The Silent Thief: Your Bone Health Guide
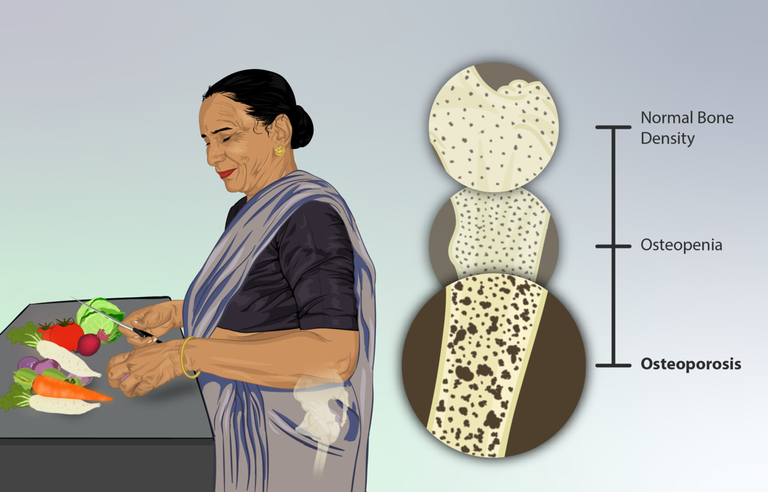
Osteoporosis is a common condition that affects the bones, making them weak and more likely to break. It is often referred to as the "silent disease" because it develops slowly over time without any symptoms until a fracture occurs. Osteoporosis can have serious consequences on a person's quality of life, leading to pain, disability, and even death in severe cases. In this essay, we will explore the causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis is a condition that occurs when the bones lose density and become more fragile. This can happen for a variety of reasons, including aging, hormonal changes, and certain medical conditions. Women are more likely to develop osteoporosis than men, especially after menopause when estrogen levels decrease. Other risk factors for osteoporosis include a family history of the disease, a sedentary lifestyle, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a diet low in calcium and vitamin D.
While osteoporosis itself does not cause any symptoms, it can lead to fractures in the spine, hip, wrist, or other bones. These fractures can be painful and may require surgery to repair. In severe cases, they can also lead to complications such as chronic pain, disability, and loss of independence. That is why it is important to diagnose and treat osteoporosis early to prevent these serious consequences.
Diagnosing osteoporosis usually involves a bone density test, also known as a DEXA scan. This test measures the density of your bones and can help determine your risk of fractures. Treatment for osteoporosis focuses on building and maintaining strong bones to prevent fractures. This may involve lifestyle changes such as eating a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, engaging in weight-bearing exercises, and quitting smoking. In some cases, medications may also be prescribed to help increase bone density and reduce the risk of fractures.
In conclusion, osteoporosis is a common condition that can have serious consequences on a person's health and well-being. It is important to be aware of the risk factors for osteoporosis and to take steps to prevent and treat the disease. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, getting regular exercise, and following your doctor's recommendations, you can help protect your bones and reduce your risk of fractures. Remember, it is never too late to start taking care of your bones – they are the foundation that supports you throughout your life.
References
(1) Pathophysiology and treatment of osteoporosis: challenges ... - Springer. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40520-021-01817-y.
(2) Osteoporosis - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/osteoporosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20351968.
(3) Osteoporosis | National Institute on Aging. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/osteoporosis.
(4) Osteoporosis | MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/osteoporosis.html.
(5) Osteoporosis Causes & Symptoms | NIAMS. https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/osteoporosis.
(6) en.wikipedia.org. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteoporosis.


Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.