The Silent Revolution: How Polymers are Shaping Our World? |ChemFam #67|
Greetings to everyone! In an era teeming with innovation and technological leaps, there's a humble hero you might not have noticed: polymers. These remarkable compounds, made up of long chains of repeating units, are playing an ever-expanding role in our daily existence. Polymers are the silent architects of our world, and in this article, we'll delve into the myriad ways they are shaping our lives.
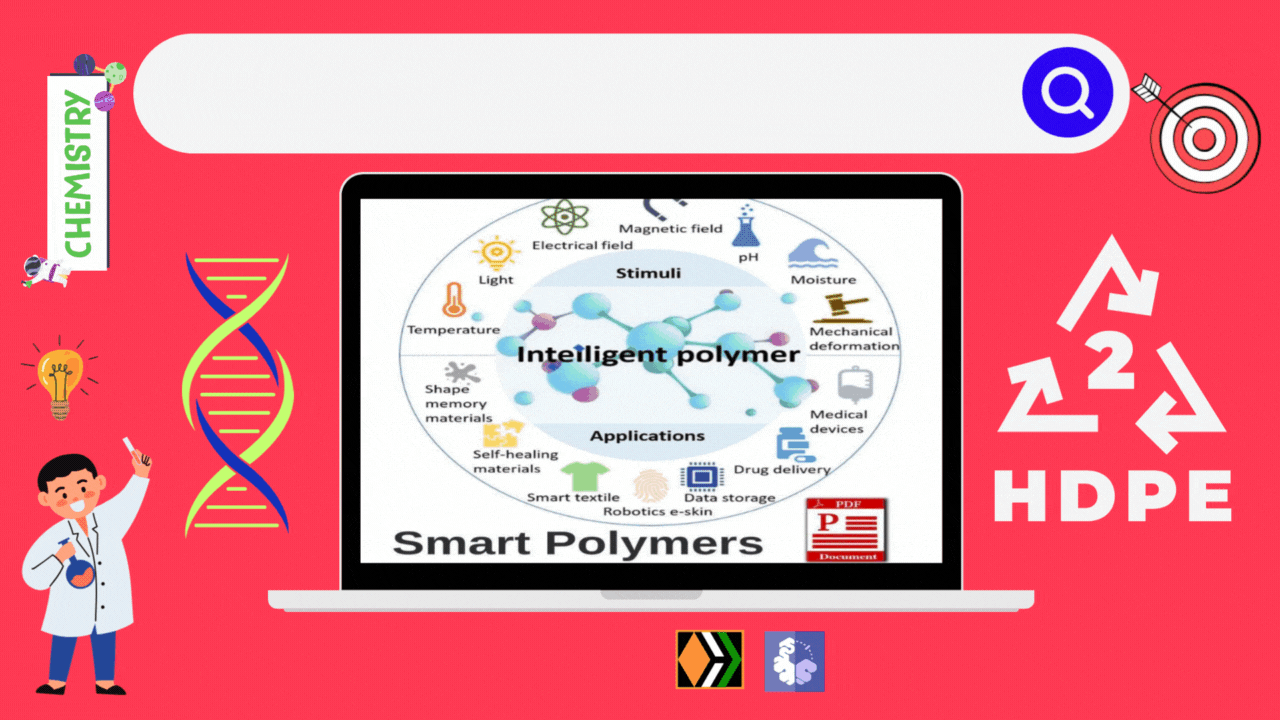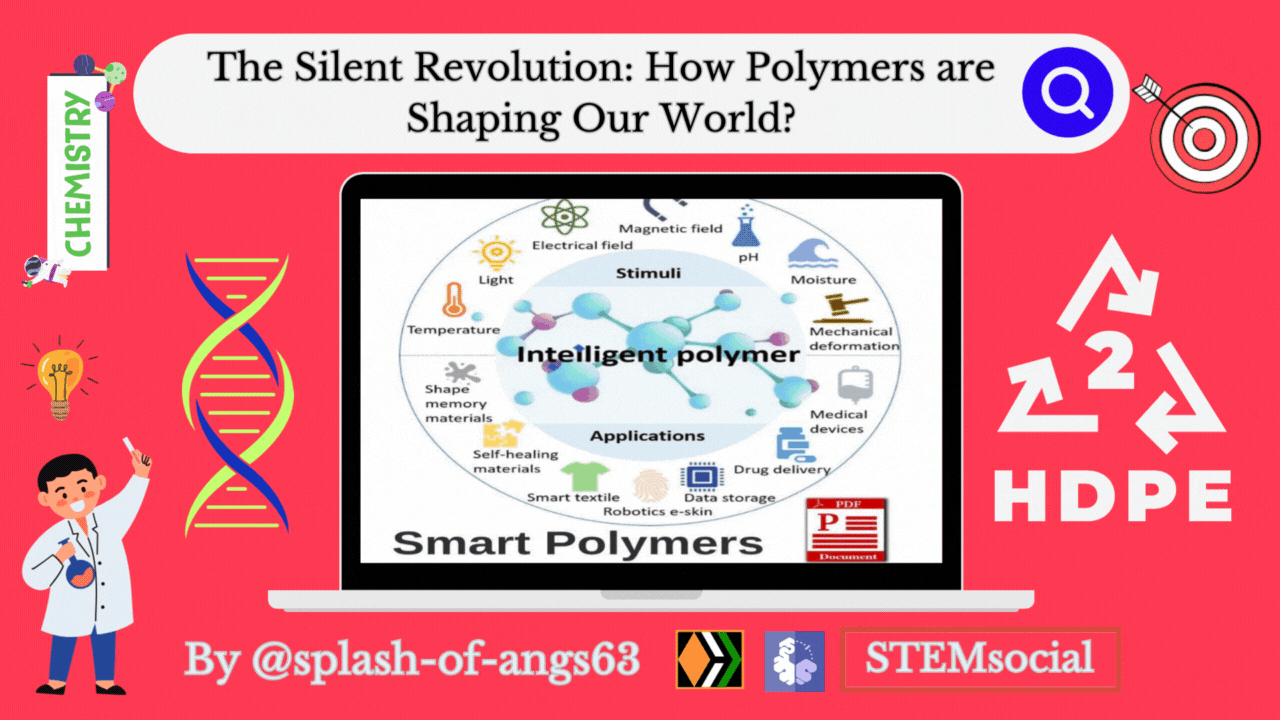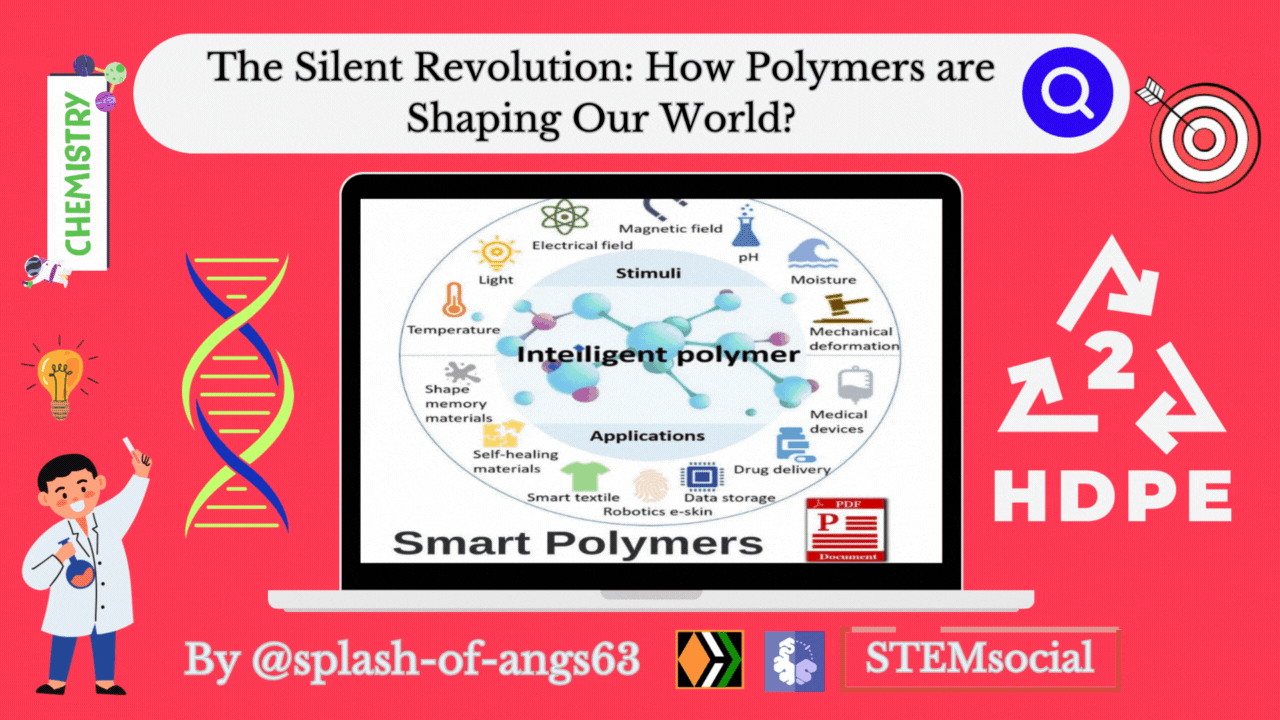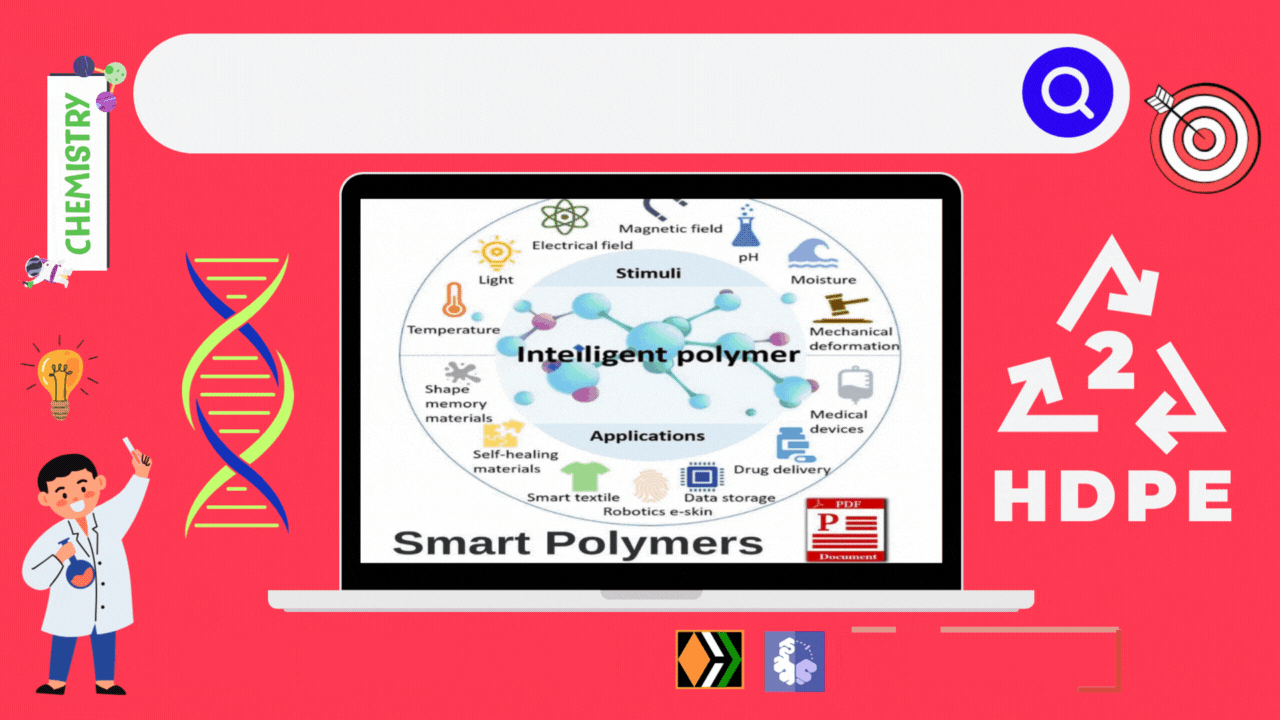
Do you actually think that daily life would have been easier and colorful without the discovery and varied applications of polymers? The use of polymers in the manufacture of plastic buckets, cups, saucers, children toys, packaging bags, synthetic clothing material, automobile tyres, electrical insulating materials have completely revolutionized the daily life as well as the industrial scenario. Indeed the polymers are the backbone of four major industriesd viz. plastic, elastomers, fibres and paints and varnishes.
Explaining the term polymer and polymerization
The word polymer is coined from two Greek words: poly means many and mer means unit or part. The term polymer is thus defines as very large molecules having high molecular mass (103-107u). These are also referred to as macromolecules, which are formed by joining or repeating structural units on a large scale. The repeating structural units are derived from some simple and reactive molecules known as monomers and are linked to each other by covalent bonds. This process of formation of polymers from respective monomers is called polymerization. The transformation of ethene to polythene and interaction of hexamethylene diamine and adipic acid leading to the formation of nylon 6,6 are examples of two different types of polymerization reactions.
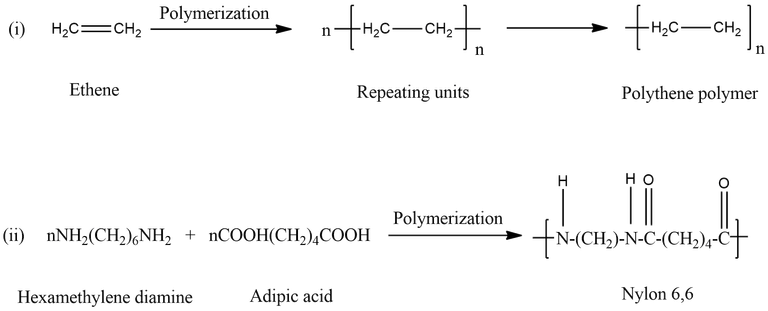
Structure of Polymer
A hydrocarbon backbones make up most of the polymers in our environment. Due to the tetravalent structure of carbon, the hydrocarbon backbone is a long chain of interconnected carbon and hydrogen atoms.
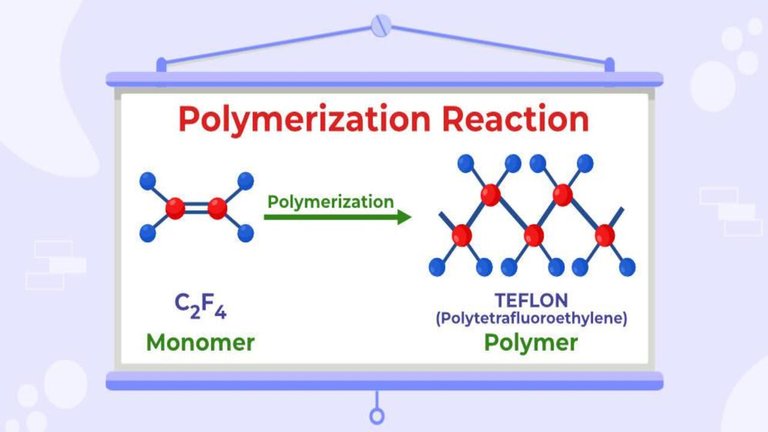
Hydrocarbon backbone polymers polypropylene, polybutylene and polystyrene are a few examples. There are also polymers that contain other elements instead of carbon in their backbone. For example, the backbone of the repeating units in nylon contains nitrogen atoms.
Uses of Polymers
Polymers find a wide range of applications in our daily lives and across various industries. Polymers have many uses such as:
- Polypropylene has many uses such as plastics, textiles, packaging, paper and aircraft.
- Polystyrene, one of the most commonly used plastics, is frequently used in packaging. Products made from polystyrene include toys, bowls, plates, TV stands, bottles and caps. Therefore, it can also be used as an electrical insulator.
- PVC is a polymer widely used in the construction of sewer pipes. This material is also used in the construction of power lines.
- Polyvinyl chloride is widely used in the manufacture of doors and windows, as well as clothing and furniture.
- Due to the higher molecular weight of the polymers, urea-formaldehyde resins can be used to create many products. These include adhesives, molds, laminates and other products.
The Versatile Friends We Depend On
Polymers are known for their versatility, adaptability, and sheer utility. They come in various forms, from natural biopolymers like proteins and DNA to the synthetic polymers that dominate our modern lives. The significance of polymers becomes abundantly clear when we consider their diverse applications:
Packaging and Plastics: The most recognizable use of polymers is in the creation of plastics. Lightweight, durable, and cost-effective, plastics have become a cornerstone of modern life, found in everything from food packaging to medical devices. But as environmental concerns grow, researchers are tirelessly working on biodegradable and eco-friendly polymers.
Medicine and Healthcare: Polymers are not just materials; they are lifesavers. Biocompatible polymers are essential for drug delivery systems, surgical implants, and medical devices. They provide controlled drug release, reduce the risk of implant rejection, and enhance patient care.
Electronics and Technology: Behind our gadgets and devices, polymers quietly work their magic. They serve as insulating materials in wires and cables and form the flexible substrates used in electronic displays. Organic polymers, like organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), are transforming electronics by enabling flexible, lightweight, and energy-efficient displays.
Aerospace and Automotive: Polymers are helping make our vehicles more fuel-efficient. Lightweight composites reinforced with polymers are increasingly used in aircraft and automobiles, making them stronger while shedding weight.
Energy Efficiency: Polymers are contributing to the renewable energy sector. Solar cells incorporating organic polymers offer a cost-effective solution for harnessing solar power, making sustainable energy generation more accessible.
Construction and Infrastructure: High-performance polymers are the underdogs behind strong and durable building materials. They are used in coatings, adhesives and insulation materials to withstand the harshest conditions and reduce maintenance costs.
Environmental solutions: Polymers are important in the recycling industry. They are used in the development of recycling technologies that transform waste plastics into useful products. Biodegradable polymers offer a promising solution to the growing problem of plastic pollution.
Sustainability and the Future of Polymers
While the importance of polymers in our lives is undeniable, the spotlight is now on the sustainability of polymer production and usage. The adverse environmental effects of single-use plastics and the growing problem of plastic waste in our oceans have ignited a passion for developing biodegradable and recyclable polymers. Scientists are dedicated to creating polymers that can be produced from renewable resources and are more eco-friendly.
In addition to the development of environmentally friendly polymers, recycling and reuse of these materials has also gained importance. Recycling services are expanding and technologies are emerging that break down polymers into their simpler components, offering a way to reduce the burden of plastic waste on our environment.
The Promise of Future Polymers
The future of polymers holds the promise of innovation and sustainability. As we journey further into the 21st century, the importance of polymers will only continue to grow. It's crucial that we explore and embrace eco-friendly alternatives and recycling methods to ensure that polymers remain a vital part of our world while reducing their environmental impact.
Innovations in polymer chemistry are all about creating materials that can meet the challenges of a changing world. The polymers of tomorrow will be:
Sustainable: Sustainable polymers will be made from renewable materials, reducing our dependence on fossil fuels and the environmental impact of production.
Biodegradable: Biodegradable polymers break down naturally, reducing long-term environmental damage. These materials are ideal for single use when reuse is not possible.
Recyclable: Improved recycling techniques will make polymers more efficient and reusable, reducing waste and saving resources.
Smart and functional: Polymers will continue to be designed for specific tasks, such as responsive materials that change properties in response to the environment or stimuli.
Energy saving: Polymers will play a key role in the development of energy-saving technologies, from advanced battery materials to improved insulation in the home.
Eco-friendly packaging: Sustainable and biodegradable polymers will revolutionize packaging by reducing plastic waste and its impact on the environment.
Conclusive thoughts
Polymers have undergone a quiet revolution, reshaping industries, technologies, and our way of life. Their versatility, adaptability, and impact are undeniable. As we look ahead, the key challenge is to harness the potential of polymers while ensuring they are environmentally responsible.
The importance of polymers in our world is immeasurable. They have become the backbone of modern life, driving progress in fields as diverse as medicine, electronics, aerospace, and sustainable energy. The polymers of the future will not just be versatile and functional; they will also be sustainable and responsible. They hold the potential to build a better and greener world, offering solutions to some of our most pressing challenges. Our world may be shaped by polymers, but it is our responsibility to shape them into a force for good and progress. These humble materials, once unnoticed, are now emerging as essential contributors to a brighter and more sustainable future.
Until we meet again :)

How Chemists Are Pushing Polymers to New Limits
Polymers remain the materials of the future for our industry
Beyond the Bin: The Many Faces of Plastic Management |ChemFam #66|
Spectrophotometry Simplified: The Beer-Lambert Law in Spectrophotometry |ChemFam #65|
Chromatography: Unraveling the Science of Separation |ChemFam #64|
Colorful Clues: The Magical World of Chemical Indicators |ChemFam #63|
Colloids in Action: Impacting Your Daily Life More Than You Think |ChemFam #62|
The Complex Landscape of Opioid Analgesics: Addressing The Concerns |ChemFam #61|
Genetic Engineering: Pioneering Progress or Ethical Predicament? |ChemFam #60|
The Guardians Against Microbial Menace: Antibacterial Agents |ChemFam #59|
The Cholesterol Conundrum: The Story of Statins |ChemFam #58|
Unveiling The Control Of Chemistry: How Hormones Dictate Our Mood |ChemFam #57|
Thermodynamic Versus Kinetic Control of Reactions |ChemFam #56|
Bosons: The Quantum Glue That Holds The Universe Together |ChemFam #55|
Extraction of Lithium Using Electrode Materials of Lithium Ion Battery-II |ChemFam #54|
Extraction of Lithium Using Electrode Materials of Lithium Ion Battery |ChemFam #53|
Helium: The First Noble Gas |ChemFam #52|
Hydrogen: The Simplest Atom |ChemFam #51|
Elements, Atoms and Atomic Theory |ChemFam #50|
Have You Thanked A Clod Today? |ChemFam #49|
Nuclear Energy: Will It Rise Again? |ChemFam #48|
Soaps: An Essential and Effective Cleansing Agent |ChemFam #47|
Chemicals in Food : Debunking Myths and Ensuring Safe Consumptions |ChemFam #46|
Unveiling The Secrets of Antiseptics and Disinfectants |ChemFam #45|
PS The thumbnail image is being created by me using canva.com



The world of polymer is really an interesting one. Unfortunately, your 1st diagram isn't looking so great on peakd. Perhaps it's just me?
Yes interesting indeed. Many more to be unveiled on later posts :)
Do you mean the thumbnail image? It is in the gif format and should run well. If you're referring to the image drawn via ChemDraw then I checked and looks ok to me in the two front ends peakd and ecency. I'll again check it tomorrow morning on my PC though.
Thank you for going through my post :)
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.