04-03-2024 - Physics - Natural convection [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
04-03-2024 - Physics - Natural convection [EN]-[IT]
Basic concepts
When we face
convective motions
Considering a system consisting of a free wall, which we later place a curtain alongside, we can state that in the two resistances G1 and G2 which form to the right and left of the curtain, they represent the convective motions of the air on the two faces of the curtain and these ensure that the thin layers of air present act, in fact, as insulators.
Natural Convection
Natural convection and forced convection differ from each other mainly in one thing.
In the case of natural convection the speed range depends on the temperature. In this case it is precisely the temperature difference that causes the speed range to vary.
Example:
Let's take into consideration the case of a vertical wall Tw with a temperature of 80°C in contact with still air which has a temperature of 20°C.
Below are the qualitative trends of the temperature, speed and density functions.
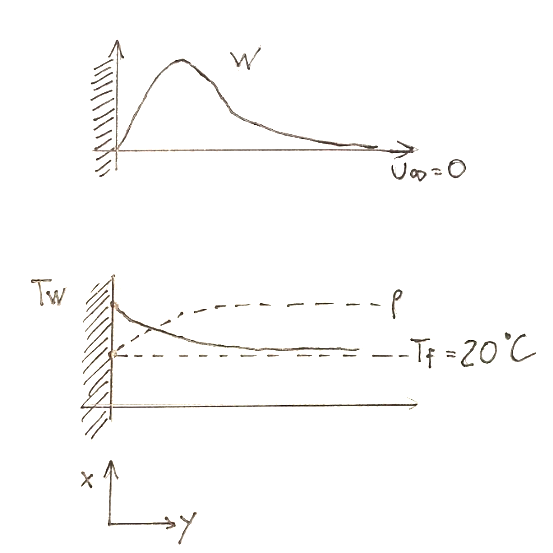
As regards the speed, we know that it is zero on the wall and that it initially increases and then tends asymptotically to zero, i.e. to the zero speed of the undisturbed fluid.
Let's consider the relationship p= ρRT to be valid, so it is as if we considered air as an ideal gas, we can know the density function ρ = ρ(T,p).
The density function is instead constant with respect to pressure and we can describe this as follows:
ρT = p/R = const.
So we can deduce that when the temperature T decreases, ρ increases and vice versa. This is shown in the two graphs inserted above, more precisely in the second.
Consideration
In the area near the wall with high values of temperature T and small values of ρ, the air will tend to rise with a certain speed.
Conclusions
The difference between natural convection versus forced convection is that in natural convection the velocity range depends on temperature.
Request
We often hear about the convective motions of the earth's mantle, did you know that despite the power involved, the operating principle of this machine is the same as that governing a common radiator? (convection)

04-03-2024 - Fisica - Convezione naturale [EN]-[IT]
Concetti base
Quando affrontiamo
moti convettivi
Considerando un sistema costituito da una parete libera, alla quale affianchiamo in un secondo momento una tenda possiamo affermare che nelle due resistenze G1 e G2 che si formano a destra e a sinistra della tenda, rappresentano i moti convettivi dell’aria sulle due facce della tenda e queste fanno in modo che i sottili strati di aria presenti funzionino, di fatto, come degli isolanti.
Convezione naturale
La convezione naturale e la convezione forzata differiscono tra di loro principalmente per una cosa.
Nel caso della convezione naturale il campo delle velocità dipende dalla temperatura. In questo caso è proprio la differenza di temperatura che fa variare il campo delle velocità.
Esempio:
Prendiamo in considerazione il caso di una parete verticale Tw con temperatura di 80°C a contatto con dell’aria in quiete che ha una temperatura di 20°C.
Qui di seguito gli andamenti qualitativi delle funzioni temperatura, velocità e densità.

Per quanto riguarda la velocità sappiamo che è nulla sulla parete e che in un primo momento aumenta per poi tendere asintoticamente a zero, cioè alla velocità nulla del fluido indisturbato.
Consideriamo di ritenere valida la relazione p= ρRT, quindi è come se considerassimo l’aria come un gas ideale, possiamo conoscere la funzione densità ρ = ρ(T,p).
La funzione densità risulta invece costante rispetto alla pressione e possiamo descrivere questo come segue:
ρT = p/R = cost.
Quindi possiamo dedurre che quando la temperatura T diminuisce, ρ aumenta e viceversa. Questo è mostrato nei due grafici qui sopra inseriti, più precisamente nel secondo.
Considerazione
Nella zona vicino alla parete con valori alti di temperatura T e piccoli valori di ρ, l’aria tenderà a salire con una certa velocità.
Conclusioni
La differenza tra convezione naturale rispetto a quella forzata è che nella convezione naturale il campo delle velocità dipende dalla temperatura.
Domanda
Si sente parlare spesso dei moti convettivi del mantello della terra, sapevate che nonostante la potenza in gioco, il principio di funzionamento di questa macchina è lo stesso che governa un comune termosifone? (la convezione)
THE END
I’m glad I learnt about natural and forced convention
Thanks for the class
Thanks for leaving a comment. Very simply we can summarize this article in the following few lines.
The difference between natural convection versus forced convection is that in natural convection the velocity range depends on temperature.
It is not correct to say that in natural convection the velocity field does not depend on the temperature at all.
Ti auguro un felice inizio settimana
Grazie Lu, Grazie per essere passato di qua. In questo articolo c'è un concetto base a riguardo della convezione.
La differenza tra convezione naturale rispetto a quella forzata è nella convezione naturale il campo delle velocità dipende dalla temperatura.
Every single series of your post, I am always opportune to learn one or two things every single time
Thanks for stopping by. We can summarize this article as follows. One may mistakenly think that:
in natural convection the temperature depends on the velocity field, while in reality it is correct to say as follows.
In natural convection the speed range depends on the temperature.
The convictional flow is really diverse and worth admiring of
Thanks for stopping by. I made this article simply to transfer or reiterate a concept that I summarize below.
The difference between natural convection versus forced convection is that in natural convection the speed range depends on the temperature.