[ESP/ENG] 🚀 Explorando los Transistores de Efecto de Campo: Versatilidad en Electrónica 🚀 🚀 Exploring Field Effect Transistors: Versatility in Electronics 🚀
[ESP]
¡Hola, apasionada comunidad de Hive! 👋
En nuestro viaje por el mundo de la electrónica, no podiamos no profundizar en los Transistores de Efecto de Campo (FET). Este tipo de transistor juega un papel crucial en la electrónica moderna debido a sus características únicas y aplicaciones versátiles. 📡💡
¿Qué son los Transistores de Efecto de Campo? 🤔
Los Transistores de Efecto de Campo, comúnmente conocidos como FET, son dispositivos que utilizan un campo eléctrico para controlar la forma y la conductividad de un "canal" en un material semiconductor. A diferencia de los transistores bipolares que requieren corriente para su operación, los FET se controlan mediante voltaje, lo que los hace extremadamente eficientes en términos de consumo de energía.
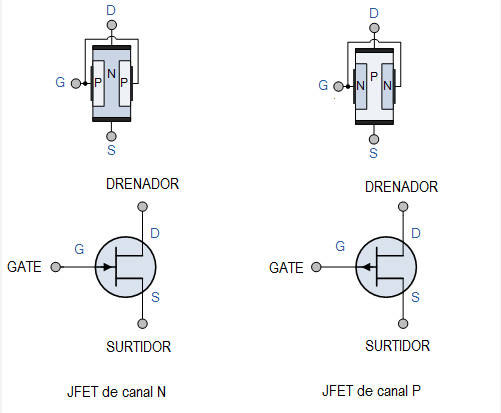
Tipos Principales de FET 🔄
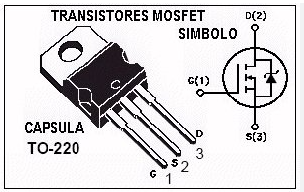
MOSFET (Transistor de Efecto de Campo de Óxido Metálico-Semiconductor): Ideal para circuitos integrados debido a su alta densidad y bajo consumo de energía.
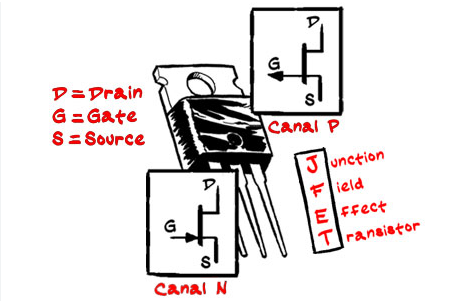
JFET (Transistor de Efecto de Campo de Unión): Utilizado en aplicaciones donde se requiere bajo ruido y alta impedancia de entrada.
Diseño y Análisis de Circuitos con FET 🔧
Al diseñar circuitos con FETs, es crucial considerar:
- La polarización: Asegurarse de que el FET opere en la región deseada de su característica de transferencia.
- La configuración del circuito: Dependiendo si se necesita un amplificador o un interruptor.
Análisis del Comportamiento
El análisis de un circuito FET incluye entender cómo el voltaje de puerta controla la corriente entre el drenaje y la fuente, y cómo los parámetros del dispositivo afectan la respuesta del circuito.
Ejemplo Práctico: Amplificador con MOSFET 🎛️
Consideremos un simple amplificador con un MOSFET:
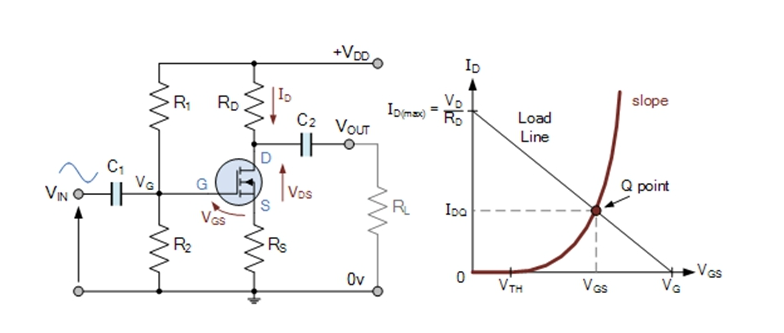
- Entrada: Señal de audio.
- Salida: Señal amplificada para altavoces.
- Configuración: MOSFET configurado como amplificador de clase A.
Este tipo de configuración es común en equipos de audio donde se busca eficiencia y fidelidad en la amplificación de señales.
Aplicaciones de los FETs 💼
- Computadoras y Tecnología Móvil: En la fabricación de procesadores y memorias debido a su capacidad para operar a voltajes muy bajos y su alta densidad de integración.
- Sistemas de Comunicación: Utilizados en transceptores y otros equipos de comunicación para funciones de conmutación y amplificación.
- Control de Potencia: En convertidores de potencia y reguladores de voltaje debido a su eficiencia y capacidad de manejo de alta potencia.
¡Gracias por leer! 📚
Espero que este post te haya sido útil. Si fue así, no olvides dejar un comentario y compartir tus pensamientos o preguntas. 📝
🔔 No te pierdas mis próximas publicaciones donde seguiremos explorando el fascinante mundo de la electrónica y los circuitos. Cada semana, voy a traer nuevos temas, ejemplos prácticos y recursos para que sigas aprendiendo y mejorando tus habilidades. 🌐
🤝 Sígueme en mis redes sociales, donde podrás conectarte con otros entusiastas de la electrónica, hacer preguntas y recibir ayuda en tiempo real. ¡Estamos aquí para ayudarte! 💬
📷 Comparte tus proyectos: Si has aplicado estos conocimientos en tus propios proyectos, ¡nos encantaría verlos! Comparte tus avances y aprende de otros en nuestra comunidad. 🛠️
🌟 Mantente en contacto: Sígueme en mis redes sociales para actualizaciones, contenido exclusivo y más consejos sobre electrónica y circuitos. Tu participación y apoyo son lo que hace que esta comunidad crezca y se enriquezca. 📈
¡Nos estamos leyendo! Hasta entonces, sigue explorando, aprendiendo y compartiendo. ¡Juntos, hacemos la electrónica más accesible y emocionante para todos! 🚀✨
[ENG]
Hello, passionate Hive community! 👋
On our journey through the world of electronics, we couldn't help but delve into Field Effect Transistors (FET). This type of transistor plays a crucial role in modern electronics due to its unique characteristics and versatile applications. 📡💡
What are Field Effect Transistors? 🤔
Field Effect Transistors, commonly known as FETs, are devices that use an electric field to control the shape and conductivity of a "channel" in a semiconductor material. Unlike bipolar transistors that require current for operation, FETs are voltage controlled, making them extremely efficient in terms of power consumption.

Main Types of FET 🔄
MOSFET (Metal Oxide Field Effect Transistor-Semiconductor): Ideal for integrated circuits due to its high density and low power consumption.

JFET (Junction Field Effect Transistor): Used in applications where low noise and high input impedance are required.

Design and Analysis of Circuits with FET 🔧
When designing circuits with FETs, it is crucial to consider:
- Biasing: Ensure that the FET operates in the desired region of its transfer characteristic.
- Circuit configuration: Depending on whether an amplifier or a switch is needed.
Behavior Analysis
Analysis of a FET circuit includes understanding how the gate voltage controls the current between drain and source, and how device parameters affect the response of the circuit.
Practical Example: Amplifier with MOSFET 🎛️
Let's consider a simple amplifier with a MOSFET:

- Input: Audio signal.
- Output: Amplified signal for speakers.
- Configuration: MOSFET configured as class A amplifier.
This type of configuration is common in audio equipment where efficiency and fidelity are sought in signal amplification.
Applications of FETs 💼
- Computers and Mobile Technology: In the manufacturing of processors and memories due to their ability to operate at very low voltages and their high integration density.
- Communication Systems: Used in transceivers and other communication equipment for switching and amplification functions.
- Power Control: In power converters and voltage regulators due to their efficiency and high power handling capacity.
Thank you for reading! 📚
I hope this post has been useful to you. If so, don't forget to leave a comment and share your thoughts or questions. 📝
🔔 Don't miss my next posts where we will continue exploring the fascinating world of electronics and circuits. Each week, I'll bring new topics, practical examples, and resources to keep you learning and improving your skills. 🌐
🤝 Follow me on my social networks, where you can connect with other electronics enthusiasts, ask questions and receive help in real time. We are here to help you! 💬
📷 Share your projects: If you have applied this knowledge in your own projects, we would love to see them! Share your progress and learn from others in our community. 🛠️
🌟 Stay in touch: Follow me on my social networks for updates, exclusive content and more tips on electronics and circuits. Your participation and support are what make this community grow and enrich. 📈
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.