02-03-2024 - Physics - Forced convection in flows [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
02-03-2024 - Physics - Forced convection in flows [EN]-[IT]
Basic concepts
When we delve into thermodynamic studies there can be many topics and each topic could itself have subdivisions depending on the case.
For this reason, even the basic concepts in thermodynamics are many.
Below I talk about some of these that I consider to be of extreme interest.
Conduction
Conduction is a way of transmitting heat between solids
Conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is linked to the production of entropy and is measured in W/m°K
Convective boundary condition
Considering the conduction of a flat plate, we mean convective boundary conditions when considering the transport of internal energy by forced or natural convection. In this case radiation, contact or osmosis have nothing to do with it.
Dimensionlessization
Dimensionlessization is a mathematical simplification in which variables are grouped with the aim of decreasing the independent variables.
Forced convection in external and internal flows
Convective heat transfer occurs when heat transfer is linked to mass transfer.
The phenomenon of convection is in fact typical of fluids because thanks to their freedom of movement they behave as thermal vectors.
The phenomenon of convection can be excluded for solids.
To properly analyze or better understand what happens during the convection phenomenon, it is best to consider a solid wall that comes into contact with a liquid. This is considering that the temperature of the liquid is lower than the wall temperature of the solid taken as a case study.
Convection can be either natural or forced.
Case with flow outside surfaces
To consider the case of forced convection in external flows we consider the flow on a flat plate. The case is schematized in the drawing below
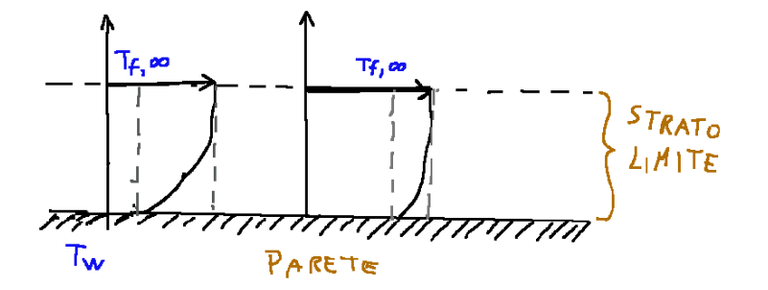
Boundary layer
In this case the thickness adjacent to the surface within which the temperature is between T w and T f,∞ is called the boundary layer of the fluid.
The temperature is between T w and T f is equal to the temperature in an undisturbed area
Thermal power
In the case of forced convection in external flows the thermal power per unit of surface is the following:
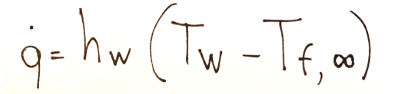
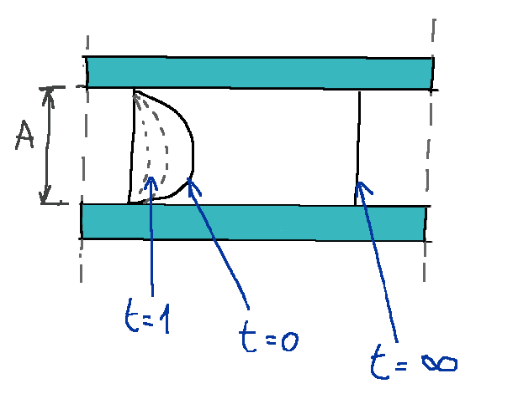
Case with flow inside
In this case with internal flow the temperatures will be different and an average temperature must be considered. In this case the concept of temperature in an undisturbed zone does not exist, that is, there is no longer what is called a boundary layer
Thermal power
To find the thermal power of the case with internal flows we can think of the temperature with the velocity weighted average
Below is the average reference temperature
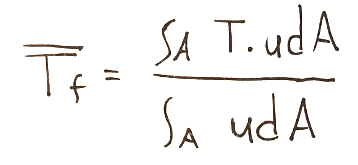
From this consideration we can obtain the thermal power.
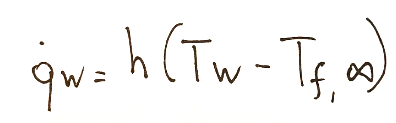
Conclusions
Convection can be either natural or forced and convection heat transmission occurs when heat transmission is linked to mass transfer.
Request
Have you ever studied heat transfer via mass transfer, i.e. via convection?

02-03-2024 - Fisica - La convezione forzata nei flussi [EN]-[IT]
Concetti base
Quando ci addentriamo negli studi termodinamici gli argomenti possono essere tanti ed ogni argomento potrebbe avere lui stesso delle suddivisioni a seconda dei casi.
Per questo motivo anche i concetti base, in termodinamica, sono tanti.
Qui di seguito parlo di alcuni di questi che ritengo oggetto di estremo interesse.
Conduzione
La conduzione è una modalità di trasmissione del calore tra solidi
Conducibilità
La conducibilità termica di un materiale è legata alla produzione di entropia e si misura in W/m°K
Condizione al contorno di tipo convettivo
Considerando la conduzione di una lastra piana, si intende per condizione al contorno di tipo convettivo, quando si considera il trasporto di energia interna per convezione forzata o naturale. In questo caso l'irraggiamento, il contatto o l'osmosi non c'entrano nulla.
Adimensionalizzazione
L'adimensionalizzazione è una semplificazione matematica in cui sono raggruppate le variabili con lo scopo di diminuire le variabili indipendenti.
La convezione forzata nei flussi esterni ed interni
La trasmissione di calore per convezione avviene quando la trasmissione del calore è legata ad un trasferimento di massa.
Il fenomeno della convezione è infatti tipico del fluidi perché grazie alla loro libertà di movimento si comportano come vettori termici.
Il fenomeno della convezione può essere escluso per i solidi.
Per analizzare bene o capire meglio ciò che avviene durante il fenomeno della convezione è bene considerare una parete solida che viene a contatto con un liquido. Questo considerando che la temperatura del liquido è più bassa della temperatura della parete del solido preso come caso studio.
La convezione può essere sia naturale che forzata.
Caso con flusso all’esterno di superfici
Per considerare il caso della convezione forzata nei flussi esterni consideriamo il flusso su lastra piana. Il caso è schematizzato nel disegno riportato qui sotto

Strato limite
In questo caso lo spessore adiacente alla superficie all’interno della quale la temperatura è compresa tra T w e T f,∞ viene chiamato strato limite del fluido.
La temperatura è compresa tra T w e T f è uguale alla temperatura in zona indisturbata
Potenza termica
Nel caso della convezione forzata nei flussi esterni la potenza termica per unità di superficie è la seguente:
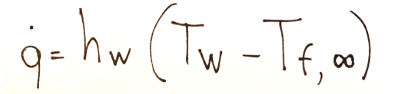
Caso con flusso all’interno
In questo caso con flusso interno le temperature saranno diverse e bisognerà considerare una temperatura media. Non esiste in questo caso il concetto di temperatura in zona indisturbata, cioè non c’è più quello che viene chiamato strato limite

Potenza termica
Per trovare la potenza termica del caso con flussi interno possiamo pensare alla temperatura con la media pesata con velocità
Qui di seguito la temperatura media di riferimento
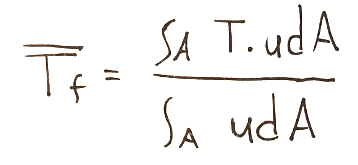
Da questa considerazione possiamo ricavare la potenza termica.
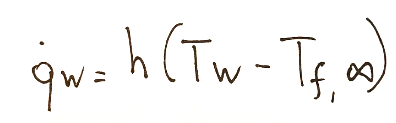
Conclusioni
La convezione può essere sia naturale che forzata e la trasmissione di calore per convezione avviene quando la trasmissione del calore è legata ad un trasferimento di massa.
Domanda
Avete mai studiato la trasmissione del calore tramite trasferimento di massa, cioè tramite convezione?
THE END
There is a lot of equations in physics at times to understand and this sometimes can really be difficult
Thanks for stopping by, In this article on forced convection in external and internal flows the most important thing is what is meant by boundary layer. It is nothing other than the thickness adjacent to the surface within which the temperature is between Tw and Tf,∞, this area is also called "temperature in the undisturbed zone"
!discovery 30
grazie per il supporto Liberty. In questo articolo sulla convezione forzata nei flussi esterni ed interni la cosa più importante è cosa di intende per strato limite. Esso non è altro che lo spessore adiacente alla superficie all'interno della quale la temperatura è compresa tra Tw e Tf,∞, questa zona viene anche chiamata "temperatura in zona indisturbata"
This post was shared and voted inside the discord by the curators team of discovery-it
Join our Community and follow our Curation Trail
Discovery-it is also a Witness, vote for us here
Delegate to us for passive income. Check our 80% fee-back Program
thanks a lot
Damn!
This is really difficult but I was able to pick up something
You don't need to understand everything. In this article on convection the most important thing is what is meant by a boundary layer. It is nothing other than the thickness adjacent to the surface within which the temperature is between Tw and Tf,∞, this area is also called "temperature in the undisturbed zone". It is mistakenly thought that it is the thickness adjacent to the surface within which the temperature is the lowest, but this is not the case
Non ho studiato questo argomento, mi fa ridere pensare che in genere rispondo la stessa cosa hahahaha, ma sai che sono sincero
Questi argomenti non sono trattati molto spesso, sono argomenti di nicchia... magari ti troverai meglio quando inizierò a fare la prossima serie di articoli basati sui principi di economia
The understanding of the free flow is really dynamic to understand and actually comprehend
Basically one of the most interesting things in this article is the concept of boundary layer which is the thickness adjacent to the surface within which the temperature is between Tw and Tf,∞. This zone is also called, disturbed zone temperature