industrial and agricultural machines
Stationary applications (Emergency generators, pumps and compressors)
Garden machinery and gardening equipment
Specialized and military applications
Main components
Below are the main components of an internal combustion engine:
Engine block
Cylinders and pistons
Cylinder head
Crankshaft
Connecting rods
Lubrication system
Cooling system
Power supply system
Exhaust system
Ignition system (for petrol engines)
Injection system (for Diesel engines)
Conclusions
Internal combustion engines represent a consolidated and indispensable technology for many industrial and transport applications. Today, however, the challenges and developments are moving towards more sustainable and cleaner technologies.
Request
In your opinion, will the automotive sector move forward with the development of internal combustion engines or with the development of electric motors?

ITALIAN
11-07-2024 - Sistemi energetici - motori a combustione interna [EN]-[IT]
motori a combustione interna
I motori a combustione interna sono macchine endotermiche volumetriche funzionanti a circuito aperto. Nei motori a combustione interna le varie trasformazioni termodinamiche dei cicli di riferimento avvengono in successione temporale nel medesimo luogo. Le turbine a gas hanno un ciclo termodinamico simile, ma eseguono le trasformazioni termodinamiche in parti diverse della macchina, non nello stesso luogo come nei motori a combustione interna.
Qui di seguito uno schizzo di un motore a combustione interna

Classificazione
I motori a combustione interna si classificano in base a diversi ragionamenti, qui di seguito alcune di queste classificazioni:
-In base al ciclo di funzionamento
-In base al metodo di accensione
-In base al tipo di combustibile
-In base alla configurazione dei cilindri
-In base al sistema di alimentazione dell'aria
-In base alla disposizione dei cilindri
-In base all'applicazione
-In base alla disposizione dell'albero motore
In particolare possiamo descrivere le seguenti particolari distinzioni:
-Classificazione in base all’accensione:
motori ad accensione comandata (motori a benzina, gpl)
motori ad accensione spontanea (motori Diesel)
-Classificazione in base il periodo del ciclo:
motori a quattro tempi (4T)
motori a due tempi (2T)
-Classificazione in base all’alimentazione
motori aspirati
motori sovralimentati
Campi di applicazione
I motori a combustione interna hanno un ampio campo di applicazione perché questi motori hanno un’ottima modularità dell’architettura costruttiva.
QUi di seguito un elenco di alcuni campi applicativi:
Automotive
Aeronautico
Navale
Macchine industriali e agricole
Applicazioni stazionarie (Generatori di emergenza, pompe e compressori)
Macchine da giardino e attrezzature da giardinaggio
Applicazioni specializzate e militari
Componenti principali
Qui di seguito i componenti principali di un motore a combustione interna:
Blocco motore
Cilindri e pistoni
Testata del cilindro
Albero motore
Bielle
Sistema di lubrificazione
Sistema di raffreddamento
Sistema di alimentazione
Sistema di scarico
Sistema di accensione (per motori a benzina)
Sistema di iniezione (per motori Diesel)
Conclusioni
I motori a combustione interna rappresentano una tecnologia consolidata e indispensabile per molte applicazioni industriali e di trasporto. Oggi però le sfide e le evoluzioni vanno verso tecnologie più sostenibili e più pulite.
Domanda
Secondo voi nel settore automotive si andrà avanti con lo sviluppo di motori a combustione interna o con lo sviluppo di motori elettrici?
THE END
Dear Steffano, you’re really good with physics courses
Keep it up!
I’m trying to get that diagram in my head but I’m unable to
It’s quite difficult
I wish you were my teacher on physics at school!
Have you considered Nicolai Tesla’s theories on free energy and vibrations?
Some talked about zero point energy.
I think electric motors will lead the way in automotive future for cleaner technologies. Nice one again brother
You are really doing a very great job in those courses