02-04-2024 - Economy - Free competition [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
02-04-2024 - Economy - Free competition [EN]-[IT]
Free competition
In economics, competition is the condition in which multiple companies compete on the same market. Anyone can choose to operate in that market, so there are no limits to the amount of businesses that can participate.
The principle
The principle of free competition says that there must be homogeneity of the product and above all freedom of entry. If this requirement is missing, this is called imperfect competition
The conditions
The free competition conditions are listed below.
-The company's objective is to maximize profit
-This market generates profit in the short term
-Many companies participating
-The entry of other companies is always permitted
-There is no profit in the long run
The demand graph
The demand curve is flat.
Even if the quantity produced increases, the price remains the same.
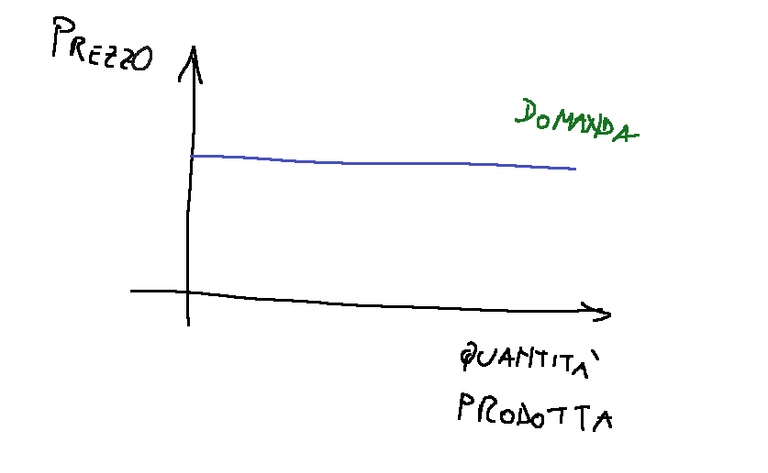
Basically, the company acting in perfect competition will be able to sell the quantity it can produce.
The main variables
The main variables of a free competition market are the following:
-Amount
-Price
-Total Revenue
-Average revenue
-Marginal Revenue
Below is an example of a data table of a company operating in the free market.
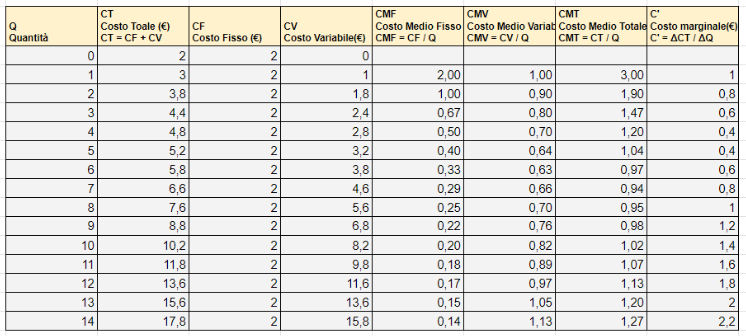
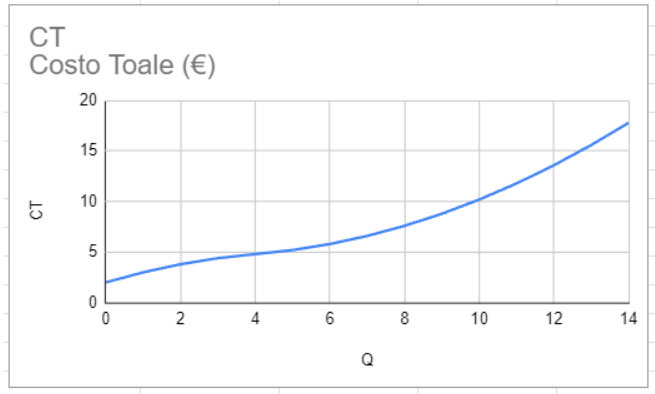
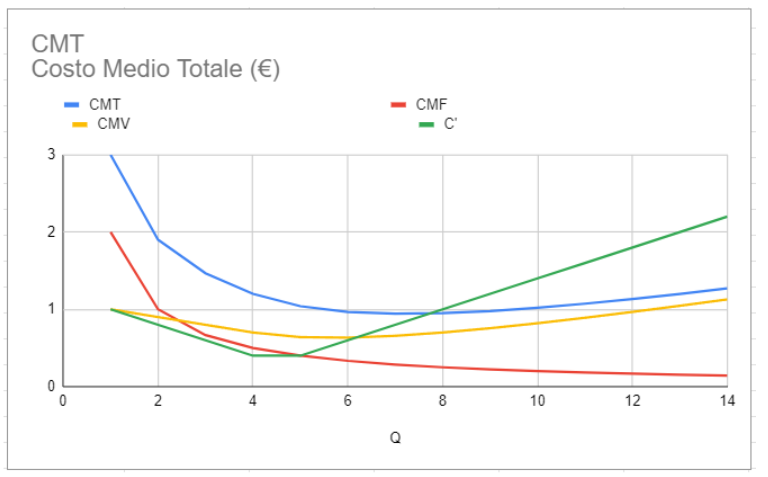
Typical curve between cost and quantity
Typical curves of the variables
Below is a typical free market graph showing the variables.
The variables considered based on quantity shown below are: average total cost, average variable cost, average fixed cost and marginal cost.
Determinant
One of the main determinants of this type of market occurs when analyzing quantity in relation to costs and revenues. From this type of graph or analysis we can see when the company maximizes profit. The firm maximizes profit by producing the quantity at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
Conclusions
In a free competition market there is no profit in the long run.
Request
Have you worked or are you working for a company that is in the free market or in a monopoly market? Or you have a business that operates in the free market or in a monopoly market

ITALIAN
02-04-2024 - Economia - La libera concorrenza [EN]-[IT]
Libera concorrenza
In economia, la concorrenza è quella condizione nella quale più imprese competono sul medesimo mercato. Chiunque può scegliere di operare in quel mercato, quindi non ci sono limiti alla quantità di imprese che possono partecipare.
Il principio
Il principio di libera concorrenza dice che ci deve essere omogeneità del prodotto e soprattutto libertà di ingresso. In caso di mancanza di questo requisito manca questo si parla di concorrenza imperfetta
Le condizioni
Qui di seguito sono elencate le condizioni di libera concorrenza.
-L'obiettivo dell’impresa è massimizzare del profitto
-Questo mercato genera profitto nel breve periodo
-Tante imprese che partecipano
-Sempre è consentito l'ingresso di altre imprese
-Non c’è profitto nel lungo periodo
Il grafico della domanda
La curva di domanda è piatta.
Anche se aumenta la quantità prodotta il prezzo rimane quello.

Sostanzialmente l’impresa che agisce in concorrenza perfetta potrà vendere la quantità che può produrre.
Le principali variabili
Le principali variabili di un mercato di libera concorrenza sono le seguenti:
-Quantità
-Prezzo
-Ricavo Totale
-Ricavo Medio
-Ricavo Marginale
Qui di seguito un esempio di una tabella dati di un'impresa che opera in libero mercato.

Curva tipica tra costo e quantità

Curve tipiche delle variabili
Qui di seguito un grafico tipico del libero mercato in cui sono mostrate le variabili.
Le variabili considerate in base alla quantità mostrate qui sotto sono: il costo medio totale, il costo medio variabile, il costo medio fisso ed il costo marginale.

Determinante
Una delle principali determinanti di questa tipologia di mercato si verifica quando si analizza la quantità in relazione ai costi e ricavi. Da questa tipologia di grafico o di analisi riusciamo a vedere quando l'impresa massimizza il profitto. L'impresa massimizza il profitto producendo la quantità per la quale il costo marginale è uguale al ricavo marginale.
Conclusioni
In un mercato di libera concorrenza non c’è profitto nel lungo periodo.
Domanda
Avete lavorato o state lavorando per un impresa che è nel libero mercato o in un mercato di monopolio? Oppure avete un impresa che opera nel libero mercato o in un mercato di monopolio
THE END
!hiqvote
!discovery 30
@libertycrypto27, the HiQ Smart Bot has recognized your request (2/1) but the daily limit has been reached. Try again later.
In addition, @stefano.massari gets !PIZZA from @hiq.redaktion.
For further questions, check out https://hiq-hive.com or join our Discord. And don't forget to vote HiQs fucking Witness! 😻
Grazie per essere passato di qua. Io lavoro in un azienda che opera nel mercato di libera concorrenza. E' nel mercato degli impianti per l'ortofrutta da 30 anni e come dicono i libri o gli studi, in un mercato di libera concorrenza nel lungo periodo non c'è profitto... lo confermo.
This post was shared and voted inside the discord by the curators team of discovery-it
Join our Community and follow our Curation Trail
Discovery-it is also a Witness, vote for us here
Delegate to us for passive income. Check our 80% fee-back Program
I really think I now understand the concept of this lecture. It helps one to understand the economic much more better
Nice course
I’ve worked for a company that is in the free market. Well, I was not in the economics department but I could still say a few things about it
Thanks!
Thanks for leaving a comment. Working for a company that operates in free competition is one of the most usual things here in Italy. What is important about this lesson is that in a free competition market every company can enter and exit whenever it wants, furthermore any company can be part of it
The competition always gives this healthy feelings of what to do and where to adjust
È libera concorrenza, è meglio del monopolio, io lavoro in un mercato libero
Anch'io se dovessi scegliere quale mercato mi piace di più sceglierei il mercato di libera concorrenza. Soprattutto per le seguenti caratteristiche.
Nel mercato di libera concorrenza l'obiettivo dell’impresa è la massimizzazione del profitto. Questo genera efficienza e miglioramenti continui del processo produttivo e del prodotto.
L'altra caratteristica importante è che è consentito sempre l'ingresso di altre imprese