10-07-2024 - Energy systems - Performance of a gas turbine plant [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
10-07-2024 - Energy systems - Performance of a gas turbine plant [EN]-[IT]
Performance of a gas turbine system
Thermodynamic efficiency
Below is the expression of the thermodynamic efficiency of a gas turbine unit.
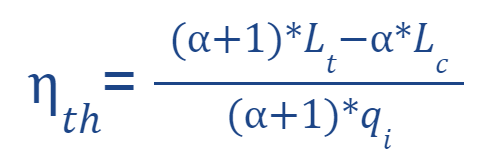
The thermodynamic efficiency of a gas turbine unit represents the efficiency with which the system converts the thermal energy of the fuel into useful mechanical energy. Therefore it is an efficiency that in this context takes on vital importance as this efficiency turns out to be a key indicator of the system's performance.
The thermodynamic efficiency of a gas turbine unit is directly influenced by the isentropic efficiencies of the compressor and turbine.
Global performance
Below is the expression of the global efficiency of a gas turbine plant
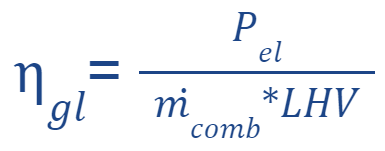
The overall performance of the system is important above all to optimize the use of the energy contained in the fuel.
The importance of this efficiency lies in the fact that improving this data means reducing the amount of fuel needed to produce the same amount of energy. Acting on this efficiency essentially contributes to improving the overall efficiency of the gas turbine system.
Net work
Below is the formula for the net work produced by a gas turbine unit
The net work produced by a gas turbine unit is expressed by considering the isentropic efficiencies of the turbine and compressor.
Below is the net work formula:
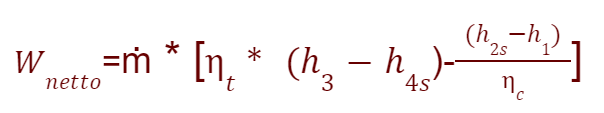
Where:
ṁ = is the mass flow rate of the working fluid
nt = isentropic efficiency of the turbine
nc = isentropic efficiency of the compressor
h1 = enthalpy of the fluid at the compressor inlet
h2s = enthalpy of the fluid at the compressor outlet in isentropic conditions
h3 = enthalpy of the fluid at the turbine inlet.
h4s = enthalpy of the fluid at the turbine outlet in isentropic conditions
Sankey diagram
Shown below is the Sankey diagram of energy flows in a gas turbine plant
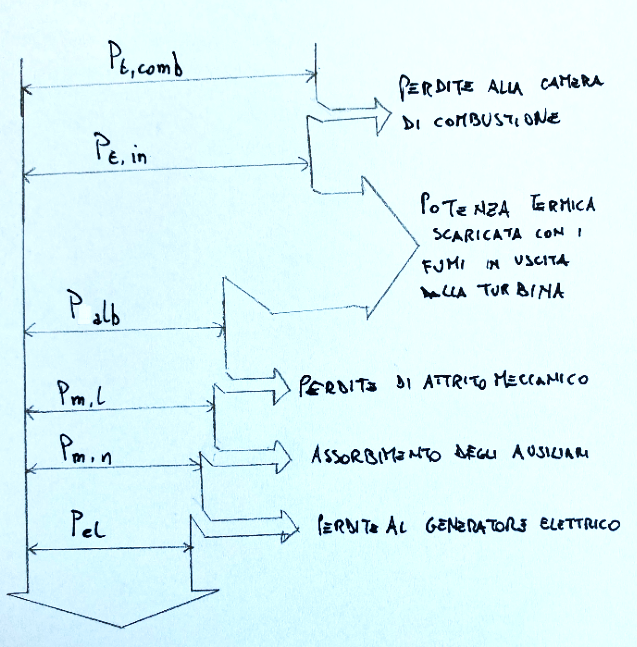
The Sankey diagram is the right tool to visualize the analysis of energy flows as it clearly shows the energy balances. It is used to improve the efficiency and sustainability of industrial and environmental processes.
Conclusions
When designing a gas turbine system, thermodynamic efficiency is very important. This allows you to save fuel and pollute less
Request
Sankey diagrams visually accentuate large transfers or flows within a system, have you seen this type of diagram before?

ITALIAN
10-07-2024 - Sistemi energetici - Prestazioni di un impianto turbogas[EN]-[IT]
Prestazioni di un impianto turbogas
Rendimento termodinamico
Qui sotto l’espressione del rendimento termodinamico di un gruppo turbogas.
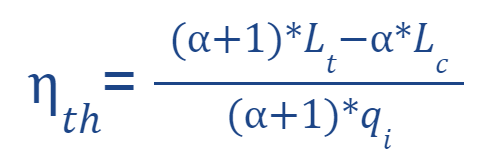
Il rendimento termodinamico di un gruppo turbogas rappresenta l’efficienza con cui l'impianto converte l’energia termica del combustibile in energia meccanica utile. Quindi è un rendimento che in questo ambito assume un importanza vitale in quanto questo rendimento risulta essere un indicatore chiave della performance dell’impianto.
Il rendimento termodinamico di un gruppo turbogas è influenzato direttamente dalle efficienze isoentropiche del compressore e della turbina.
Rendimento globale
Qui di seguito l’espressione del rendimento globale di un impianto turbogas
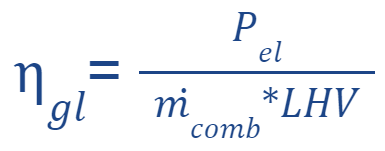
Il rendimento globale dell'impianto è importante soprattutto per ottimizzare l’uso dell’energia contenuta nel combustibile.
L’importanza di questo rendimento sta nel fatto migliorare questo dato significa ridurre la quantità di combustibile necessario per produrre la stessa quantità di energia. Agendo su questo rendimento sostanzialmente si contribuisce a migliorare l’efficienza complessiva dell’impianto turbogas.
Lavoro netto
Qui di seguito la formula del lavoro netto prodotto da un gruppo turbogas
Il lavoro netto prodotto da un gruppo turbogas viene espresso considerando le efficienze isoentropico della turbina e del compressore.
Qui di seguito la formula del lavoro netto:
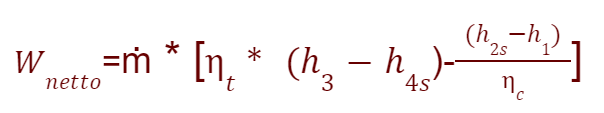
Dove:
ṁ = è la portata massica del fluido di lavoro
nt = efficienza isoentropica della turbina
nc = efficienza isoentropica del compressore
h1 = entalpia del fluido all'ingresso del compressore
h2s = entalpia del fluido all'uscita del compressore in condizioni isoentropiche
h3 = entalpia del fluido all'ingresso della turbina.
h4s = entalpia del fluido all'uscita della turbina in condizioni isoentropiche
Diagramma di Sankey
Qui di seguito è mostrato il diagramma di Sankey dei flussi energetici in un impianto turbogas

Il diagramma di Sankey è lo strumento adatto per visualizzare l’analisi dei flussi energetici in quanto mostra in modo chiaro i bilanci energetici. Viene utilizzato per migliorare l’efficienza e la sostenibilità dei processi industriali e ambientali.
Conclusioni
Quando si progetto un sistema turbogas il rendimento termodinamico è importantissimo. Questo permette di risparmiare combustibile ed inquinare meno
Domanda
I diagrammi di Sankey accentuano visivamente i grandi trasferimenti o flussi all'interno di un sistema, avevate già visto questa tipologia di diagrammi?
THE END
Nice course
I’ve never seen this kind of diagram before but I’m glad to see it
This is very insightful brother. The Sankey diagram effectively illustrates energy flows within the turbine plant. Great work on it
This is well explained
I have seen such diagram before
Thank you!
At first it was really difficult for me to understand this diagram but as time goes on, I actually understand