05-03-2024 - Physics - Momentum equation [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
05-03-2024 - Physics - Momentum equation [EN]-[IT]
Basic concepts
In thermodynamics it is good to remember some basic concepts to better understand the study of the various thermodynamic states.
Below are some concepts on resistivity and cylindrical symmetry.
resistivity
In a wall with partitions that has multiple screens, the insulation depends on the resistivity of the material and increases as the number of screens increases. Among the materials it is good to remember that glass has a lower resistivity.
cylindrical symmetry
In a hollow cylinder it must be considered that:
-edge effects are negligible
-the temperature range is at steady state
-production is zero
Under these conditions we will have that the balance equation in cylindrical symmetry is the following:
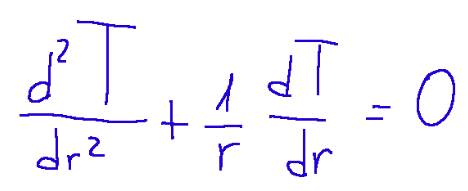
Momentum Equation
For the momentum balance equation we can remember Newton's second law which says:
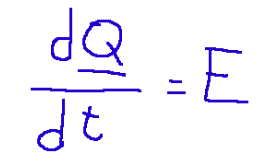
That is, the momentum of a material volume divided by the variation over time is equal to the resultant of the forces applied on the system.
The momentum equation will be similar to that of forced convection, but in this case mass forces will be considered.
Mass forces will enforce velocity dependence on temperature.
The momentum equation is shown below without simplifications.
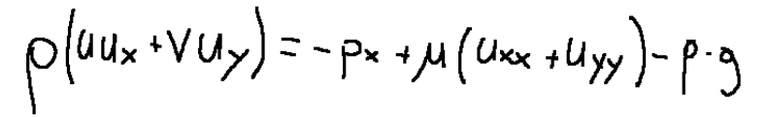
In this equation we have the term representing the mass forces
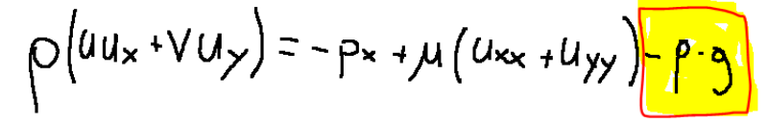
The isolated term representing the mass forces is as follows
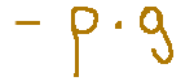
We can then make a series of considerations
-we can divide the terms of the equation written above by ρ
-we consider small speed values
At this point the equation described above becomes like the following:
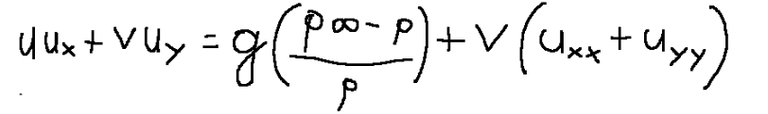
Let's now move on to other considerations:
-Let's consider ρ = ρ(T,p)
-We introduce and use the expansion coefficient β which represents the percentage change in density for a change in temperature.
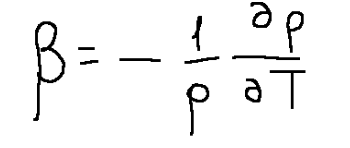
At this point we can rewrite the momentum balance equation with the following formula
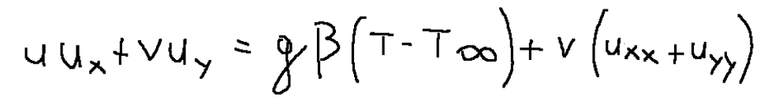
Conclusions
In studying the quantity equation we will encounter the expansion coefficient. This represents the percentage change in density for a change in temperature.
Request
Have you ever dealt with the momentum equation? Do you also think like me that this topic is rather complex?

05-03-2024 - Fisica - Equazione quantità di moto [EN]-[IT]
Concetti base
Nella termodinamica è bene ricordare alcuni concetti base per comprendere meglio lo studio dei vari stati termodinamici.
Qui di seguito alcuni concetti sulla resistività e sulla simmetria cilindrica.
resistività
In una parete con divisori che dispone di molteplici schermi, la coibentazione dipende dalla resistività del materiale e aumenta all'aumentare degli schermi. Tra i materiali è bene ricordare che il vetro ha una resistività minore.
simmetria cilindrica
In un cilindro cavo bisogna considerare che:
-gli effetti di bordo sono trascurabili
-il campo di temperature è a regime stazionario
-la produzione è nulla
In queste condizioni avremo che l’equazione di bilancio nella simmetria cilindrica è a la seguente:
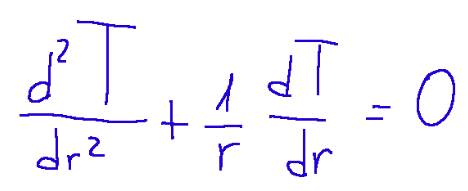
Equazione quantità di moto
Per l’equazione di bilancio della quantità di moto possiamo ricordare lla seconda legge di Newton che dice:
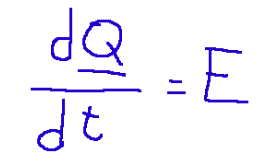
Cioè che la quantità di moto di un volume materiale fratto la variazione nel tempo è uguale alla risultante delle forze applicate sul sistema.
L’equazione della quantità di moto sarà simile a quella della convezione forzata, però verranno, in questo caso, considerate le forze di massa.
Le forze di massa applicheranno la dipendenza della velocità dalla temperatura.
Qui di seguito viene mostrata l’equazione della quantità di moto senza semplificazioni.
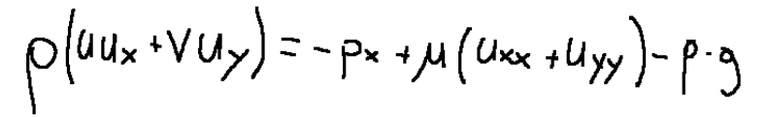
In questa equazione abbiamo il termine che rappresenta le forze di massa
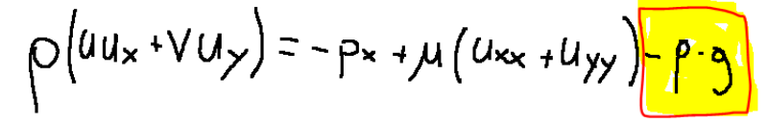
Il termine isolato che rappresenta le forze di massa è il seguente
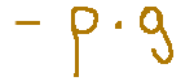
Possiamo poi fare una serie di considerazioni
-possiamo dividere i termini dell’equazione scritta sopra per ρ
-consideriamo valori piccoli di velocità
A questo punto l’equazione descritta sopra diventa come la seguente:
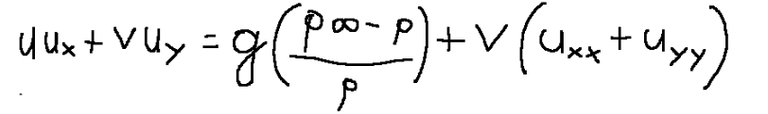
Passiamo ora a fare altre considerazioni:
-Consideriamo ρ = ρ(T,p)
-Introduciamo ed usiamo il coefficiente di espansione β il quale rappresenta la variazione di percentuale di densità per una variazione di temperatura.
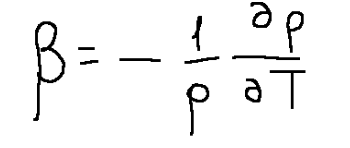
A questo punto possiamo riscrivere l’equazione di bilancio della quantità di moto con la seguente formula
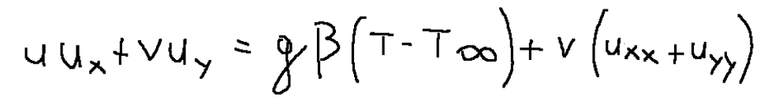
Conclusioni
Nello studio dell'equazione della quantità incontreremo il coefficiente di espansione. Questo rappresenta la variazione percentuale di densità per una variazione di temperatura.
Domanda
Avete mai avuto a che fare con l'equazione della quantità di moto? Anche voi ritenete come me che questo argomento è piuttosto complesso?
THE END
Sono passato da 69 a 68 abbastanza velocemente hahahaha, non sento più niente, ma mi ha fatto molto arrabbiare, non lo nego.
Come, non capisco, hai avuto una diminuzione di reputazione? Ho capito bene?
At this point and seeing the equation at first, it might be very difficult to understand but as time goes on it becomes easy
Thanks for visiting my blog. We can summarize everything by saying that the momentum equation is similar to that of forced convection, but in this case the mass forces cannot be neglected, which will imply the speed dependence of the temperature (these do not occur in convection forced). In fact, the term representing the mass forces is present in the equation. I point it out clearly below.
Thermodynamics, the branch of physics that studies the concept of heat energy. Good to see a science teacher on the chain.
Thanks for your kind words. The main part of this article is as follows and I will summarize it briefly
Below I insert the momentum equation
The momentum equation is substantially similar to that of forced convection, but in this case the mass forces cannot be neglected
Thank you for the explanation
The momentum topic at first quite looks difficult to understand but as time goes on, I begin to discover it is not really that hard as I was thinking
Thanks for leaving a comment. In this article I talk about the momentum equation. Apart from the formula representing the momentum, the other interesting thing is the concept of the expansion coefficient. The expansion coefficient represents the percentage change in density for a change in temperature.
Physics! I got just a Diploma in Physics 🥰 I didn't get to go far because of the much Mathematics in it😀
Thanks for leaving a comment. One of the most important things in this article is the expansion coefficient which I rewrite below.
The expansion coefficient represents the percentage change in density for a change in temperature
Okay, you are actually taking me back to the classroom and my interest is drawn to it
Anche la meccanica classica è piuttosto complessa. Vedo che le equazioni qui su Hive vanno scritte in… jpeg 😂 immaginavo non ci fossero altri sistemi. Da domani pubblicherò qualcosina per i miei studenti, niente di così accurato purtroppo, cercherò di mantenere una qualità così alta nonostante tutto, complimenti per il bel post.
Salve omodei, ci sono altri sistemi per scrivere lìequazioni e molto più professionali, confermo. Grazie per aver lasciato un commento. Sarebbe bello se pubblicasse qualcosa su HVE per i suoi studenti! Insieme possiamo iniziare a diffondere cultura qui su HIVE. Grazie per essere passato di qua
This momentum equation seem easy
I was able to assimilate it fast
Thanks for following my blog. We can say that one of the most important things in this article is the appearance of the expansion coefficient. It is mistakenly thought that this is the percentage change in density for a change in speed, but this is not true. The expansion coefficient represents the percentage change in density for a change in temperature. It also allows you to rewrite the energy balance and I propose it again below.
β = expansion coefficient