[ESP/ENG]🔌 Circuito Serie RLC: Análisis de Comportamiento y Respuesta parte 20 📈 |🔌 RLC Series Circuit: Behavior Analysis and Response part 20 📈
ESP
¡Hola hermosa comunidad de Hive! Hoy vamos a explorar el fascinante mundo de los circuitos serie RLC. Este tipo de circuito es fundamental en muchas aplicaciones electrónicas, como filtros, osciladores y sistemas de comunicación. Comprender cómo funciona un circuito RLC es esencial para diseñar y analizar sistemas electrónicos más complejos. 🚀⚡
Introducción al Circuito Serie RLC 📚
Un circuito RLC en serie consiste en una resistencia (R), un inductor (L), y un capacitor (C) conectados en serie a una fuente de voltaje. Este circuito presenta una respuesta dinámica compleja debido a la interacción entre la resistencia, la inductancia y la capacitancia.
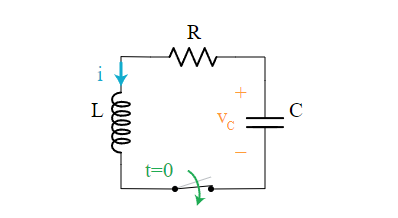
Componentes del Circuito 🔧
- Resistencia (R): Se opone al flujo de corriente y disipa energía en forma de calor.
- Inductor (L): Almacena energía en un campo magnético y se opone a cambios rápidos en la corriente.
- Capacitor (C): Almacena energía en un campo eléctrico y se opone a cambios rápidos en el voltaje.
Ecuaciones Fundamentales 📝
La ecuación diferencial que describe el comportamiento de un circuito serie RLC es: 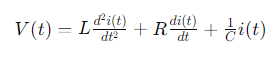
Donde:
- 𝑉(𝑡) es el voltaje aplicado.
- 𝑖(𝑡) es la corriente que circula por el circuito.
- 𝐿 es la inductancia de la bobina.
- 𝑅 es la resistencia.
- 𝐶 es la capacitancia.
Análisis del Comportamiento del Circuito Serie RLC ⏱️
El comportamiento del circuito serie RLC se puede analizar dividiendo su respuesta en diferentes casos dependiendo del factor de amortiguamiento (𝜁):
- Sobre-amortiguado (𝜁>1): La corriente vuelve a cero sin oscilar.
- Críticamente amortiguado (𝜁=1): La corriente vuelve a cero tan rápido como sea posible sin oscilar.
- Sub-amortiguado (𝜁<1): La corriente oscila antes de estabilizarse.
La constante de tiempo (τ) y el factor de amortiguamiento (ζ) están dados por: 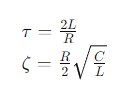
Respuesta del Circuito a una Excitación Paso 🚀
Aplicación del Voltaje: Al aplicar un voltaje 𝑉0 al circuito, la respuesta depende de los valores de R, L, y C.
Oscilación y Amortiguamiento: Dependiendo del valor de 𝜁, el circuito puede oscilar o no.
Estabilización: Con el tiempo, la corriente se estabiliza en un valor determinado por el voltaje aplicado y los valores de los componentes.
La solución general para la corriente en un circuito serie RLC sub-amortiguado es: 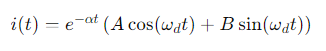
Donde:
Ejemplo Práctico de un Circuito Serie RLC 🛠️
Consideremos un circuito serie RLC con una resistencia de 10Ω, un inductor de 2𝐻, y un capacitor de 0.5𝐹. Supongamos que se aplica un voltaje de 10𝑉.
Constante de Tiempo (τ):
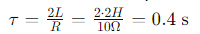
Factor de Amortiguamiento (𝜁):
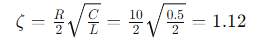
Frecuencia Natural (𝜔0):
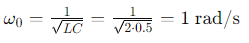
📢 ¡Gracias por Leer! Mantenete Conectado para Más Contenido Educativo 📚
Espero que este post te haya sido útil. Si fue así, no olvides dejar un comentario y compartir tus pensamientos o preguntas. 📝
🔔 No te pierdas mis próximas publicaciones donde seguiremos explorando el fascinante mundo de la electrónica y los circuitos. Cada semana, voy a traer nuevos temas, ejemplos prácticos y recursos para que sigas aprendiendo y mejorando tus habilidades.
🤝 Seguime en mis redes sociales, donde podrás conectarte con otros entusiastas de la electrónica, hacer preguntas y recibir ayuda en tiempo real. ¡Estamos aquí para ayudarte!
📷 Comparte tus Proyectos: Si has aplicado estos conocimientos en tus propios proyectos, ¡nos encantaría verlos! Comparte tus avances y aprende de otros en nuestra comunidad.
🌟 Mantente en Contacto: Sígueme en mis redes sociales para actualizaciones, contenido exclusivo y más consejos sobre electrónica y circuitos. Tu participación y apoyo son lo que hace que esta comunidad crezca y se enriquezca.
¡Nos estamos leyendo! Hasta entonces, sigue explorando, aprendiendo y compartiendo. ¡Juntos, hacemos la electrónica más accesible y emocionante para todos! 🚀✨
ENG
🔌 RLC Series Circuit: Behavior Analysis and Response 📈
Hello beautiful Hive community! Today we are going to explore the fascinating world of RLC series circuits. This type of circuit is essential in many electronic applications, such as filters, oscillators, and communication systems. Understanding how an RLC circuit works is essential for designing and analyzing more complex electronic systems. 🚀⚡
Introduction to the RLC Series Circuit 📚
A series RLC circuit consists of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C) connected in series to a voltage source. This circuit presents a complex dynamic response due to the interaction between resistance, inductance and capacitance.

Circuit Components 🔧
- Resistance (R): Opposes the flow of current and dissipates energy in the form of heat.
- Inductor (L): Stores energy in a magnetic field and opposes rapid changes in current.
- Capacitor (C): Stores energy in an electric field and opposes rapid changes in voltage.
Fundamental Equations 📝
The differential equation that describes the behavior of an RLC series circuit is: 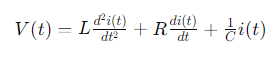
Where:
- 𝑉(𝑡) is the applied voltage.
- 𝑖(𝑡) is the current that circulates through the circuit.
- 𝐿 is the inductance of the coil.
- 𝑅 is the resistance.
- 𝐶 is the capacitance.
Analysis of the Behavior of the RLC Series Circuit ⏱️
The behavior of the RLC series circuit can be analyzed by dividing its response into different cases depending on the damping factor (𝜁):
- Over-damped (𝜁>1): The current returns to zero without oscillating.
- Critically damped (𝜁=1): The current returns to zero as quickly as possible without oscillating.
- Underdamped (𝜁<1): The current oscillates before stabilizing.
The time constant (τ) and the damping factor (ζ) are given by: 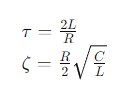
Circuit Response to a Step Excitation 🚀
Application of Voltage: When applying a voltage 𝑉0 to the circuit, the response depends on the values of R, L, and C.
Oscillation and Damping: Depending on the value of 𝜁, the circuit may or may not oscillate.
Stabilization: Over time, the current stabilizes at a value determined by the applied voltage and component values.
The general solution for the current in an underbuffered RLC series circuit is: 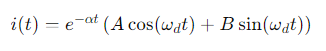
Where:
Practical Example of an RLC Series Circuit 🛠️
Let's consider a series RLC circuit with a 10Ω resistor, a 2𝐻 inductor, and a 0.5𝐹 capacitor. Suppose a voltage of 10𝑉 is applied.
Time Constant (τ):
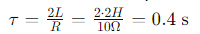
Damping Factor (𝜁):
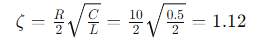
Natural Frequency (𝜔0):
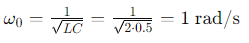
📢 Thanks for reading! Stay Connected for More Educational Content 📚
I hope this post has been useful to you. If so, don't forget to leave a comment and share your thoughts or questions. 📝
🔔 Don't miss my next posts where we will continue exploring the fascinating world of electronics and circuits. Each week, I'll bring new topics, practical examples, and resources to keep you learning and improving your skills.
🤝 Follow me on my social networks, where you can connect with other electronics enthusiasts, ask questions and receive help in real time. We are here to help you!
📷 Share your Projects: If you have applied this knowledge in your own projects, we would love to see them! Share your progress and learn from others in our community.
🌟 Stay in Touch: Follow me on my social networks for updates, exclusive content and more tips on electronics and circuits. Your participation and support are what make this community grow and enrich.
We are reading each other! Until then, keep exploring, learning and sharing. Together, we make electronics more accessible and exciting for everyone! 🚀✨
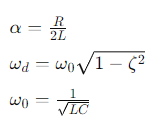
Congratulations @profwhitetower! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 4000 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPCheck out our last posts:
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.