Plant secondary metabolites ;Phytochemicals pt III
In the last two posts, I did an introduction on phytochemicals. The links to them are found here and here.
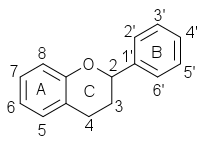
In this part, I will focus on Flavonoids which is another example of polyphenol. They are a group of plant secondary metabolites that consist of 15 carbon atoms and readily soluble in water. They are composed of two benzene rings joined together by three carbon atoms which also form a heterocyclic ring( a ring structure that has more than two different atoms as ring member, in this case, Carbon and oxygen as it is shown in the image below). One of the carbons in the heterocyclic ring is joined to the benzene rings directly or alternatively through an oxygen bridge.

When you are in a flower garden or in a farm and you see yellow, purple, pink, blue or red coloured petals of flowers, it is a particular flavonoid called Anthocyanins that is responsible for that colour. This is because flavonoids are responsible for plant pigmentations. Plant smart way of protecting themselves against fungal parasites, herbivores pathogens as well as ultraviolet radiation from the sunlight is by the production of these group of natural products. You know that just as human communicate with their environment, one of the ways plants do so with the aid of flavonoids.
The flavonoids act to deal with intimidating situations just as earlier explained. However, plant also interacts with environments using their colour skills. As human get attracted to beautiful flowers in the gardens so also are the pollinators are attracted to the beautiful flowers on plants. Without flavonoids that make flowers beautiful with attractive colours, pollination would be a difficult task and if that is difficult, it will be a great task for seed-bearing plants (Spermatophytes) to bear fruits, in another word, beautiful flowers attract the pollinators. They are also present in gymnosperm, angiosperms and pteridophytes.
 )
)
pixabay.com red-apple
When you include parsley, banana, apple, blueberries, with other berries, cocoa, red wine, black tea and green teas in your diet, you are actually consuming flavonoids because your body can not synthesize them, so they must be consumed from plant source since they are plant product. You could find them in citrus fruits as well. You know when your orange or any fruits changes colour from green to yellow or orange colour, you will say its ripening, it's the flavonoids which are in plant cell vacuole that makes them change colour. They are at that point said to have ripe. Flavonoids provide great health benefits to human when consumed because of their antioxidant activities as well as their cell signalling pathways which will be discussed towards the latter part of this post. ( Appart from antioxidant activities of flavonoids, they also assist cells to perceive and respond effectively to cells immediate microenvironment, thereby preventing certain diseases which might result from an error in signalling response and how cells process information received which can lead to life-threatening diseases such as diabetes, cancer and autoimmunity.)
Synthesis and Classification of Flavonoids
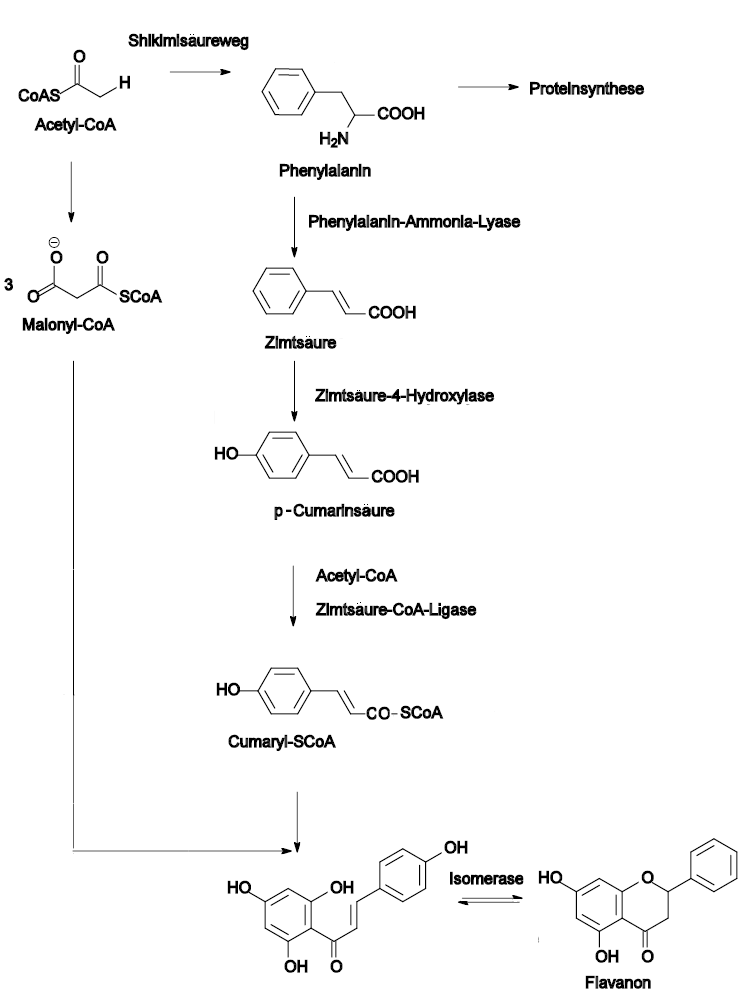
Synthesis of flavonoids in a plant is based on their biosynthetic origin. As earlier stated, flavonoids basic skeleton has 15 carbon atoms. These carbon atoms are arranged in order of C6-C3-C6 meaning that the first benzene ring has 6 carbon atom and there is a bridge of 3 carbon atoms also with oxygen as a bridge connecting to another benzene ring of 6 carbon atoms. The first step in the synthesis involves condensation of one molecule of p-coumaroyl-CoA molecule and three molecules of malonyl-CoA in the presence of an enzyme called chalcone synthase (CHS).
 )
)
Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0 Flavonoid structre showing three rings(Ring A C6, Ring C C3 and Ring B C6
The second ring or B ring is derived from the p-coumaroyl-CoA while the first or A ring is derived from the three molecules of malonyl-CoA. The obtained product is chalcone (2′, 4′, 6′, 4-tetrahydroxychalcone). The product obtained further undergo isomerization reaction with an enzyme called chalcone flavanone isomerase (CHI) which then gives another flavonoid called flavanone. These are the foundational intermediates or central pathway from which the remaining flavonoids are then made as a result of many other side branches.
The biosynthesis of flavonoid in a plant depends on the plant species and a group of enzymes that makes changes to the skeletal makeup of flavonoid. These enzymes include hydroxylases, isomerases, reductases. It is these enzymes that modify primary structures of flavonoid and then lead to the all the different classifications of flavonoid starting from the intermediate classes(chalcones and flavanones) to the end products of the biosynthesis (Anthocyanins, flavones, flavonols and proanthocyanidins). These end products could be found in different plant parts.
In plants, especially higher plants, flavonoid act as a nitrogen-fixing agent in the root noodles of plant. When they are secreted in the roots of plant, their main purpose for such secretion is to aid the symbiotic relationship between the plants such as beans,clover and peas and rhizobia responsible for root nodles. The bacteria genus called rhizobia produces nodles as a result of the presence of flavonoids.
Flavonoids assisting the of cell survival signalling pathways
When you consume flavonoids in fruits and vegetables, your body is at a great advantage because they help to protect the heart against cardiovascular diseases, they also help to prevent neuronal injury and death of neurons by inhibiting cell dysfunctioning as a result of free radicals. They also prevent cell inflammations and are also chemoprotective agents. However, their functions are not limited to antioxidants properties alone, research has also found out that flavonoids and their metabolites also have a modulatory effect on the cell system as a result of their direct actions on many signalling pathways. For the sake of simplicity, signalling pathway is a term that explains several chemical reactions in which a group of molecules inside a cell control the cell function as a result of synergy among the molecules. For instance, a molecule that is attached to a cell receives a signal from the cell environment after the molecule as bind itself to a protein receptor, this molecule then activates the next molecule and that one too activate the next one until all the molecule inside that cell are completely activated in that pathway and the cell performs its physiological role. But if abnormal pathway activation takes place, this might lead to diseases such as cancer. Some of these pathways include; tyrosine kinases, protein kinase C, phosphoinositide 3-kinase, mitogen-activated protein kinase and Akt/protein kinase B. So what Flavonoids do to modulate the survival of the cell in a pathway is to alter the phosphorylation of the molecules that are targeted in the cell either by its inhibitory or stimulatory actions which are attributed to their structure. Binding between the protein receptor [enzyme] and the molecule [substrate] must be under control so as to control how phosphate is added to the molecule. For instance, the kinase activity of CK2α′(known to be responsible for the phosphorylation of several physiological substrates ) which is a protein kinase in human was found to be decreased by a derivative of luteolin (a flavonoid).
Summary
In summary, Flavonoids polyphenolic compounds produced by plant and needed for the survival of plants and human. These class of phytochemicals gives plants beautiful colour in the field. Human need these flavonoids because they help to prevent several diseases in the body by curtailing unnessarily reaction that can destroy the cell and thereby leading to serious health challenges.
References
https://www.news-medical.net/health/What-are-Flavonoids.aspx
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flavonoid
https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/signaling-pathway
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_signaling
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider supporting our funding proposal, approving our witness (@stem.witness) or delegating to the @stemsocial account (for some ROI).
Thanks for using the STEMsocial app and including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which give you stronger support.