02-04-2024 - Physics - Fundamentals of thermodynamics (12/13)[EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
02-04-2024 - Physics - Fundamentals of thermodynamics (12/13)[EN]-[IT]
Forced convection
Study
In the study of heat transfer in the convective mode the balance equations will be differential, punctual and non-integral.
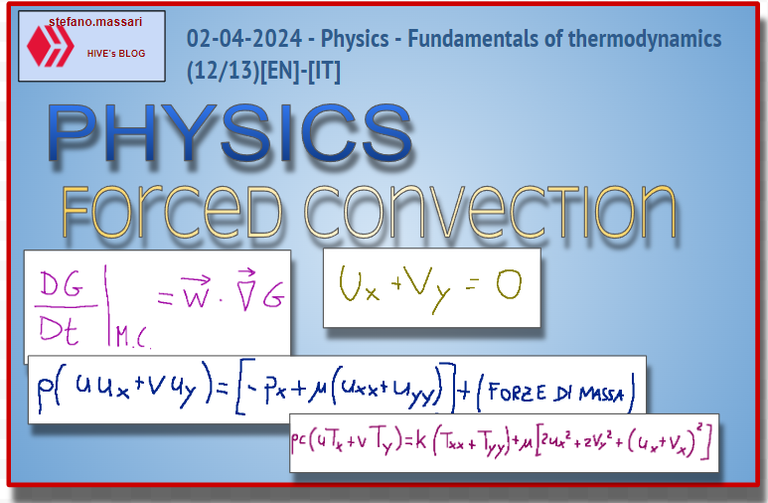
The transport theorem can also be used to explain forced convection. This theorem links the variation of a generic quantity G according to the concept of control mass (M.C.) to that of the control volume (V.C.):
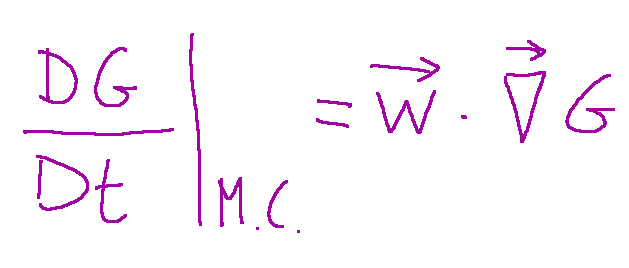
Mass continuity equation
Formula
The mass continuity equation is shown below.
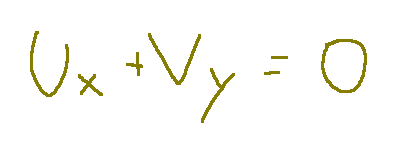
Momentum equation
Balance
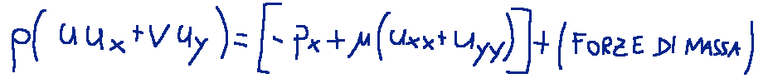
In this case there are two flows at play:
- the convective flow =
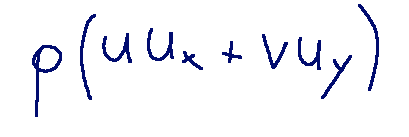
- the diffusive flow =
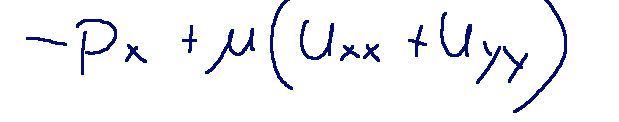
Energy equation
Formula
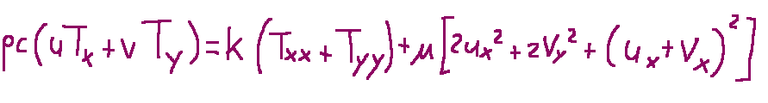
Remember that the energy balance can be written as follows:
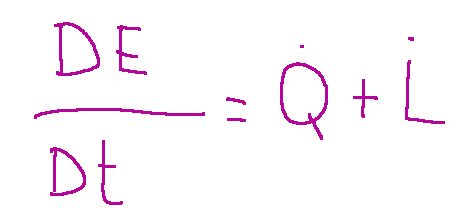
Where:
-Q̇ is the net thermal power entering by conduction;
-L̇ is the mechanical power exerted on the system by the acting forces (mass + contact);
-E is the sum of internal energy and kinetic energy (derived from collisions between particles).
Dimensionless groups
Dimensionless groups for forced convection
In dimensionless groups for forced convection the Prandtl number number will be relevant.
The Prandtl number represents the relationship between two phenomena at the molecular level. We can say that it represents the ways in which energy exchanges occur at the molecular level, through collisions and momentum; it is a function of state, as is the Reynolds number, but the latter is also a function of the geometry of the system and the speed of the fluid.

Conclusions
Convection is a type of transport and in the case of forced convection, the motions are caused artificially. In this case, heat transport occurs because external work is performed to maintain the currents in the fluid.
Request
Have you ever studied convective motions?

02-04-2024 - Fisica - Fondamenti di termodinamica (12/13)[EN]-[IT]
Convezione forzata
Studio
Nello studio del trasferimento di calore nel modo convettivo le equazioni di bilancio saranno differenziali, puntuali e non integrali.
Per spiegare la convezione forzata si può usare anche il teorema del trasporto. Questo teorema lega la variazione di una generica grandezza G secondo il concetto di massa di controllo (M.C.) a quello del volume di controllo (V.C.):
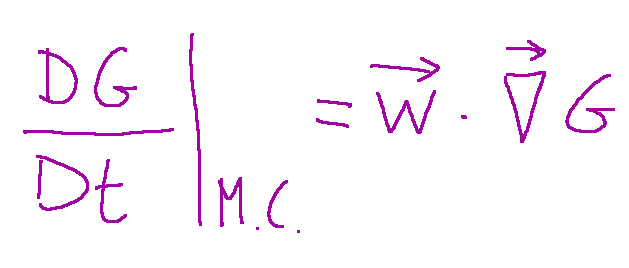
Equazione di continuità della massa
Formula
Qui di seguito è mostrata l'equazione di continuità di massa.
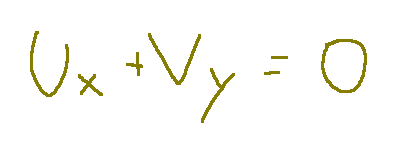
Equazione della quantità di moto
Bilancio
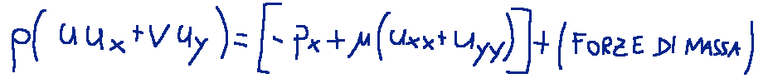
In questo caso i flussi in gioco sono due:
- il flusso convettivo =
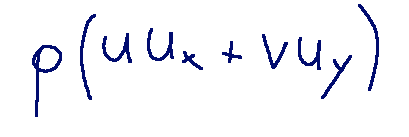
- il flusso diffusivo =
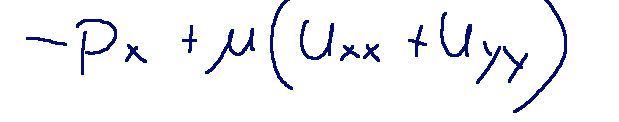
Equazione dell’energia
Formula
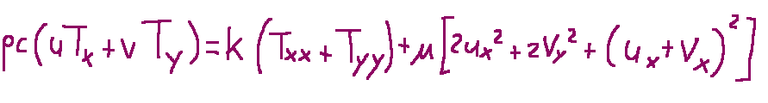
Da ricordare che il bilancio dell'energia può essere scritto come segue:
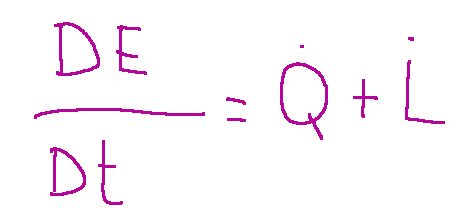
dove:
-Q̇ è la potenza termica netta entrante per conduzione;
-L̇ è la potenza meccanica fatta sul sistema dalle forze agenti (di massa + contatto);
-E è la somma dell’energia interna e di quella cinetica (derivata dagli urti tra particelle).
Gruppi adimensionali
Gruppi adimensionali per la convezione forzata
Nei gruppi adimensionali per la convezione forzata il numero di numero di Prandtl sarà rilevante.
Il numero di Prandtl rappresenta il rapporto tra due fenomeni a livello molecolare. Possiamo dire che rappresenta i modi in cui avvengono gli scambi di energia a livello molecolare, per urti e per quantità di moto; è una funzione di stato, come lo è anche il numero di Reynolds, ma quest’ultimo è anche funzione della geometria del sistema e delle velocità del fluido.

Conclusioni
La convezione è un tipo di trasporto e nel caso della convezione forzata, i moti sono provocati artificialmente. In questo caso il trasporto di calore avviene perché si compie un lavoro esterno per mantenere le correnti nel fluido.
Domanda
Avete mai studiato i moti convettivi?
THE END
Complimenti ottima analisi 👋🏼
Convection is actually a very lovely course
Nice one!
!DHEDGE
!discovery 25
This post was shared and voted inside the discord by the curators team of discovery-it
Join our Community and follow our Curation Trail
Discovery-it is also a Witness, vote for us here
Delegate to us for passive income. Check our 80% fee-back Program
The principle of thermodynamic apply to everywhere
Qui fuori dai post , sono motivato a continuare a lavorare, lascerò liquidità in attesa dell’halving