11-03-2025 - Chemistry Basics - Chemical Reactions [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
11-03-2025 - Chemistry Basics - Chemical Reactions [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction regarding the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_86)
Chemical Reactions
Definition of chemical reaction
Let's first establish what is meant in the chemical field when we talk about chemical reaction. When one or more substances are transformed into one or more other different substances, a process occurs and this process is defined as chemical reaction.
Where:
-Reagents = the substances
-Products = the substances that have been transformed
The most common examples of chemical reactions are:
-Combustion
-Synthesis
-Decomposition
-Exchange reactions
Example of a chemical reaction:
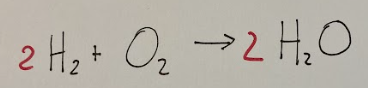
Balancing chemical reactions
Balancing chemical reactions ensures that the number of atoms of each element is the same in both the reactants and the products.
In this case, the law of conservation of mass is respected
Law of conservation of mass in chemistry*
This law states that the total mass of the reactants must be equal to the total mass of the products.
Example

In this case we have that 1 molecule of nitrogen can react with 3 molecules of hydrogen to give 2 molecules of ammonia.
We can also look at it this other way.
1 mole (of molecules) of nitrogen can react with 3 moles (of molecules of hydrogen) to give 2 moles (of molecules) of ammonia.
Basically to balance a chemical reaction we have to add coefficients (stoichiometric coefficients) to balance the number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation. You have to make sure that the coefficients are as small as possible.
Limiting reagent
When a chemical reaction starts there is a reagent that is consumed first which limits the amount of product that can be formed. This reagent is called the limiting reagent.
It should be noted that once the limiting reagent is exhausted, the reaction process does not continue, that is, the chemical reaction stops.
Excess reagent
At this point, after having expressed the concept of limiting reagent, we can introduce the concept of excess reagent. Very simply, the excess reagent is the reagent that remains after the chemical reaction has exhausted the limiting reagent, therefore the reaction stops. Therefore, this reagent will not be completely consumed because the limiting reagent has been exhausted.
When we want to optimize chemical reactions, the concept of excess reagent is very important. If we know the chemical reaction well, we can reduce the waste of the various substances.
Yield of a reaction
The word yield derives precisely from the word efficiency. Therefore, the yield of a reaction is in reality, the actual quantity that is obtained from a chemical reaction compared to the theoretical quantity.
Therefore, from what has just been written, we can immediately understand that there are two types of yield, the theoretical one and the actual one.
WHERE:
Theoretical yield = maximum quantity of product that could be obtained assuming that the chemical reaction does not produce losses.
Actual yield = quantity of product actually obtained from the chemical reaction.
The yield of a reaction is influenced by several factors:
-Losses during handling
-Collateral reactions
-Inefficiencies of the process
Below is the formula for the yield of a reaction in percentage.
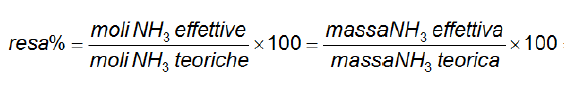
Conclusions
To optimize a chemical reaction, that is, to have as few wastes of reagents as possible, we must consider several things: the balance of the chemical reaction we are considering, the limiting reagent, the excess reagent and the yield of the reaction.
Question
Have you ever tried to trigger a chemical reaction between two substances in a laboratory? Have you ever mixed two reagents in two different test tubes by pouring the contents of one into the other?

[ITALIAN]
11-03-2025 - Basi di chimica - Reazioni chimiche [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_86)
Reazioni chimiche
Definizione di reazione chimica
Stabiliamo innanzitutto che cosa si indica nell'ambito chimico quando si parla di reazione chimica. Quando una o più sostanze si trasformano in una o altre sostanze diverse avviene un processo e questo processo è definito reazione chimica.
Dove:
-Reagenti = le sostanze
-Prodotti = le sostanze che si sono trasformate
Gli esempi più comuni delle reazioni chimiche sono:
-La combustione
-La sintesi
-La decomposizione
-Le reazioni di scambio
Esempio di una reazione chimica:
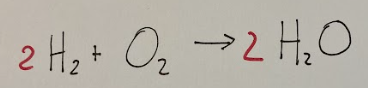
Bilanciamento delle reazioni chimiche
Il bilanciamento delle reazioni chimiche fa in modo che il numero di atomi di ciascun elemento sia lo stesso sia nei reagenti che nei prodotti.
In questo caso viene rispettata la legge di conservazione della massa
Legge di conservazione della massa in chimica*
Questa legge afferma che la massa totale dei reagenti deve essere uguale alla massa totale dei prodotti.
Esempio

In questo caso abbiamo che 1 molecola di azoto può reagire con 3 molecole di idrogeno per dare 2 molecole di ammoniaca.
Possiamo anche vedere la cosa in questa altra maniera.
1 mole (di molecole) di azoto può reagire con 3 moli (di molecole di idrogeno) per dare 2 moli (di molecole) di ammoniaca.
Sostanzialmente per bilanciare una reazione chimica dobbiamo aggiungere dei coefficienti (coefficienti stechiometrici) per bilanciare il numero di atomi di ciascun elemento su entrambi i lati dell'equazione. Bisogna assicurarsi che i coefficienti siano i più piccoli possibili.
Reagente limitante
Quando si innesca una reazione chimica c'è un reagente che viene consumato per primo il quale limita la quantità di prodotto che può essere formata. Questo reagente viene appunto chiamato reagente limitante.
Si precisa che una volta che il reagente limitante si esaurisce il processo di reazione non prosegue, cioè la reazione chimica si ferma.
Reagente in eccesso
A questo punto, dopo aver espresso il concetto di reagente limitante possiamo introdurre il concetto di reagente in eccesso. Molto semplicemente il reagente in eccesso è il reagente che rimane dopo che la reazione chimica ha esaurito il reagente limitante, quindi la reazione si ferma. Quindi questo reagente non verrà completamente consumato perché il reagente limitante è stato esaurito.
Quando vogliamo ottimizzare le reazioni chimiche il concetto di reagente in eccesso è molto importante. Se conosciamo bene la reazione chimica, possiamo ridurre gli sprechi delle varie sostanze.
Resa di una reazione
La parola resa deriva appunto dalla parola rendimento. Quindi la resa di una reazione è in realtà, la quantità effettiva che si ottiene da una reazione chimica rispetto alla quantità teorica.
Quindi da quanto appena scritto possiamo subito comprendere che ci sono due tipi di resa, quella teorica e quella effettiva.
DOVE:
Resa teorica = quantità massima di prodotto che si potrebbe ottenere supponendo che la reazione chimica non produca perdite.
Resa effettiva = quantità di prodotto realmente ottenuta dalla reazione chimica.
La resa di una reazione è influenzata da diversi fattori:
-Perdite durante la manipolazione
-Reazioni collaterali
-Inefficienze del processo
Qui di seguito la formula della resa di una reazione in perceentuale.
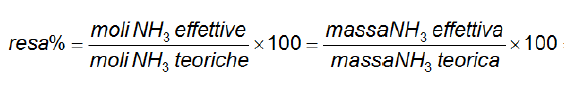
Conclusioni
Per ottimizzare una reazione chimica, cioè avere meno sprechi di reagenti possibili, dobbiamo considerare diverse cose: il bilanciamento della reazione chimica che stiamo considerando, il reagente limitante, il reagente in eccesso e la resa della reazione.
Domanda
Avete mai provato ad innescare una reazione chimica tra due sostanze in un laboratorio? Avete mai mischiato due reagenti in due provette diverse versando il contenuto dell'una nell'altra?
THE END
Wow, that's awesome
#hive #chemistry
https://x.com/jewellery_all/status/1899374578163732978
This is beyond my knowledge😅
Thanks for the lecture
Thanks for stopping by. We can summarize the concept of this article by simply saying that chemical reactions are those reactions that transform substances into other substances. For example, ideogen and oxygen can react to form water.
I remember trying to understand this particular topic back then in school. It was really difficult
Thanks for stopping by. Chemical reactions are processes that transform initial substances into new substances. This process occurs through the breaking of chemical bonds and the formation of new chemical bonds. The example I gave in the post, that of water, I think is the most understandable example
@stefano.massari, I paid out 0.268 HIVE and 0.064 HBD to reward 2 comments in this discussion thread.