Simplifying the Anatomy of the upper limb: Arterial Supply of the Arm
In our previous discussion, we explored the arterial supply to the shoulder region, particularly focusing on the Subclavian artery's role. Today, we shall progress to examine the extension of the Subclavian artery, known as the Brachial artery, which is responsible for supplying blood to the arm and forearm. For a comprehensive understanding, it is advisable to review the preceding article on this topic to reinforce your knowledge of the arterial supply to the upper limb.
The Brachial artery is not merely an ordinary artery; it serves as the principal conduit for blood to the arm, playing a critical role in delivering oxygen and nutrients to the arm's components, thereby sustaining its vitality and function. We invite you to join us on an informative exploration to better grasp the significance of this essential artery.Origin and Course
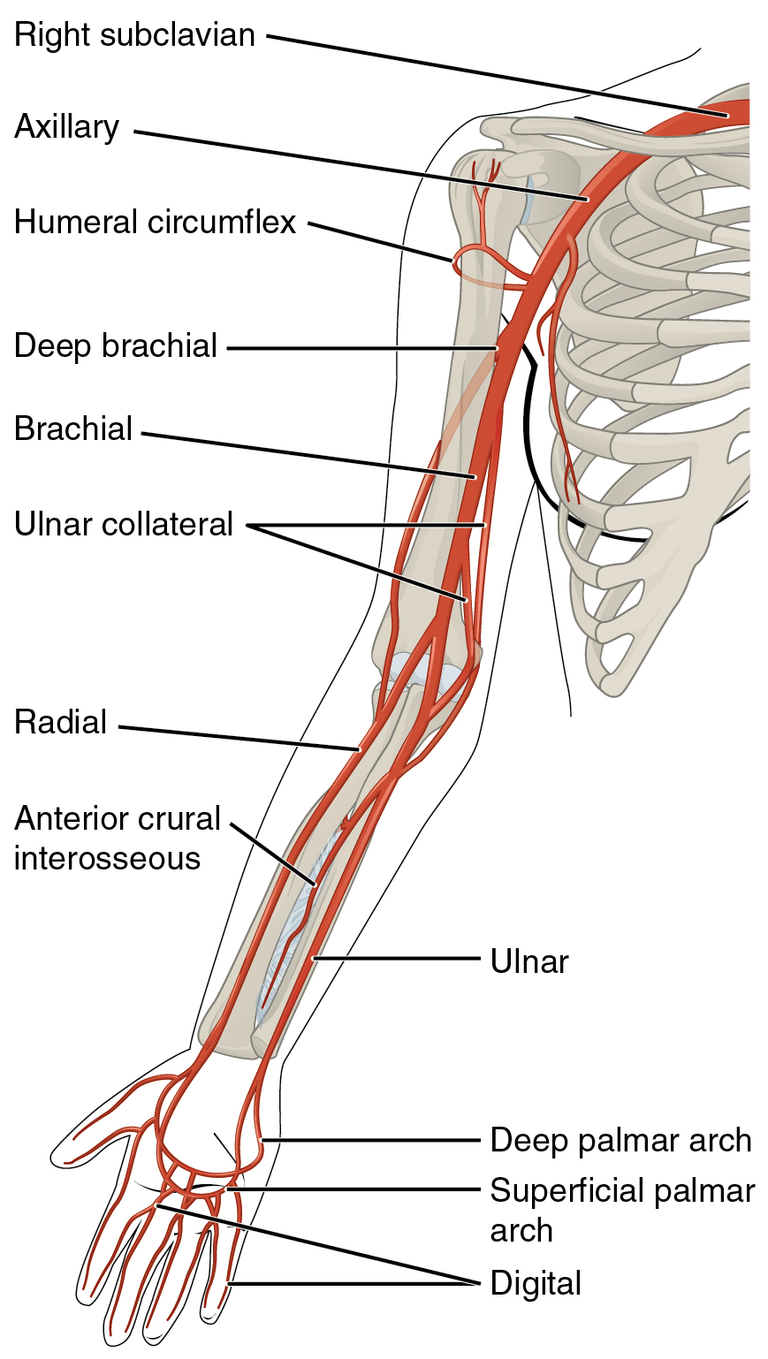
The origin of the brachial artery is central to the circulatory system in the upper limb. It starts as the continuation of the axillary artery at the lower margin of the teres major muscle. This transition point, which marks the beginning of the brachial artery, occurs around the level of the lower border of the teres major muscle, approximately at the armpit's lower edge.
From its origin, the brachial artery extends down the arm's length, traveling through the anterior compartment of the upper arm. It runs medially to the humerus bone and is accompanied along its course by the median nerve, among other structures. As the brachial artery progresses down the arm, it supplies blood to the arm's muscles through its branches, including the deep artery of the arm (profunda brachii artery) which typically branches off near the artery's beginning.
The brachial artery ends at the level of the elbow, around the neck of the radius, where it bifurcates into two major branches: the radial artery and the ulnar artery. These arteries continue the task of supplying blood to the forearm, wrist, and hand.
Branches
The brachial artery gives off several branches as it courses down the arm. These branches can be categorized based on their location along the artery's path:
Profunda Brachii Artery (Deep Artery of the Arm): This is typically the first major branch, arising near the upper part of the brachial artery. It travels posteriorly with the radial nerve, supplying the triceps brachii muscle and giving off branches that contribute to the arterial network around the elbow.
Nutrient Arteries to the Humerus: Although small, these are important for supplying blood to the bone.
Superior Ulnar Collateral Artery: Arising from the middle third of the brachial artery, it courses alongside the ulnar nerve and eventually participates in the formation of the arterial network around the elbow, specifically contributing to the blood supply of the medial aspect of the elbow.
Inferior Ulnar Collateral Artery: Typically branches lower than the superior ulnar collateral artery, near the artery's end. It also approaches the elbow and helps form the anastomotic network around the elbow, supplying the ulnar side.
Muscular Branches: Throughout its course, the brachial artery gives off numerous small muscular branches. These branches supply the arm muscles, including both the flexors and extensors.
It's worth noting that the exact branching pattern can vary among individuals. The profunda brachii artery and the collateral arteries play crucial roles in providing an alternative path for blood flow, especially around the elbow, ensuring the distal part of the limb remains well-supplied even if the main artery is compressed or partially occluded during movement.
Towards its end, at the elbow, the brachial artery bifurcates into the radial and ulnar arteries, which are not branches of the brachial artery in the proper sense but are its continuations into the forearm, serving to distribute blood further into the lower parts of the upper limb.
The Profunda Brachii
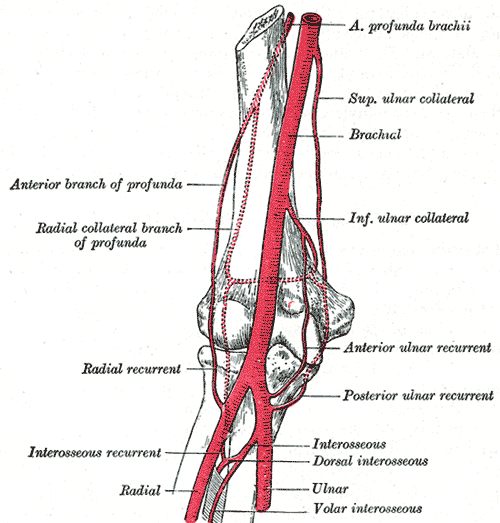
The Profunda Brachii Artery, also known as the deep artery of the arm, is a major vessel that plays a crucial role in the vascular supply to the structures of the upper arm. It typically branches from the brachial artery, which itself is a continuation of the axillary artery. This branching usually occurs near the lower border of the teres major muscle. The Profunda Brachii Artery is an essential artery within the arm, providing blood to various muscle groups and contributing to anastomoses around the elbow region.
Anatomy and Branching:
After its origin, the Profunda Brachii Artery follows a path along the radial nerve, travelling in the radial groove on the posterior surface of the humerus, accompanied closely by the nerve. It thus supplies the posterior compartment of the arm, nourishing the triceps brachii muscle, among others. The artery also gives rise to several branches, including the radial collateral artery and the middle collateral artery, and contributes to the vascular network surrounding the elbow.
Function:
The primary function of the Profunda Brachii Artery is to supply blood to the muscles of the posterior compartment of the arm, especially the triceps brachii. Additionally, its branches contribute to the elaborate network of vessels around the elbow, ensuring a rich blood supply to the joint and adjacent regions. This network is pivotal in maintaining vascular integrity and function during the extensive movement and load-bearing activities of the upper limb.
Clinical Significance
The Profunda Brachii Artery is of particular interest in clinical settings for several reasons:
- Injury: Given its location near the humerus, the artery may be at risk during fractures or surgeries in this area.
- Compartment Syndrome: This condition, involving increased pressure within a muscle compartment, can affect blood flow through the Profunda Brachii, potentially leading to muscle and nerve damage.
- Vascular Access: In specific procedures, understanding the anatomy of the Profunda Brachii Artery is crucial for accessing the arterial system of the upper limb.
In summary, the Profunda Brachii Artery is a vital arterial vessel in the upper arm, providing necessary blood supply to the arm's posterior compartment and contributing to the vascular network around the elbow. Its anatomical course alongside the radial nerve underscores the intricate relationship between the vascular and nervous systems in this region.
References
(1) Brachial artery: Anatomy and branches | Kenhub. https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/brachial-artery.
(2) Brachial artery - Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brachial_artery.
(3) Brachial artery | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org. https://radiopaedia.org/articles/brachial-artery.
(4) Brachial Artery | Complete Anatomy - Elsevier. https://www.elsevier.com/resources/anatomy/cardiovascular-system/arteries/brachial-artery/19890.
(5) en.wikipedia.org. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brachial_artery.
(6) Elbow Joint: Anatomy [+video] - Lecturio Medical. https://www.lecturio.com/concepts/elbow-joint/.
(7) The Elbow Joint - Structure - Movement - TeachMeAnatomy. https://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/joints/elbow-joint/.
(8) Elbow joint: Anatomy, ligaments, movements, blood supply | Kenhub. https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/elbow-joint.
(9) Elbow joint: Pain, joint type, anatomy, and more - Medical News Today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/elbow-joint.
(10) The Anatomy of the Elbow - Washington University Orthopedics. https://www.ortho.wustl.edu/content/Patient-Care/3151/Services/Shoulder-Elbow/Overview/Elbow-Arthroscopy-Information/The-Anatomy-of-the-Elbow.aspx.
(11) Arterial anastomosis of the elbow - Radiopaedia.org. https://radiopaedia.org/articles/arterial-anastomosis-of-the-elbow.


I am a complete beginner who resides in Africa's Western Hemisphere. My name is James, but you may reach out to me through the Facebook page [James Kossy] (https://www.facebook.com/christ.messenger.904) Physics, chemistry, and biology are the three topics that I find most enjoyable. My current studies are taking place at the university level, with the intention of becoming a recognized professional in physiotherapy. I am fascinated by all things technological, and I take pleasure in contributing to the fascinating technological advancements that are taking place throughout the world today. In my spare time, I'd like to learn more about programming and help others with any technical problems they may be having. 💞 ***🌹❤️ Thank you so much to everyone who has supported me thus far. ****💞 At the moment, I don't have the right words to say how much I appreciate all of your help. You never cease to astonish me with your generosity. For me, this has turned into a haven of enjoyment. Thanks to colleagues like you, this has all been possible. You've been a great support for me. Everything you have done for me and my family has been greatly appreciated, and I will always be grateful to you. 💕.
Posted Using InLeo Alpha
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.
I love studying about the artery
Really? It means you are definitely a medical student?
no I am still in high school