06-04-2024 - Economy - demand for free competition [EN]-[IT]

~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
06-04-2024 - Economy - demand for free competition [EN]-[IT]
free competition application
brief notes
The conditions of free competition exist when we are in a market in which the objective of companies is to maximize profit. When there is free competition you are in a market that generates profit in the short term and which is crowded with companies. The other two important conditions of the free competition market are:
1-Entry is free and any business can choose to enter at any time
2-There is no profit in the long run.
Demand curve
When we are in a free market condition and we find ourselves in front of a graph like the one shown below (price graph, quantity produced), we can say that the demand curve is flat and is only sold at a price, whatever the quantity produced.
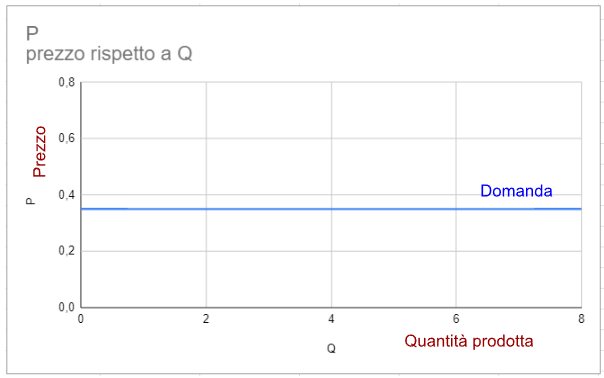
In this case the company acts in perfect competition and will be able to sell the quantity it can produce at that specific price, not at a different price.
Free market variables
The main variables to consider when analyzing a free competition market are the following:
-The price
-The total revenue
-The average revenue
-Marginal revenue
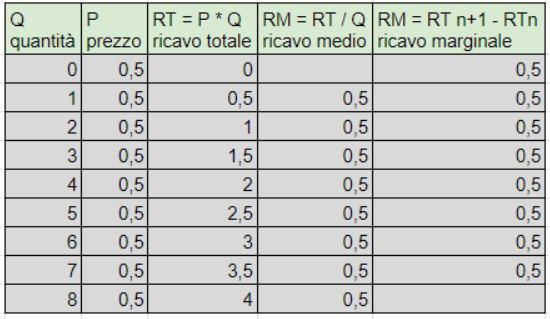
The characteristics of a free competition market show a total revenue that increases as the quantity increases. Another characteristic is that the average revenue remains constant like the price. Finally, it is verified that the marginal revenue is equal to the price.
These considerations and these characteristics then lead to the graph shown previously, the one where the slope of the demand line is horizontal.
Below is an example of a table with the main variables described above
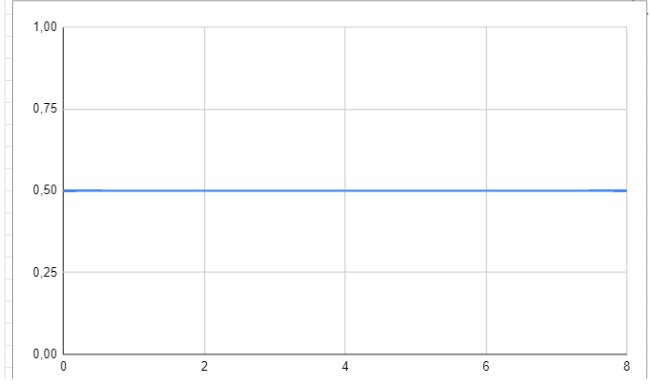
Below is the graph where we have the quantity produced on the abscissae and the price on the ordinate. The curve is a straight line.
Conclusions
When we are faced with a perfectly competitive market, the price never changes even if the quantity produced increases or decreases.
Request
Do you work in any company? If YES, in which market does the company you work for operate?

ITALIAN
06-04-2024 - Economia - domanda di libera concorrenza [EN]-[IT]
domanda di libera concorrenza
brevi cenni
Le condizioni di libera concorrenza ci sono quando siamo in un mercato in cui l’obiettivo delle imprese è quello di massimizzare il profitto. Quando c’è libera concorrenza si è in un mercato che genera profitto nel breve periodo e che è affollato di imprese. Le altre due condizioni importanti del mercato di libera concorrenza sono:
1-L’ingresso è libero e qualsiasi impresa può scegliere di entrare in qualsiasi momento
2-Non c’è profitto nel lungo periodo.
Curva di domanda
Quando siamo in una condizione di libero mercato e ci troviamo davanti un grafico come quello qui sotto rappresentato (grafico prezzo, quantità prodotta), possiamo dire che la curva di domanda è piatta e si vende solo ad un prezzo, qualsiasi sia la quantità prodotta.

In questo caso l’impresa agisce in concorrenza perfetta e potrà vendere la quantità che può produrre a quel determinato prezzo, non ad un prezzo diverso.
Variabili del libero mercato
Le principali variabili da considerare quando si analizza un mercato di libera concorrenza sono le seguenti:
-Il prezzo
-Il ricavo totale
-Il ricavo medio
-Il ricavo marginale
Le caratteristiche di un mercato di libera concorrenza mostrano un ricavo totale che aumenta all’aumentare della quantità. Un’altra caratteristica è che il ricavo medio rimane costante come il prezzo. Si verifica infine che il ricavo marginale è uguale al prezzo.
Queste considerazioni e queste caratteristiche portano poi al grafico mostrato in precedenza, quello dove la pendenza della retta della domanda è orizzontale.
Qui di seguito un esempio di una tabella con le principali variabili descritte sopra

Qui di seguito il grafico dove abbiamo la quantità prodotta sulle ascisse e il prezzo sulle ordinate. La curva è una retta.

Conclusioni
Quando siamo di fronte ad un mercato di concorrenza perfetta, avremo che il prezzo non cambia mai anche se aumenta o diminuisce la quantità prodotto.
Domanda
Lavorate in qualche impresa? Se SI, in che mercato opera l'impresa per cui lavorate?
THE END
What market do you prefer?
Is it the free competitive or perfectly competitive?
I prefer competitive market. The case of the market in perfect competition is almost an ideal case, I would say that it exists in a few cases... I believe that the coffee market or the rice market are markets of perfect competition, the product is more or less always sold at that price. Instead, the main variables of a freely competitive market are price, total revenue, average revenue and marginal revenue. In this market the costs in the short and long term are different, this must be taken into consideration.
!discovery 30
Grazie per essere passato di qua. Il discorso più interessante di questo articolo è il mercato di libera concorrenza in uno stato chiamato perfetto. Significa che il prezzo è sempre lo stesso, cioè che il prodotto si può vendere sempre e solo a quel prezzo li, altrimenti i consumatori non comprano. In questo mercato qualsiasi impresa può entrare e vendere le quantità che può produrre
This post was shared and voted inside the discord by the curators team of discovery-it
Join our Community and follow our Curation Trail
Discovery-it is also a Witness, vote for us here
Delegate to us for passive income. Check our 80% fee-back Program
Grazie per il supporto!
I concetto principale di questo articolo è che il profitto si misura, quindi un'impresa può capire, tramite le curve di costo, quel è il punto in cui può ottenere profitto.
@tipu curate
Upvoted 👌 (Mana: 0/49) Liquid rewards.
Grazie per il tipu Liberty, purtroppo due profili che seguivano i miei articoli tecnici erano profili spammer. Hivewatchers mi ha segnalato la cosa.. adesso avrò meno commenti del solito da qui in poi, ma io provo ad insistere. Avanti Tutta!
Se lavoro per un'azienda di marketing, adoro lavorare su questo, mi sento fortunato a lavorare su ciò che mi piace così tanto.