01-04-2024 - Physics - Fundamentals of thermodynamics (10/13) [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
01-04-2024 - Physics - Fundamentals of thermodynamics (10/13) [EN]-[IT]
Incident energy
Incident radiation is the radiation that encounters any body to which it releases all or part of its energy.
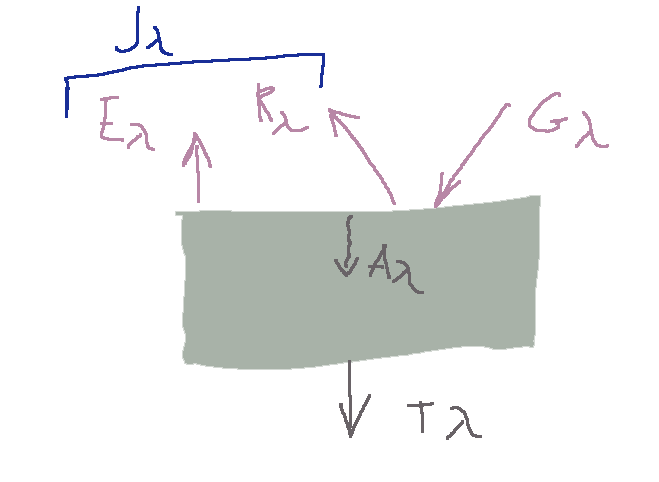
Energy radiating on a surface
When radiant energy impacts the surface of a body, part of the radiation is reflected (Rλ), while the remaining part enters the body; this portion will be absorbed (Aλ) as it passes through it.
Relationship between quantities
Below is the relationship between the quantities that revolve around the incident energy.
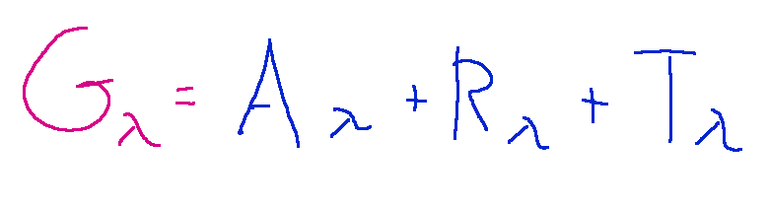
Where:
Gλ = radiant energy affects the surface of a body
Aλ = reflected radiation
Rλ = absorbed radiation
Tλ = transmitted radiation
radiance
The radiosity Jλ is the emissive power (Eλ) plus the contribution of the reflected incident energy (Rλ)
Black body
Definition
Below we describe how a black body is defined in physics.
The black body is an ideal body that absorbs all the radiant thermal energy incident on it, whatever the spectral and spatial distribution of the incident radiation: the black body is therefore the perfect absorber.
Monochromatic emissive power
The hemispherical monochromatic emissive power of the black body therefore depends on the wavelength as well as on the temperature
Radiative characteristics
Monochromatic emission
Monochromatic, or spectral, emission is a function of the thermodynamic state of the emitting surface.
Grey body
Definition
The gray body in physics is a model according to which the spectral emission, at a certain temperature T, is constant throughout the wavelength range.
Mathematically this statement can be expressed in the following way.
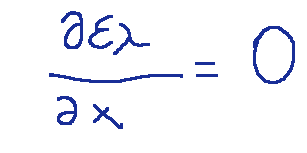
Illuminated surface
Matte body
An opaque body is a body in which Tλ, i.e. the transmitted radiation, is equal to zero.
So we can mathematically define an opaque body as follows:
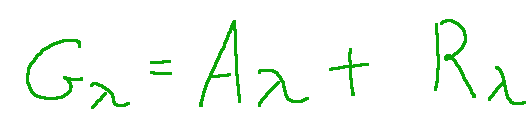
Where:
Gλ = radiant energy affects the surface of a body
Aλ = reflected radiation
Rλ = absorbed radiation
Conclusions
When radiant energy impacts the surface of a body, part of the radiation is reflected, while the remaining part enters the body.
Request
Have you ever carried out studies on incident energy?

01-04-2024 - Fisica - Fondamenti di termodinamica (10/13) [EN]-[IT]
Energia incidente
La radiazione incidente è la radiazione che incontra un corpo qualsiasi al quale cede tutta o una parte della propria energia.
Energia raggiante su una superficie
Quando un'energia raggiante incide su una superficie di un corpo parte della radiazione viene riflessa (Rλ), mentre la restante parte entra nel corpo; questa aliquota verrà assorbita (Aλ) mentre lo attraversa.
Relazione tra le grandezze
Qui di seguito la relazione tra le grandezze che ruotano attorno all'energia incidente.
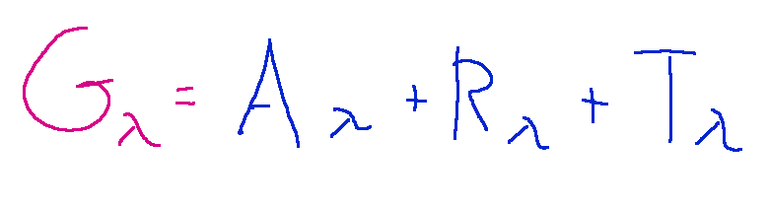
Dove:
Gλ = energia raggiante incide sulla superficie di un corpo
Aλ = radiazione riflessa
Rλ = radiazione assorbita
Tλ = radiazione trasmessa
radiosità
La radiosità Jλ è il potere emissivi (Eλ) più il contributo dell'energia incidente riflessa (Rλ)

Corpo nero
Definizione
Qui di seguito viene descritto come si definisce un corpo nero in fisica.
Il corpo nero è un corpo ideale che assorbe tutta energia termica raggiante incidente su di esso, quale che sia la distribuzione spettrale e spaziale della radiazione incidente: il corpo nero è pertanto l'assorbitore perfetto.
Potere emissivo monocromatico
Il potere emissivo monocromatico emisferico del corpo nero dipende dunque dalla lunghezza d’onda oltre che dalla temperatura
Caratteristiche radiative
Emittenza monocromatica
L'emittenza monocromatica, o spettrale, è una funzione dello stato termodinamico della superficie emittente.
Corpo grigio
Definizione
Il corpo grigio in fisica è un modello secondo il quale l'emittenza spettrale, ad una certa temperatura T, è costante in tutto il campo delle lunghezze d'onda.
Matematicamente questa affermazione si può esprimere nella seguente maniera.
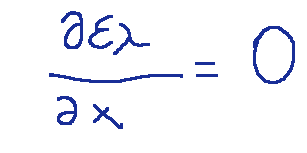
Superficie illuminata
Corpo opaco
Un corpo opaco è un corpo in cui Tλ, cioè la radiazione trasmessa, è uguale a zero.
Quindi possiamo definire matematicamente un corpo opaco come segue:
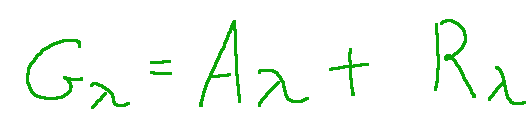
Dove:
Gλ = energia raggiante incide sulla superficie di un corpo
Aλ = radiazione riflessa
Rλ = radiazione assorbita
Conclusioni
Quando l'energia raggiante incide sulla superficie di un corpo, parte della radiazione viene riflessa, mentre la restante parte entra nel corpo.
Domanda
Avete mai effettuato degli studi sull'energia incidente?
THE END
Congratulations @stefano.massari! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPCheck out our last posts:
Really miss a lot of your classes this last week. Thank you for refreshing my brain. The radiant energy that falls on a surface is partly reflect and partly absorbed
I so much always enjoy every bit of your lectures as it always opens my eyes to a lot of things beyond which we can ever imagine of
Congratulations @stefano.massari! You received a personal badge!
Wait until the end of Power Up Day to find out the size of your Power-Bee.
May the Hive Power be with you!
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
Check out our last posts:
Honestly, this subject seem very tough to me, lol
I found it hard trying to cram the formula but it was a good one
Thanks!
So straightforward to understand clearly. Thank you for this great labour
Ho già interrotto power down, decidi tu