Analysis of the image generated in a convex mirror attached to a flat side mirror of an automobile
In this opportunity we will seek to analyze an image, but now the reflecting surface will not be inside the spherical cap, but on the outside, that is, we will relate to a spherical mirror, but now convex, this in order to analyze the generation of images between one type of mirror and another, despite being both from the cap of a sphere, however, varies the position of the reflecting surface and thus vary the characteristics of the projected or reflected image in both types of mirrors.
The elements present in a convex mirror are similar to those of a concave mirror, there being a center of curvature (C) and, with it radius of curvature (r), on an optical axis, but now, the difference will be the reflecting or specular part, since it will be located in the convex part and not in the concave part, as we could analyze in the previous article and, in addition, we can observe them in our cars to help us to have a better visualization of the environment that we have behind us when driving and, personally I confess that this type of convex mirror is of great help when driving.
All light rays arriving or incident on the vertex of a convex mirror will be reflected with similar angles, that is, incident angle will be equal to the reflected angle, in the case that a ray of light is directed to the center of curvature, this (ray) will be reflected on itself, and, any ray that strikes parallel to the optical axis in the convex mirror, will be reflected from the focus and, with these characteristics it is possible to analyze the generation of an image in a convex mirror, therefore, it is important to know the following statement in order to analyze the characteristics of an image in this type of convex mirror and see what are the differences with the image in a concave mirror.
Exercise
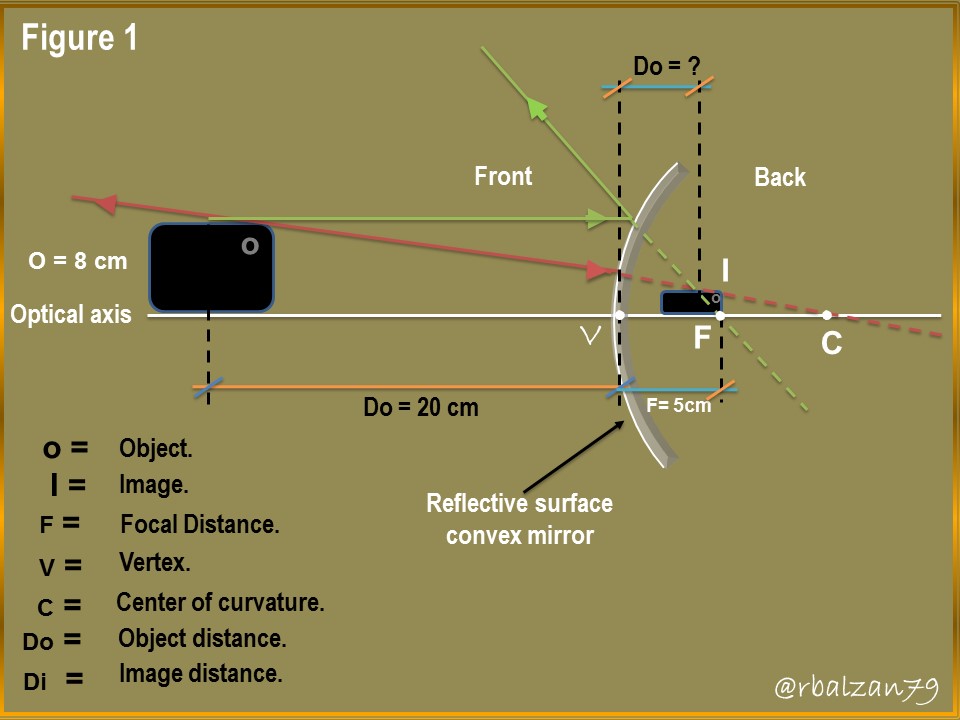
We have a convex spherical mirror attached to one of the side flat mirrors of our car, when taking a picture with our cell phone, we can notice the difference of the images generated in both mirrors (flat and convex), the objective of this opportunity is to analyze the generation of the image in the convex mirror and, from this we have the following data; height of the object (cellular, horizontal position) 8 cm, located at a distance of 20 cm, where the focal length is 5 cm, therefore, in relation to the above expressed answer the following questions:
a.- What will be the main characteristics of our image in the convex mirror?
Solución
Data:
Ao = 8 cm (Object height).
Do = 20 cm (Object distance).
C = - 10 cm (Center of curvature or radius of curvature).
F = - 5 cm (Focal length).
Convex Mirror Image Characteristics = ?
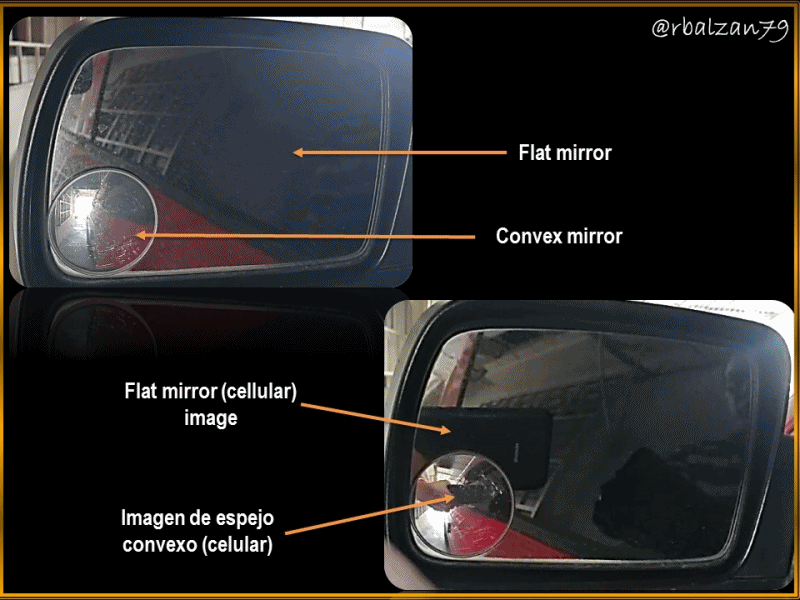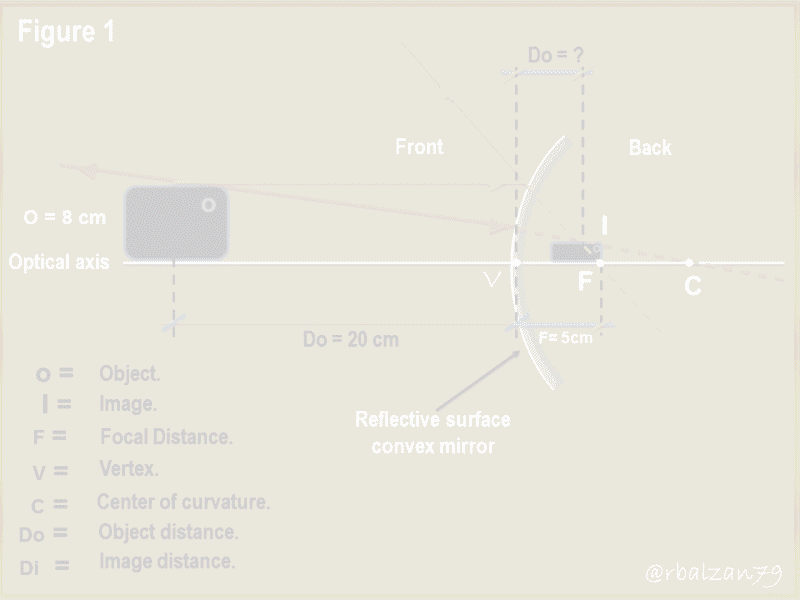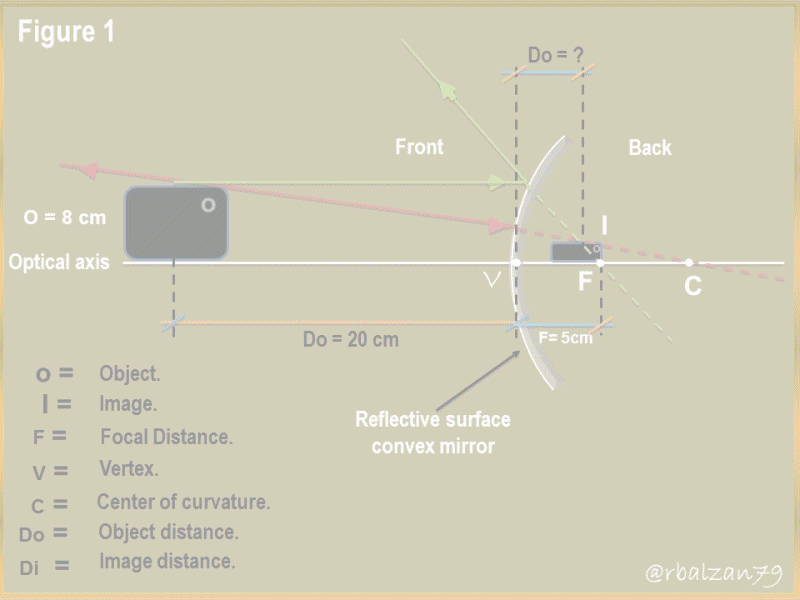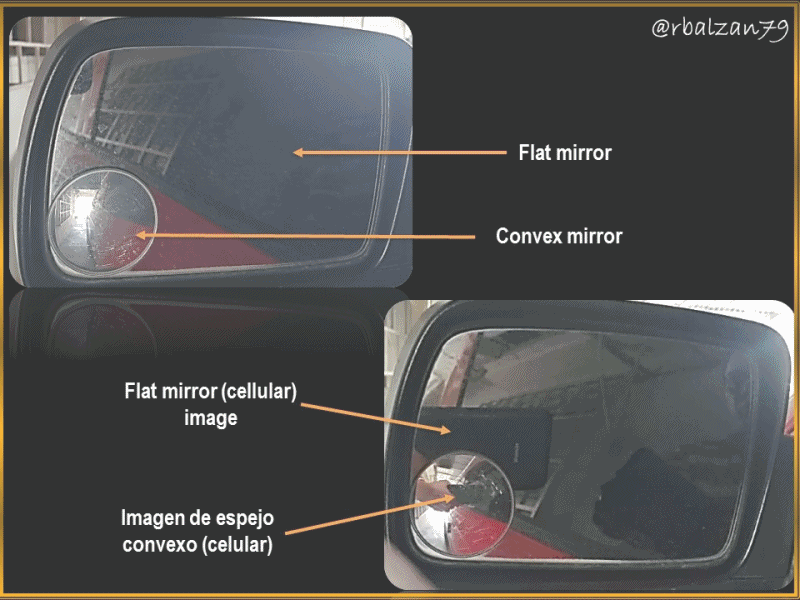
a.- To begin to answer our question, it is important to use the general equation of mirrors, even though we are now dealing with a spherical mirror of convex type, focusing on the ray diagram in figure 1.

In this way we proceed to the substitution of the known values and see what, operation results us to find some variable that allows us to begin to know the characteristics of the image generated or formed in our convex mirror glued in a lower corner of a flat side mirror of a car, therefore, we have:
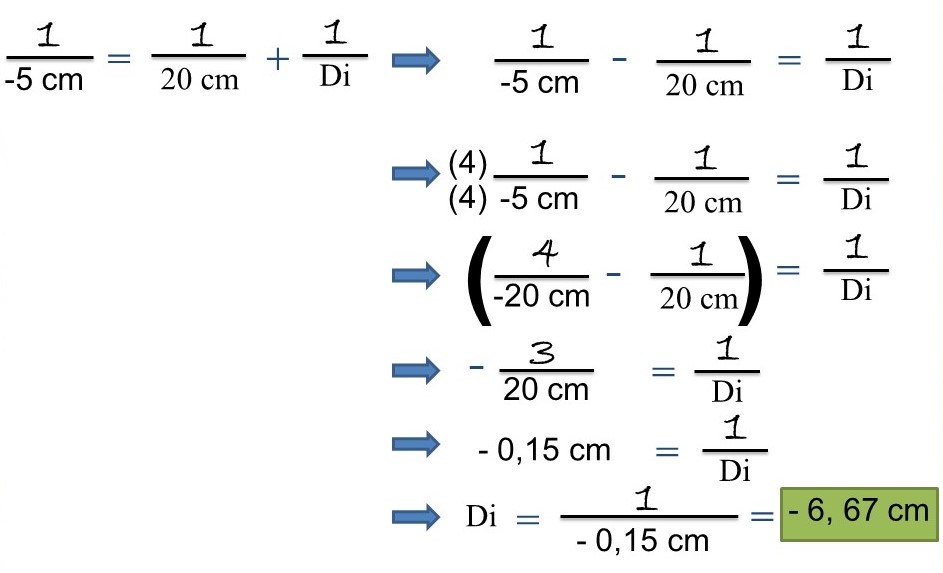
For this opportunity all the values behind the reflecting surface (convex mirror) will have negative values and all the values in front of the mirror will be positive, that is why we take the focal length with a negative value, therefore, by substituting the known values, we can calculate at what distance the image was formed in our convex mirror which was generated behind the mirror and, therefore, with a negative value of - 6.67 cm.
Now using the following formulation we will see another aspect of great value in the formation of the image in that mirror, so we have:
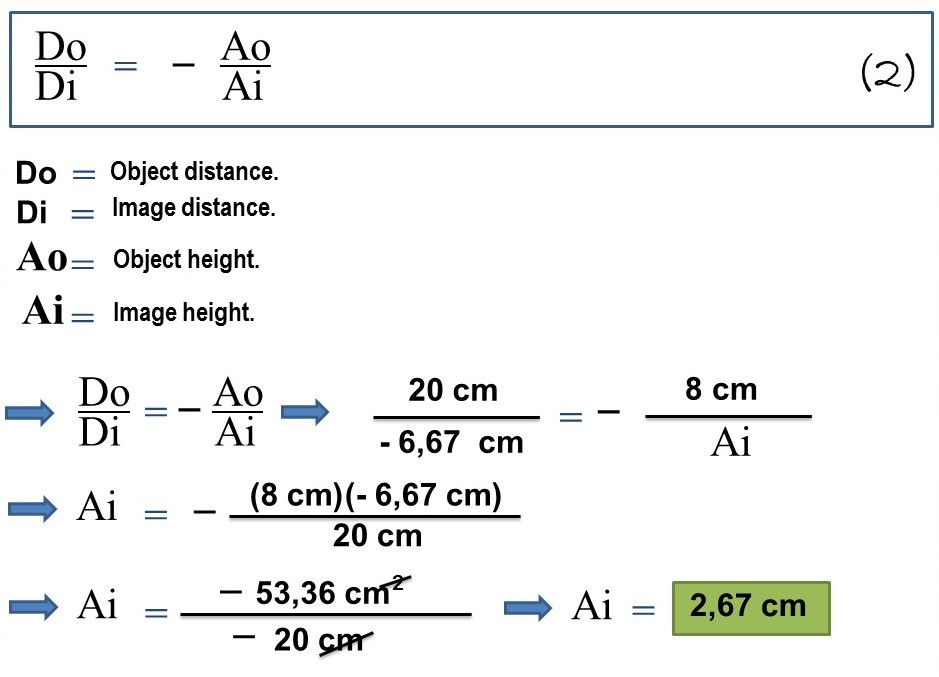
For this case we searched with the known values the height of the generated image, so we obtained a positive value of 2.67 cm, the positive sign indicates the orientation of the image, which in this case is right, that is, not inverted, this aspect is of a virtual image formed on the other side of where the object is (cell phone) and thus we could know both the distance at which the virtual image is formed behind the convex mirror and its size.
Conclusion
In this opportunity I wanted to develop a simple example, but, very practical in our daily life, maybe many of you have been able to make use of this type of convex mirror, as the example here analyzed, that is, a small convex mirror attached to the lower left side of a flat side mirror of a car, the function of this convex spherical mirror is wonderful, since it allows us to have a greater range of visibility of what is behind us and this is because it offers us a panoramic view in smaller proportion or size, but with better visualization of the space-time we want to see through these convex mirrors.
The formulations are the same for spherical mirrors, both concave and convex, what I wanted to do is to differentiate the way images are generated in each of these simple but essential optical systems such as mirrors in all their presentations, in fact, in the cover image you can see or observe the difference in the generation of the cell phone image in the flat mirror as in the convex mirror analyzed.
The characteristics obtained from our image were the following, smaller in size 2.67 cm compared to the 8 cm height of the cell phone in reality, the image is formed straight, therefore, not inverted, this makes it a virtual image and, therefore, formed behind the spherical convex mirror, hence the negative value (- 6.67 cm) of its distance in relation to the vertex of the convex mirror.
In fact, the main purpose was to highlight and thus demonstrate that the characteristics of the images formed in a spherical mirror are different, both concave and convex, and the diagram of light rays does not describe them in this way, although we were able to implement the same formulations, but the reflection of the rays varies according to the type of reflecting or specular surface used, as in each of the cases analyzed, concave and convex spherical mirrors.
Until another opportunity my dear friends.
Note: The images were created by the author using Power Point and Paint, the animated gif using PhotoScape.
Recommended bibliographic references
[1] GEOMETRIC OPTICS. Link.
[2] Convex Mirrors. Link..
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.
Thank you dear community for your valuable support. Best regards.