[ES ❀ EN] Principios básicos del metabolismo ❀ Basic principles of metabolism
En este apartado se hace referencia a la definición del metabolismo de los seres vivos, en el cual existen intercambios de materia y energía en sus procesos metabólicos. Además, se presenta la explicación de los dos grandes procesos metabólicos: catabolismo y anabolismo.
This section refers to the definition of the metabolism of living beings, in which there are exchanges of matter and energy in their metabolic processes. In addition, an explanation of the two major metabolic processes: catabolism and anabolism is presented.
Toda la investigación forma parte de un desarrollo introductorio a los procesos químicos y físicos que se producen en el cuerpo humano, en donde se transforman los elementos (nutrientes) que ingresan al cuerpo, como: oxigeno, agua, alimentos y otros productos químicos, que se convierten en energía para luego usarla como “combustible” en el funcionamiento del organismo.
All the research is part of an introductory development to the chemical and physical processes that occur in the human body, where the elements (nutrients) that enter the body, such as oxygen, water, food and other chemicals, are transformed into energy and then used as "fuel" in the functioning of the organism.
La composición de esta palabra define su significado como las características de los seres vivos en la facultad de modificar químicamente la naturaleza de algunas sustancias. Según la bibliografía encontrada ocurre en explicar lo siguiente:
The composition of this word defines its meaning as the characteristics of living beings in the faculty of chemically modifying the nature of some substances. According to the bibliography found it occurs in explaining the following:
“Hace referencia a todos los procesos físicos y químicos del cuerpo que convierten o usan energía, tales como: respiración, circulación sanguínea, regulación de la temperatura corporal, contracción muscular, digestión de alimentos y nutrientes, eliminación de los desechos a través de la orina y de las heces y funcionamiento del cerebro y los nervios. Estos complejos procesos interrelacionados son la base de la vida a escala molecular y permiten las diversas actividades de las células: crecer, reproducirse, mantener sus estructuras y responder a estímulos, entre otras…” ❀ Metabolismo
“It refers to all physical and chemical processes in the body that convert or use energy, such as: respiration, blood circulation, regulation of body temperature, muscle contraction, digestion of food and nutrients, elimination of waste through urine and feces, and brain and nerve function. These complex interrelated processes are the basis of life at the molecular scale and enable the various activities of cells: growth, reproduction, maintenance of their structures, and response to stimuli, among others…” ❀ Metabolismo
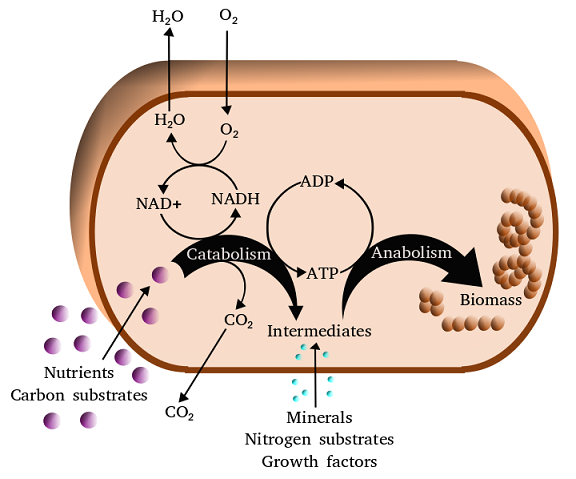
Entre los principios básicos del metabolismo, se puede decir que son procesos fisicoquímicos ocurridos en la célula, además del conjunto de reacciones bioquímicas que se producen en los organismos, por medio de las cuales las sustancias tomadas del exterior se transforman y se utilizan para formar las estructuras orgánicas, o para obtener energía. En los procesos metabólicos hay siempre un intercambio de materia y energía con el exterior, gracias al cual pueden los seres vivos mantener el alto grado de organización de sus células y tejidos.
Among the basic principles of metabolism, we can say that they are physicochemical processes occurring in the cell, in addition to the set of biochemical reactions that occur in organisms, by means of which substances taken from the outside are transformed and used to form organic structures, or to obtain energy. In the metabolic processes there is always an exchange of matter and energy with the exterior, thanks to which living beings can maintain the high degree of organization of their cells and tissues.

Hay organismos que utilizan como material los compuestos inorgánicos del medio, mientras que otros aprovechan sólo la materia orgánica, previamente elaborada por otro ser vivo. En el primer caso se trata de seres Autótrofos, y en el segundo caso, de seres Heterótrofos. A su vez, unos y otros pueden obtener la energía que necesitan para vivir bien directamente de la luz solar o bien de las reacciones químicas. Un ejemplo típico de organismos autótrofos que utilizan una fuente luminosa de energía son los vegetales y las Cianofíceas, mientras que muchas bacterias, aun siendo autótrofas, deben obtener la energía de una fuente química. Ejemplos de organismos heterótrofos y a la vez dependientes de la energía química son los animales y los hongos.
There are organisms that use as material the inorganic compounds of the environment, while others use only organic matter, previously elaborated by another living being. In the first case we are dealing with autotrophic beings, and in the second case, with heterotrophic beings. In turn, both can obtain the energy they need to live either directly from sunlight or from chemical reactions. A typical example of autotrophic organisms that use a light source of energy are plants and Cyanophyceae, while many bacteria, although autotrophic, must obtain their energy from a chemical source. Examples of heterotrophic organisms that are also dependent on chemical energy are animals and fungi.

La fuente de energía química requerida por numerosos seres vivos deriva de los Procesos de Oxidación-Reducción o Reacciones Redox, en los cuales una sustancia se oxida, es decir, pierde electrones, con lo que experimenta una pérdida de energía, y simultáneamente otra se reduce ganando electrones, con lo que incrementa su energía. En los organismos, la oxidación se produce paso a paso, para evitar los cambios bruscos de temperatura y un desprendimiento masivo del calor que mataría a la célula. Así, el nivel de oxidación de los átomos de carbono es gradual; es mínimo en los hidrocarburos (-CH3), algo mayor en los alcoholes (-CH2OH), intermedio en los aldehídos (-CHO), más elevado en los ácidos (-COOH) y máximo en el CO2. Este es el producto natural de la combustión completa de las moléculas orgánicas.
The source of chemical energy required by many living beings derives from Oxidation-Reduction Processes or Redox Reactions, in which one substance is oxidized, i.e. it loses electrons, thus experiencing a loss of energy, and simultaneously another is reduced by gaining electrons, thus increasing its energy. In organisms, oxidation occurs step by step, to avoid sudden changes in temperature and a massive release of heat that would kill the cell. Thus, the level of oxidation of carbon atoms is gradual; it is minimal in hydrocarbons (-CH3), somewhat higher in alcohols (-CH2OH), intermediate in aldehydes (-CHO), higher in acids (-COOH) and maximal in CO2. This is the natural product of the complete combustion of organic molecules.

La energía contenida en los enlaces C–H se pierde, en parte, en forma de calor y en parte se almacena en los enlaces de alto contenido energético del ATP. Este puede formarse tanto por deshidrogenación de la molécula combustible como por transferencia de los hidrógenos hasta el oxígeno, la cual se lleva a cabo por medio de las moléculas como el NAD, FAD, citocromos, etc. Como es lógico suponer, todas aquellas rutas que sean aerobias, es decir, que se verifiquen en presencia de oxígeno hasta la combustión total, producirán mucha mayor energía, y más ATP por consiguiente, que las rutas anaerobias.
The energy contained in the C-H bonds is partly lost as heat and partly stored in the high-energy bonds of ATP. ATP can be formed either by dehydrogenation of the fuel molecule or by transfer of the hydrogens to oxygen, which is carried out by molecules such as NAD, FAD, cytochromes, etc. As it is logical to suppose, all those routes that are aerobic, that is to say, that take place in the presence of oxygen until total combustion, will produce much more energy, and therefore more ATP, than anaerobic routes.
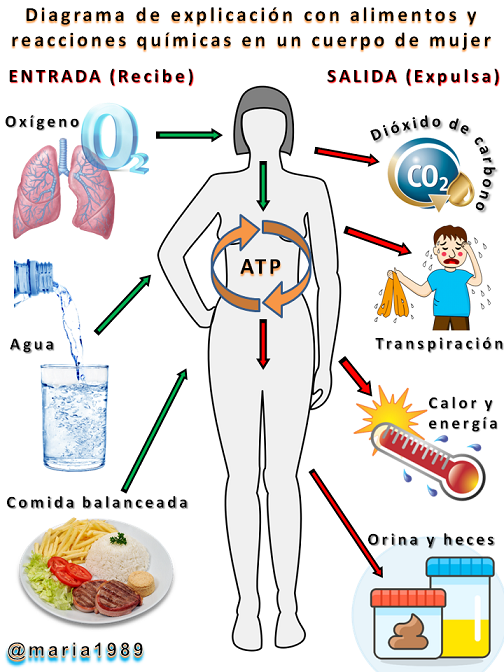
Dióxido de carbono❀Transpiración❀Calor y energía❀Orina y heces❀
Los dos grandes procesos metabólicos son:
The two major metabolic processes are:
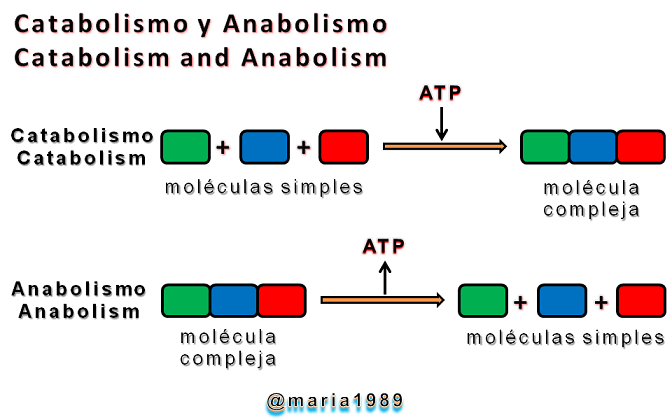
1) Catabolismo o degradación de las moléculas absorbidas del medio, en que dichas moléculas se oxidan y se fragmentan. En este proceso, se produce energía (reacciones exegónicas).
2) Síntesis de nuevas biomoléculas, o Anabolismo, por el cual se reponen las estructuras del organismo que han sufrido un desgaste en el transcurso del tiempo. En éste se consume (reacciones endergónicas).
1) Catabolism or degradation of molecules absorbed from the medium, in which these molecules are oxidized and fragmented. In this process, energy is produced (exogenous reactions).
2) Synthesis of new biomolecules, or Anabolism, by which the structures of the organism that have suffered wear and tear over time are replaced. In this process, energy is consumed (endergonic reactions).
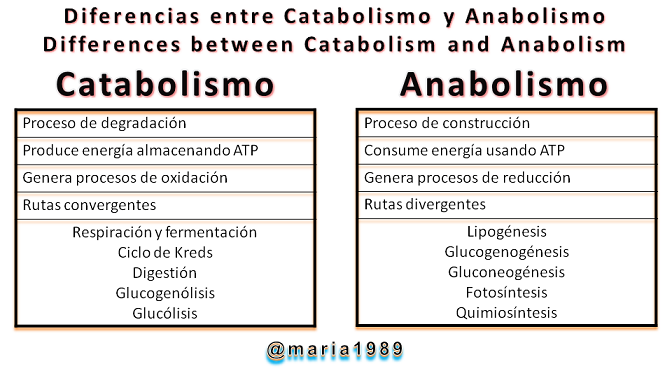
El catabolismo de los carbohidratos se produce en los procesos de fermentación, anaerobios, entre los que se incluyen la Glucólisis, la cual es una sucesión de atenuación de compuestos como la glucosa, en donde la reacción es la liberación de energía conservada en los enlaces químicos; y la Fermentación Alcohólica.
Carbohydrate catabolism occurs in anaerobic fermentation processes, including Glycolysis, which is a succession of attenuation of compounds such as glucose, where the reaction is the release of conserved energy in chemical bonds; and Alcoholic Fermentation.
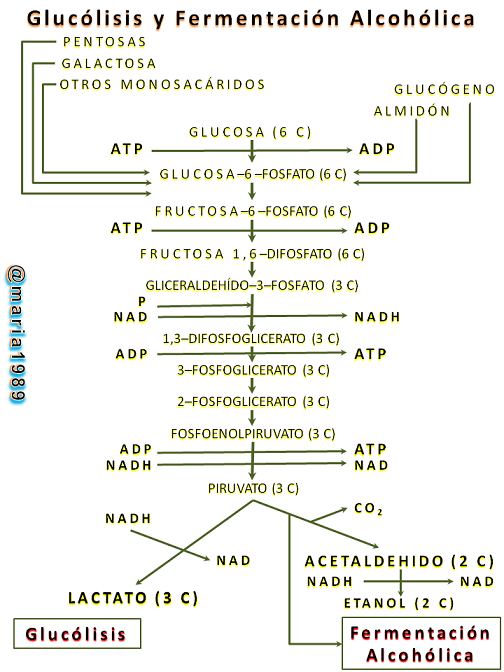
Por otra parte están las reacciones anabólicas, estas utilizan la energía liberada recomponiendo los enlaces químicos, además que construyen componentes celulares como proteínas y ácidos nucleicos. Los lípidos, por su parte, se descomponen en sus elementos constituyentes, alcoholes y ácidos grasos, en donde, estos últimos, experimentan la denominada β–oxidación de los ácidos grasos. En cuanto a los aminoácidos, unos se ven sometidos a reacciones de transaminación y otros a la desaminación oxidativa. Los productosa resultantes del catabolismo, tanto de los carbohidratos como de los lípidos y aminoácidos, se integran posteriormente en el denominado Ciclo de Krebs, en algunas de cuyas reacciones se liberan protones que son transportados hasta la Cadena Respiratoria. En ella, dichos protones se unen finalmente con el oxígeno, produciéndose H2O y ATP (fosforilación oxidativa).
On the other hand, there are the anabolic reactions, which use the energy released to recompose chemical bonds and build cellular components such as proteins and nucleic acids. Lipids, on the other hand, are broken down into their constituent elements, alcohols and fatty acids, where the latter undergo the so-called β-oxidation of fatty acids. As for amino acids, some are subjected to transanimation reactions and others to oxidative deamination. The products resulting from catabolism, both of carbohydrates and of lipids and amino acids, are subsequently integrated into the so-called Krebs Cycle, in some of whose reactions protons are released and transported to the respiratory chain. There, these protons finally unite with oxygen, producing H2O and ATP (Oxidative Phosphorylation).

En los dos grandes procesos metabólicos, catabolismo y anabolismo, ambos no pueden ejecutarse aisladamente, ya que uno precisa del otro: son organizados de forma natural como procesos acoplados, ya que sus reacciones tienen costumbre de agruparse de modo que el producto de una es el sustrato de la subsecuente, recibiendo el nombre de rutas metabólicas.
In the two major metabolic processes, catabolism and anabolism, both cannot be carried out in isolation, since one needs the other: they are naturally organized as coupled processes, since their reactions have a habit of grouping together so that the product of one is the substrate of the subsequent one, receiving the name of metabolic pathways.

Los procesos anabólicos siguen, en su mayor parte, rutas que no se corresponden con el camino inverso de los procesos catabólicos, debido a que muchas reacciones de éstos últimos no son reversibles y se desprende en ellas una elevada cantidad de energía, de forma que constituyen auténticas “cestas energéticas” imposibles de remontar en sentido inverso.
Anabolic processes follow, for the most part, routes that do not correspond to the inverse path of catabolic processes, because many reactions of the latter are not reversible and a high amount of energy is released in them, so that they constitute real "energy baskets" impossible to go back in the opposite direction.
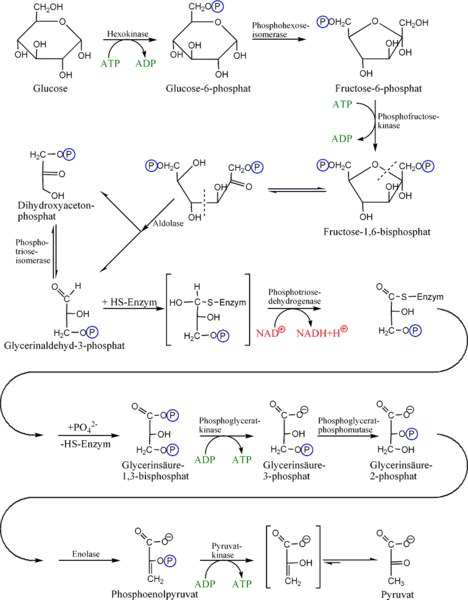
[ES] “La glucólisis, ejemplo de ruta metabólica en la que se transforma una molécula de glucosa en dos moléculas de piruvato,
y se genera energía ATP y poder reductor (NADPH)”
[EN] “Glycolysis, an example of a metabolic pathway in which one molecule of glucose is transformed into two molecules of pyruvate,
generating ATP energy and reducing power (NADPH)”
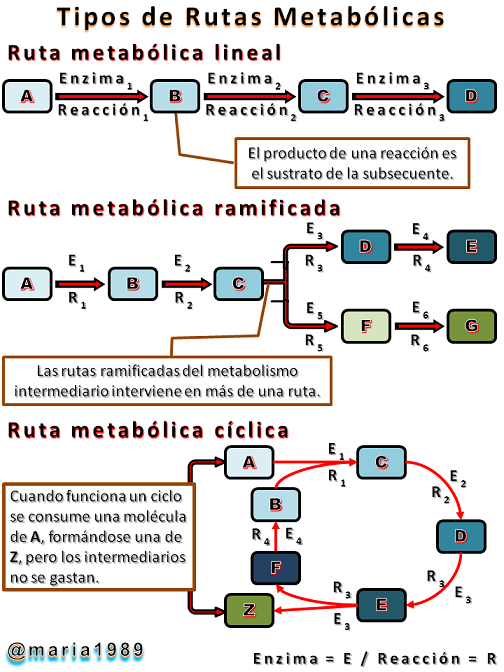
Un sustrato inicial denominado Precursor, en la ruta metabólica, es convertido en Producto final; en la ruta a los compuestos intermedios se les dice intermediarios metabólicos. Estas rutas pueden clasificarse como:
- Rutas Lineales: son reacciones en cadena, que de forma secuencial, el producto de una respuesta es por su parte el reactivo de la posterior.
- Rutas Ramificadas: a través de un precursor se forman diversos productos, en donde un metabolismo interviene a su vez en más de una ruta.
- Rutas Cíclicas: los intermediarios metabólicos que intervienen en este tipo de ruta no son consumidos en el transcurso de la modificación del precursor en el producto.
An initial substrate called Precursor, in the metabolic pathway, is converted into an End Product; in the pathway the intermediate compounds are called metabolic intermediates. These pathways can be classified as:
- Linear Routes: they are chain reactions, which sequentially, the product of one response is in turn the reactant of the subsequent one.
- Branched Routes: several products are formed through a precursor, where a metabolism is involved in more than one pathway.
- Cyclic Routes: the metabolic intermediates involved in this type of pathway are not consumed in the course of the modification of the precursor into the product.
La concepción del metabolismo nos hace considerar que en nuestro organismo se desarrollan grandes procesos, los cuales de manera compleja se interrelacionan creando el fundamento de la vida, a una escala molecular; permitiendo las variadas acciones de las células, como: “crecer, reproducirse, mantener sus estructuras y responder a estímulos”, etc.
The conception of metabolism makes us consider that in our organism great processes are developed, which in a complex way are interrelated creating the foundation of life, at a molecular scale; allowing the varied actions of the cells, such as: “growing, reproducing, maintaining their structures and responding to stimuli”, etc.
¡ SIEMPRE GRACIAS
POR SU AMABLE ATENCIÓN !
POR SU AMABLE ATENCIÓN !
ALWAYS THANK YOU
FOR YOUR LOVING CARE !
FOR YOUR LOVING CARE !

I dedicate this report to the educational and cultural training of everyone who knows its importance and respects the value of integral education
Dedico este informe a la formación educativa y cultural de todo aquel que conoce su importancia y respeta lo valioso de la educación integral
❀ @maria1989 ❀
Reference articles (Artículos de consulta):
❀ Catabolismo y Anabolismo (Catabolism and Anabolism)
❀ Rutas Matabólicas (Matabolic Routes)
❀ Metabolismo (Metabolism)
C R E D I T S (Créditos):
❀ Las imágenes de dominio público fueron reeditadas con las aplicaciones: Paint y Microsoft Office Power Point, formateadas como archivo PNG
❀ The images (public domain) were re-edited with the applications: Paint and Microsoft Office Power Point, formatted as PNG file.
❀ Todo este material es producto de una investigación universitaria para la cátedra de Biología (L.U.Z.), va dirigido al nivel escolar de primaria y también secundaria, para el agrado y satisfacción de quienes estén solicitando dicha información.
❀All this material is the product of a university research for the Biology department (L.U.Z.), it is directed to the primary school level and high school, for the pleasure and satisfaction of those who are requesting this information.

Congratulations @maria1989! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s):
Your next target is to reach 100 posts.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Check out the last post from @hivebuzz:
Support the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!
https://twitter.com/Jogonz18/status/1574833069491720192
The rewards earned on this comment will go directly to the people sharing the post on Twitter as long as they are registered with @poshtoken. Sign up at https://hiveposh.com.
O wow, this is good education on the body workings. Catabolism and Anabolism. Are you a scientist?
Cheers
I am not a scientist, I only work as an elementary school teacher.
Thank you for commenting. Regards @ogeewitty
No soy científica, sólo trabajo como maestra de escuela primaria
Gracias por comentar. Saludos @ogeewitty
Yes an extremely indepth look for sure!
An intelligent post from an intelligent person! 👍🏼⚡🧠⚡👍🏼
Thank You for posting and have an Amazing Mid-Week!
Thank you very much for your gratifying words. Greetings @lesmann
Muchísimas gracias por sus gratificantes palabras. Saludos @lesmann
Absolutely and Greetings to you @maria1989 !
Thank You for sharing your knowledge!
👍🏼🤓👍🏼
You have a Amazing Sunday!
🙋🏻♀️✨🌄✨🙋🏻♀️
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.
¡Felicitaciones!
1. Invierte en el PROYECTO ENTROPÍA y recibe ganancias semanalmente. Entra aquí para más información.
3. Suscríbete a nuestra COMUNIDAD, apoya al trail de @Entropia y así podrás ganar recompensas de curación de forma automática. Entra aquí para más información sobre nuestro trail.
4. Creación de cuentas nuevas de Hive aquí.
5. Visita nuestro canal de Youtube.
Atentamente
El equipo de curación del PROYECTO ENTROPÍA
Muchísimas gracias @entropia por el reconocimiento