The basal ganglia and Modulations
Introduction
The basal ganglia may sound like a complicated term, but they play an important role in helping us move, think, and feel. You can imagine them as a team of brain cells working together like a well-oiled machine to help us perform everyday tasks. In this article, we will discuss the basal ganglia and how they influence different aspects of our lives. The structure is part of the brain and we understand that it shapes our behaviours and emotions.
Structure of the Basal Ganglia
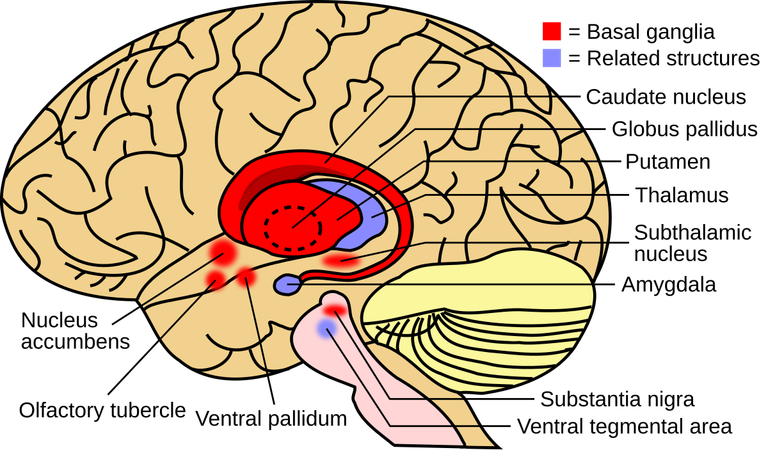
The basal ganglia are a collection of nuclei deep within the brain that form a complex network responsible for coordinating movement, cognition, and emotions. These nuclei include the striatum, globus pallidus, substantia nigra, and subthalamic nucleus, each playing a specific function in the overall performance of the basal ganglia.
The striatum, often considered the input centre of the basal ganglia, receives signals from various parts of the brain, especially the cerebral cortex, related to movement, decision-making, and reward. It processes these signals and sends outputs to other nuclei within the basal ganglia to coordinate motor functions and cognitive processes. The globus pallidus and substantia nigra act as output centres, fine-tuning the signals sent to the thalamus and influencing movement initiation or inhibition.
Another important nucleus is the subthalamic nucleus, which acts as a relay station, facilitating communication between different parts of the basal ganglia. Together, these nuclei work to ensure that our movements are coordinated, our decisions are well-informed, and our emotions are regulated.
Role of the Basal Ganglia in Modulations
The basal ganglia exhibit their function in modulating a wide range of signals in our bodies, including motor control, cognitive processes, and emotional responses. Let's take a closer look at how the basal ganglia influence these vital aspects of our daily lives.
Motor Control: One of the primary functions of the basal ganglia is to regulate voluntary movement. Let's assume you want to reach for a cup of coffee or take a step forward, your basal ganglia are at work behind the scenes, ensuring that your movements are smooth and coordinated.

Dysfunction in the basal ganglia can lead to movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease, where patients experience tremors, muscle rigidity, and slowness of movement due to a lack of dopamine production in the substantia nigra.
Cognitive Processes: In addition to motor control, the basal ganglia also play a role in cognitive functions such as decision-making, executive control, and learning. The striatum, which is a key component of the basal ganglia, is involved in forming habits and routines, thus allowing us to perform tasks automatically without conscious effort. Disruptions in the basal ganglia can manifest as cognitive impairments seen in conditions like Huntington's disease, characterized by progressive cognitive decline and movement disorders.
Emotional Responses: Our emotional responses are also influenced by the basal ganglia, particularly in regulating reward and motivation. The nucleus accumbens, part of the striatum process rewarding stimuli and reinforcing behaviours. Dysregulation of the basal ganglia circuitry can contribute to mood disorders such as depression or addiction, where an imbalance in the brain's reward system affects emotional well-being.
All that you have read above shows that the basal ganglia is an important part of our brain which interferes with almost all our daily activities. Any disorder to the performance of the basal ganglia would result in a serious problem which we'll see later.
Disorders Associated with Basal Ganglia Dysfunction
Even though the basal ganglia are important for normal brain function, disruptions in this complex network can lead to a variety of neurological and psychiatric disorders. Below are some of the disorders or challenges faced with impaired basal ganglia.
Parkinson's Disease: Perhaps one of the most well-known disorders linked to basal ganglia dysfunction is Parkinson's disease.
This progressive neurological condition is characterised by the degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra, leading to motor symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia (slowness of movement). The loss of dopamine in the basal ganglia disrupts the balance of neurotransmitters that regulate motor control, resulting in the hallmark symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
Huntington's Disease: Huntington's disease is a genetic disorder that causes degeneration of neurons in the basal ganglia and other brain regions. Individuals with Huntington's disease experience involuntary movements (chorea), cognitive decline, and psychiatric symptoms. The abnormal accumulation of a mutated protein in the basal ganglia leads to dysfunction in the circuitry responsible for movement and cognition, contributing to the wide range of symptoms seen in Huntington's disease.
Tourette Syndrome:Tourette syndrome is a neurological disorder characterised by repetitive, involuntary movements and vocalisations known as tics. While the exact cause of Tourette syndrome is not fully understood, research suggests that abnormalities in the basal ganglia circuitry may play a role in the development of tics. Dysfunction in the pathways connecting the basal ganglia to the cortex can result in the disinhibition of motor programs, leading to the manifestation of tics in individuals with Tourette syndrome.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Obsessive-compulsive disorder is a mental health condition characterised by intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviours (compulsions). The basal ganglia are thought to be involved in the pathophysiology of OCD, as disruptions in the circuitry connecting the basal ganglia to the prefrontal cortex can contribute to the persistent thoughts and compulsive behaviours seen in individuals with OCD. Treatments targeting the basal ganglia pathways, such as cognitive-behavioural therapy and medications that affect neurotransmitter levels, are often used to manage OCD symptoms.
Advances in neuroscience continue to enhance our understanding of these disorders and pave the way for innovative treatments that target the underlying mechanisms of basal ganglia dysfunction.
Challenges in Treatment and Future Directions:
While significant progress has been made in the management of basal ganglia disorders, several challenges remain in optimising treatment outcomes and addressing the diverse needs of individuals affected by these conditions. Let us discuss some of the key challenges in current treatment approaches and determine the potential future directions for advancing care for basal ganglia-related disorders.
Individual Variability in Treatment Response:
One of the major challenges in treating basal ganglia disorders is the considerable variability in treatment response among individuals. Factors such as genetic variability, disease progression, and comorbidities can influence how patients respond to medications, therapies, or surgical interventions. Personalised medicine approaches, including genetic testing and precision medicine strategies, may help tailor treatments to individual characteristics and optimise therapeutic outcomes.Motor and Non-Motor Symptom Management:
Many basal ganglia disorders present with a constellation of motor and non-motor symptoms that can significantly impact quality of life. While current treatments primarily focus on managing motor symptoms like tremors or bradykinesia, addressing non-motor symptoms such as cognitive impairment, mood disturbances, and sleep disturbances remains a challenge. Future research is needed to develop holistic treatment approaches that target both motor and non-motor aspects of these disorders.Long-Term Treatment Efficacy and Side Effects:
For chronic conditions like Parkinson's disease, sustaining treatment efficacy and managing medication-related side effects over the long term pose significant challenges. Patients may experience fluctuations in symptom control, medication tolerance, and adverse effects that necessitate frequent adjustments in treatment regimens. Developing therapies with prolonged efficacy, reduced side effects, and novel delivery methods could enhance treatment outcomes and quality of life for individuals with basal ganglia disorders.Access to Specialized Care and Resources:
Access to specialised care, including neurologists, movement disorder specialists, and neuropsychologists with expertise in basal ganglia disorders, can be limited in certain geographic regions or healthcare settings. Additionally, resources for comprehensive multidisciplinary care, such as deep brain stimulation programs or cognitive-behavioural therapy services, may not be readily available to all individuals in need. Efforts to improve access to specialised care and promote interdisciplinary collaboration are essential for optimising treatment outcomes and supporting patients with basal ganglia-related conditions.Emerging Therapeutic Strategies:
The field of neurology is rapidly evolving, with ongoing research and clinical trials exploring novel therapeutic strategies for basal ganglia disorders. From gene therapy and stem cell transplantation to advanced neurostimulation techniques and targeted drug delivery systems, innovative approaches hold the potential to revolutionise treatment options for individuals with conditions like Huntington's disease, dystonia, or Tourette syndrome. Collaborative efforts between researchers, clinicians, and industry partners are necessary for advancing these promising therapeutic avenues.
In conclusion, while treating basal ganglia disorders presents challenges, ongoing research and interdisciplinary collaboration offer hope for improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions. By addressing the complexities of these disorders, prioritising personalised care, and embracing innovative treatment modalities, healthcare providers can continue to enhance the standard of care for basal ganglia-related disorders and support patients on their journey towards improved well-being and function.
References
(1) Basal Ganglia: What It Is, Function & Anatomy - Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/23962-basal-ganglia.
(2) The Basal Ganglia - Direct - Indirect - Nuclei- TeachMeAnatomy. https://teachmeanatomy.info/neuroanatomy/structures/basal-ganglia/.
(3) Frontiers | Basal ganglia for beginners: the basic concepts you need to .... https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/systems-neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnsys.2023.1242929/full.
(4) Role of Basal ganglia in motor control - Physiopedia. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Role_of_Basal_ganglia_in_motor_control.
(5) Basal ganglia: Gross anatomy and function | Kenhub. https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/basal-ganglia.
(6) en.wikipedia.org. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basal_ganglia.
(7) Albin, R. L., Young, A. B., & Penney, J. B. (1989). The functional anatomy of basal ganglia disorders. Trends in Neurosciences, 12(10), 366-375.
(8) Graybiel, A. M. (2005). The basal ganglia: learning new tricks and loving it. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 15(6), 638-644.


I am a complete beginner who resides in Africa's Western Hemisphere. My name is James, but you may reach out to me through the Facebook page [James Kossy] (https://www.facebook.com/christ.messenger.904) Physics, chemistry, and biology are the three topics that I find most enjoyable. My current studies are taking place at the university level, with the intention of becoming a recognized professional in physiotherapy. I am fascinated by all things technological, and I take pleasure in contributing to the fascinating technological advancements that are taking place throughout the world today. In my spare time, I'd like to learn more about programming and help others with any technical problems they may be having. 💞 ***🌹❤️ Thank you so much to everyone who has supported me thus far. ****💞 At the moment, I don't have the right words to say how much I appreciate all of your help. You never cease to astonish me with your generosity. For me, this has turned into a haven of enjoyment. Thanks to colleagues like you, this has all been possible. You've been a great support for me. Everything you have done for me and my family has been greatly appreciated, and I will always be grateful to you. 💕.
Posted Using InLeo Alpha
Hello.
There is reasonable evidence that this article is machine-generated. We would appreciate it if you could avoid publishing AI-generated content (full or partial texts, art, etc.).
Thank you.
Guide: AI-Generated Content = Not Original Content
If you believe this comment is in error, please contact us in #appeals in Discord.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.
Congratulations @jsalvage! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 91000 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP