[ESP/ENG] Diseño de Circuitos de Alimentación para Microcontroladores - Parte 1: Fundamentos y Reguladores Lineales 🔋🔧 // Microcontroller Power Supply Circuit Design - Part 1: Fundamentals and Linear Regulators 🔋🔧
[ESP]
¡Saludos, constructores del futuro digital! 👋
En esta primera parte de nuestra serie sobre diseño de circuitos de alimentación para microcontroladores, nos centraremos en los conceptos básicos y el uso de reguladores lineales. La alimentación adecuada es fundamental para el correcto funcionamiento de cualquier proyecto basado en microcontroladores, ya que una fuente de energía estable y limpia garantiza que nuestros componentes funcionen de manera óptima. En esta publicación, aprenderás sobre los conceptos clave, los reguladores lineales y cómo diseñar una fuente de alimentación básica para microcontroladores. ⚡🔍
Fundamentos de la Alimentación para Microcontroladores ⚙️
Para que un microcontrolador funcione correctamente, es esencial suministrarle un voltaje estable y limpio. La mayoría de los microcontroladores, como el Arduino (ATmega328P) o el ESP32, operan a 5V o 3.3V, y un voltaje incorrecto puede dañarlos o hacer que funcionen de manera inestable.
Conceptos Clave:
- Voltaje (V): La diferencia de potencial eléctrico que impulsa el flujo de corriente. Los microcontroladores más comunes suelen operar a 5V o 3.3V.
- Corriente (A): La cantidad de carga eléctrica que fluye a través de un circuito, medida en amperios. Es importante asegurarse de que la fuente de alimentación pueda suministrar suficiente corriente para todos los componentes.
- Ruido y Ondulaciones: Las variaciones en el voltaje pueden afectar el rendimiento del microcontrolador. Utilizar capacitores ayuda a suavizar estas fluctuaciones.
Reguladores Lineales: Simplicidad y Estabilidad 📏
Un regulador lineal es un componente que convierte un voltaje de entrada más alto en un voltaje de salida más bajo de manera estable. Los reguladores lineales son populares por su simplicidad, pero no son muy eficientes, ya que disipan el exceso de energía en forma de calor.
Reguladores Lineales Comunes:
- LM7805: Regula un voltaje de entrada (por ejemplo, 12V) para obtener una salida estable de 5V.
- LD1117-3.3: Convierte un rango de voltaje de entrada a una salida fija de 3.3V, ideal para microcontroladores como el ESP32.
Ventajas:
- Simplicidad: Fácil de integrar en un circuito.
- Estabilidad: Proporciona una salida de voltaje muy estable.
- Bajo Ruido: Ideal para aplicaciones que requieren señales limpias.
Desventajas:
- Ineficiencia: La energía sobrante se disipa como calor, lo que no es ideal para aplicaciones que requieren alta eficiencia.
- Pérdida de Energía: Cuanto mayor sea la diferencia entre el voltaje de entrada y el de salida, más energía se pierde como calor.
Ejemplo de Circuito con Regulador LM7805:
Supongamos que queremos alimentar un Arduino desde una fuente de 12V. Usaremos un LM7805 para reducir el voltaje a 5V de manera estable.
Componentes:
- LM7805
- Condensadores: 0.22µF (entrada) y 0.1µF (salida)
- Fuente de alimentación: 12V
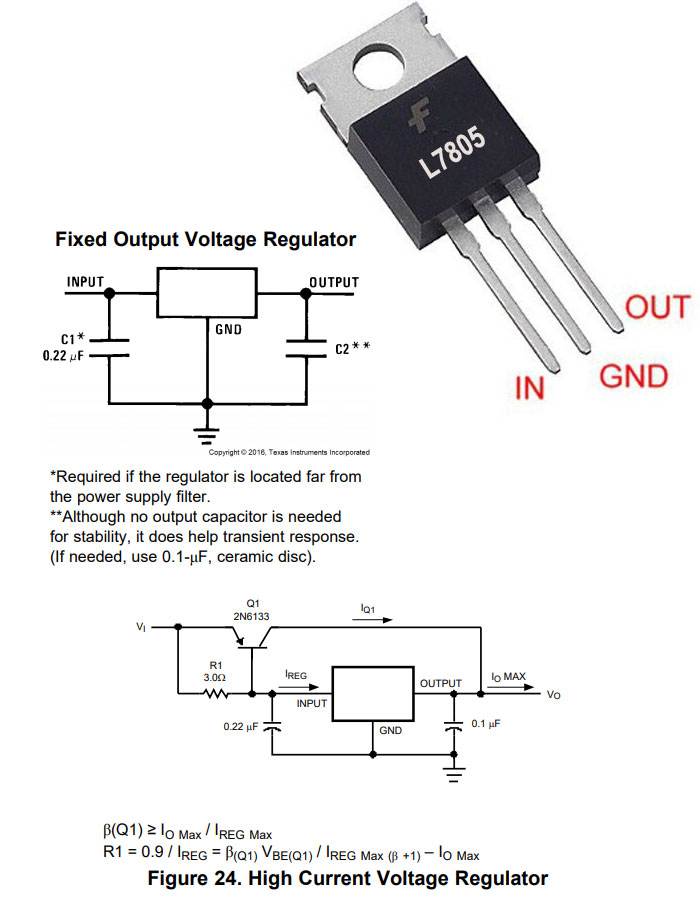
El LM7805 recibe 12V en su entrada y entrega 5V en su salida, que luego se conectan al pin de alimentación del Arduino. Los condensadores ayudan a filtrar el ruido en la entrada y salida.
Ventajas y Aplicaciones de los Reguladores Lineales 🌟
Los reguladores lineales son la mejor opción cuando se necesita una fuente de voltaje estable y el consumo de corriente no es demasiado alto. Sin embargo, si tu proyecto debe ser energéticamente eficiente, como en dispositivos que funcionan con baterías, es mejor considerar otras opciones, como los reguladores conmutados (que exploraremos en la segunda parte).
Aplicaciones Comunes:
- Proyectos con Arduino: Alimentación de sensores y módulos.
- Prototipos de bajo consumo: Donde la simplicidad es más importante que la eficiencia.
- Sistemas de audio: Donde el bajo ruido de los reguladores lineales es una gran ventaja.
📢 ¡Gracias por explorar los reguladores lineales conmigo! 📘
Espero que esta primera parte de la serie te haya ayudado a entender los fundamentos de la alimentación para microcontroladores y cómo usar reguladores lineales. Si tienes experiencias diseñando circuitos de alimentación o quieres compartir tus proyectos, ¡déjalos en los comentarios! 📝
🔔 No te pierdas la segunda parte de esta serie, donde exploraremos reguladores conmutados y cómo diseñar circuitos de alta eficiencia para proyectos más avanzados. 🌐
[ENG]
Greetings, builders of the digital future! 👋
In this first part of our series on designing power circuits for microcontrollers, we will focus on the basics and use of linear regulators. Proper power supply is critical to the proper functioning of any microcontroller-based project, as a stable and clean power source ensures that our components operate optimally. In this post, you will learn about key concepts, linear regulators, and how to design a basic microcontroller power supply. ⚡🔍
Microcontroller Power Supply Basics ⚙️
For a microcontroller to work properly, it is essential to supply it with a stable and clean voltage. Most microcontrollers, such as the Arduino (ATmega328P) or ESP32, operate at 5V or 3.3V, and an incorrect voltage can damage them or cause them to operate unstable.
Key Concepts:
- Voltage (V): The electrical potential difference that drives current flow. Most common microcontrollers typically operate at 5V or 3.3V.
- Current (A): The amount of electrical charge flowing through a circuit, measured in amps. It's important to make sure the power supply can supply enough current for all components.
- Noise and Ripple: Variations in voltage can affect microcontroller performance. Using capacitors helps smooth out these fluctuations.
Linear Regulators: Simplicity and Stability 📏
A linear regulator is a component that converts a higher input voltage to a lower output voltage in a stable manner. Linear regulators are popular for their simplicity, but they are not very efficient, as they dissipate excess power as heat.
Common Linear Regulators:
- LM7805: Regulates an input voltage (e.g. 12V) to a stable 5V output.
- LD1117-3.3: Converts a range of input voltages to a fixed 3.3V output, ideal for microcontrollers such as the ESP32.
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Easy to integrate into a circuit.
- Stability: Provides a very stable voltage output.
- Low Noise: Ideal for applications requiring clean signals.
Disadvantages:
- Inefficiency: Excess power is dissipated as heat, which is not ideal for applications requiring high efficiency.
- Power Loss: The greater the difference between the input and output voltage, the more power is lost as heat.
LM7805 Regulator Circuit Example:
Suppose we want to power an Arduino from a 12V source. We will use an LM7805 to reduce the voltage to 5V in a stable manner.
Components:
- LM7805
- Capacitors: 0.22µF (input) and 0.1µF (output)
- Power supply: 12V

The LM7805 receives 12V at its input and delivers 5V at its output, which is then connected to the Arduino's power pin. The capacitors help filter out noise at the input and output.
Advantages and Applications of Linear Regulators 🌟
Linear regulators are the best choice when you need a stable voltage source and the current draw isn't too high. However, if your project needs to be energy efficient, such as in battery-powered devices, it's better to consider other options, such as switching regulators (which we'll explore in part 2).
Common Applications:
- Arduino projects: Powering sensors and modules.
- Low-power prototyping: Where simplicity is more important than efficiency.
- Audio systems: Where the low noise of linear regulators is a big advantage.
📢 Thanks for exploring linear regulators with me! 📘
I hope this first part of the series has helped you understand the basics of microcontroller power supply and how to use linear regulators. If you have experiences designing power supply circuits or want to share your projects, leave them in the comments! 📝
🔔 Don't miss the second part of this series, where we'll explore switching regulators and how to design high-efficiency circuits for more advanced projects. 🌐
Congratulations @profwhitetower! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 100 posts.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP