[ESP/ENG] 🔥 La Ley de Joule: Cómo se Transforma la Energía en Calor en los Circuitos 🔥 🔥 Joule's Law: How Energy is Transformed into Heat in Circuits 🔥
[ESP]

¡Hola, comunidad de apasionados por la electrónica! 🚀
Hoy vamos a hablar de un principio fundamental en la electricidad y la electrónica: la Ley de Joule. Esta ley explica cómo la energía eléctrica se convierte en calor cuando circula corriente por un conductor. Es clave para entender desde el calentamiento de resistencias hasta el funcionamiento de dispositivos como planchas, estufas y fusibles. ¡Vamos a explorarlo juntos! 🔌⚙️
🔎 ¿Qué dice la Ley de Joule?
La Ley de Joule establece que la energía térmica generada en un conductor debido al paso de corriente es directamente proporcional a la resistencia, al cuadrado de la corriente y al tiempo de conducción. Matemáticamente, se expresa así:
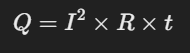
Donde:
🔹 Q = Energía disipada en forma de calor (Joules, J)
🔹 I = Corriente eléctrica (Amperios, A)
🔹 R = Resistencia del conductor (Ohmios, Ω)
🔹 t = Tiempo durante el cual fluye la corriente (segundos, s)
Esto significa que a mayor resistencia y corriente, más calor se genera en un circuito.
🔢 Ejemplo Práctico
Supongamos que tenemos una resistencia de 10 Ω por la que circula una corriente de 2 A durante 5 segundos.
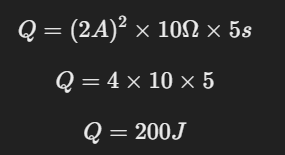
Esto significa que la resistencia liberará 200 Joules en forma de calor.
⚡ Relación con la Ley de Potencia
Si combinamos la Ley de Joule con la Ley de Potencia (P = V × I), obtenemos nuevas expresiones útiles:
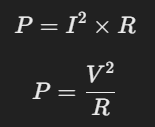
Esto nos permite calcular cuánta potencia disipa un resistor sin necesidad de conocer la energía total en Joules.
🔥 Aplicaciones de la Ley de Joule
✔️ Diseño de fusibles y protectores térmicos 🛑: Se utilizan materiales que se funden con cierto calor para cortar la corriente y evitar incendios.
✔️ Calefacción eléctrica 🌡️: Desde estufas hasta hornos eléctricos, todos aprovechan la conversión de energía en calor.
✔️ Eficiencia en circuitos electrónicos 🏗️: Se busca minimizar pérdidas de calor en microcontroladores y chips.
✔️ Diseño de disipadores y refrigeración ❄️: Se evita el sobrecalentamiento de componentes en fuentes de alimentación, amplificadores y CPU.
📢 Conclusión
La Ley de Joule es clave para entender cómo la electricidad genera calor en los circuitos. Nos ayuda a calcular el consumo energético y a diseñar sistemas más eficientes.
💡 ¿Quieres un ejemplo con Arduino, o cómo evitar pérdidas de calor en proyectos electrónicos? ¡Déjamelo en los comentarios! 📲💬
⚡ ¿Sobre qué otro principio eléctrico te gustaría leer? ¡Dímelo y seguimos explorando juntos el mundo de la electrónica! 🚀🔌
[ENG]

Hello, community of electronics enthusiasts! 🚀
Today we are going to talk about a fundamental principle in electricity and electronics: Joule's Law. This law explains how electrical energy is converted into heat when current flows through a conductor. It is key to understanding everything from the heating of resistors to the operation of devices such as irons, stoves, and fuses. Let's explore it together! 🔌⚙️
🔎 What does Joule's Law say?
Joule's Law states that the thermal energy generated in a conductor due to the passage of current is directly proportional to the resistance, the square of the current, and the conduction time. Mathematically, it is expressed as follows:
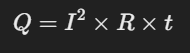
Where:
🔹 Q = Energy dissipated in the form of heat (Joules, J)
🔹 I = Electric current (Amperes, A)
🔹 R = Resistance of the conductor (Ohms, Ω)
🔹 t = Time during which the current flows (seconds, s)
This means that the greater the resistance and current, the more heat is generated in a circuit.
🔢 Practical Example
Let's say we have a 10 Ω resistor through which a current of 2 A flows for 5 seconds.
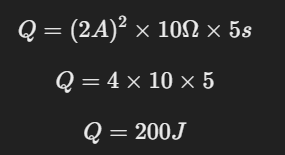
This means that the resistor will release 200 Joules in the form of heat.
⚡ Relationship with the Power Law
If we combine Joule's Law with the Power Law (P = V × I), we get new useful expressions:
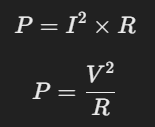
This allows us to calculate how much power a resistor dissipates without needing to know the total energy in Joules.
🔥 Applications of Joule's Law
✔️ Design of fuses and thermal protectors 🛑: Materials that melt with a certain heat are used to cut off the current and prevent fires.
✔️ Electric heating 🌡️: From stoves to electric ovens, all take advantage of the conversion of energy into heat.
✔️ Efficiency in electronic circuits 🏗️: We seek to minimize heat losses in microcontrollers and chips.
✔️ Design of heatsinks and cooling ❄️: Overheating of components in power supplies, amplifiers and CPUs is avoided.
📢 Conclusion
Joule's Law is key to understanding how electricity generates heat in circuits. It helps us calculate energy consumption and design more efficient systems.
💡 Do you want an example with Arduino, or how to avoid heat losses in electronic projects? Leave it in the comments! 📲💬
⚡ What other electrical principle would you like to read about? Tell me and we'll continue exploring the world of electronics together! 🚀🔌
Wow this is amazing we used to study this back on my first year in first semester in college but i didn't listen hahaha lol but it's great that you're sharing this
Thank you! 😃 I'm glad this brings back memories from your studies. It's never too late to revisit those concepts, and if you ever want to review or learn something new, I'll be here sharing more. 🔌💡 Cheers! 🚀