Simplifying the Anatomy of the upper limb: Arterial Blood Supply to the Forearm and Hand
Introduction

The arterial blood supply of the forearm and hand plays a role in maintaining the functionality and health of these intricate anatomical regions. The study of the complex network of arteries that nourish the forearm and hand will help you as a medical professionals, students, and individuals seeking to comprehend the human anatomy.
Within the forearm and hand, arteries ensures the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the tissues, as well as the removal of metabolic waste products. This system of blood vessels sustains the delicate balance necessary for the proper functioning of these essential regions.
In this article, we will explore the anatomy of the arterial blood supply to the forearm and hand, highlighting the key arteries involved, their origins, courses, and branches. By delving into the detailed structure of these arteries, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of how blood is distributed throughout the forearm and hand, supporting various physiological processes.
Moreover, we will discuss the clinical relevance of the arterial blood supply of the forearm and hand, addressing common pathologies that can affect these arteries and the resulting symptoms that may manifest when blood flow is compromised. Recognizing the signs of impaired arterial blood supply for timely diagnosis and intervention to prevent potential complications.
By shedding light on the surgical interventions available to address arterial blood supply disorders in the forearm and hand, we seek to underscore the advancements in modern medical practices aimed at restoring blood flow and improving patient outcomes. From angioplasty to bypass surgery, these interventions play a role in managing arterial pathologies and ensuring optimal blood supply to the affected regions.
In exploring the arterial blood supply of the forearm and hand, I invite readers to delve into anatomy, pathology, and surgical interventions that shape our understanding of this essential vascular network. Through this exploration, we hope to underscore the significance of a comprehensive understanding of arterial blood supply in providing quality healthcare and promoting well-being in individuals affected by related conditions.
Anatomy of the Arterial Blood Supply
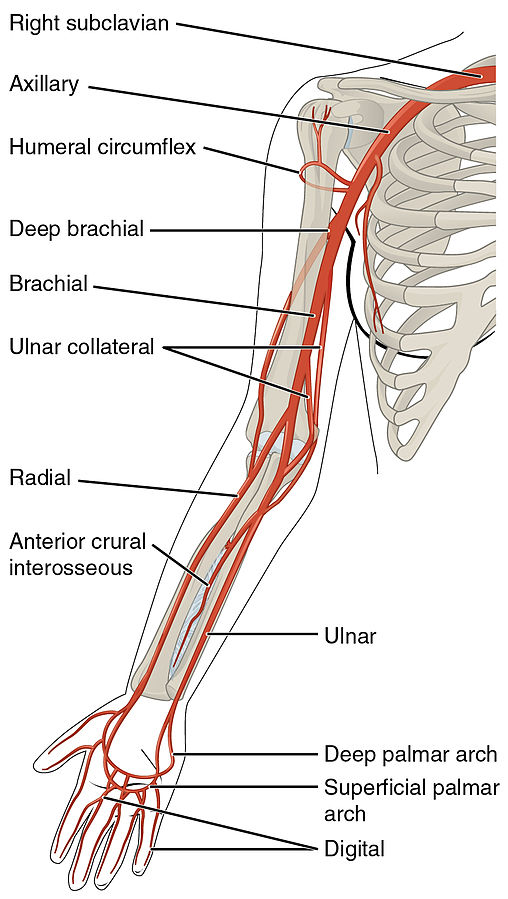
The arterial blood supply of the forearm and hand encompasses a sophisticated network of blood vessels that ensure the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the tissues, supporting their essential functions. Understanding the anatomy of these arteries is fundamental for healthcare professionals and students to comprehend the intricate structure and functionality of this vital vascular system.
Brachial Artery
The brachial artery, a major artery of the upper limb, originates from the axillary artery at the lower border of the teres major muscle. Descending along the medial aspect of the arm, the brachial artery gives rise to various branches that supply blood to different structures within the forearm and hand. Branches such as the profunda brachii artery and the superior ulnar collateral artery play essential roles in ensuring adequate blood supply to the surrounding tissues.
Radial Artery
Originating from the brachial artery just below the elbow, the radial artery descends along the lateral aspect of the forearm, providing arterial supply to the structures in this region. Branches of the radial artery, including the radial recurrent artery and the superficial palmar branch, contribute to the blood vessels that nourish the forearm and hand, supporting their physiological functions.
Ulnar Artery
The ulnar artery, another major artery of the forearm, runs alongside the ulnar nerve and provides arterial supply to the medial aspect of the forearm and hand. Arising from the brachial artery just below the elbow, the ulnar artery gives off branches such as the common interosseous artery and the anterior ulnar recurrent artery, which contribute to the vascular supply of the forearm and hand.
Superficial Palmar Arch
The superficial palmar arch is a vital arterial structure located in the palm of the hand, formed by the anastomosis of the ulnar and radial arteries. This arch gives rise to digital arteries that supply blood to the fingers, contributing to the rich vascular network that supports the intricate movements and sensory functions of the hand.
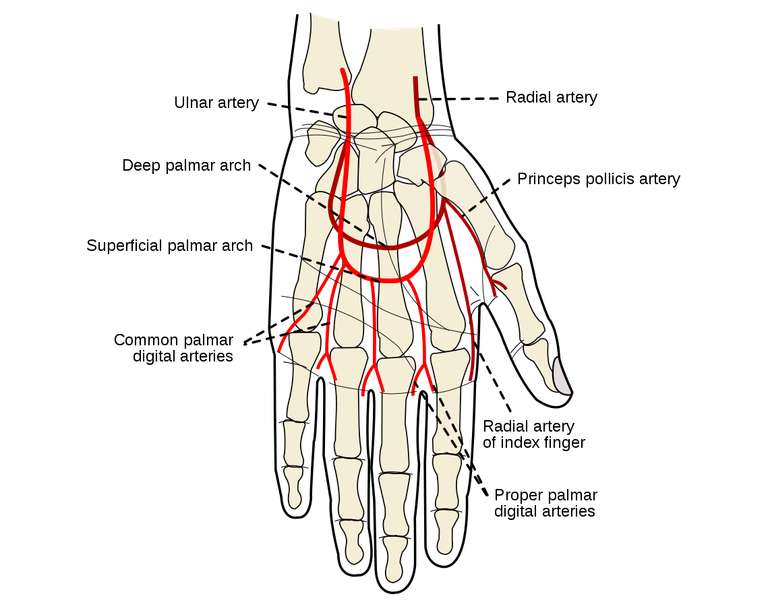
Deep Palmar Arch
The deep palmar arch, situated deep within the palm of the hand, is formed primarily by the continuation of the radial artery. This arch provides arterial supply to the deeper structures of the hand, forming an essential part of the vascular network that ensures optimal blood flow to the tissues involved in various hand movements and functions.
Clinical Relevance and Pathologies
The clinical relevance of the arterial blood supply of the forearm and hand becomes evident when considering common pathologies that can affect these vital arteries, leading to symptoms that may impact an individual's quality of life. Understanding these pathologies is crucial for healthcare professionals to recognize warning signs, make accurate diagnoses, and implement appropriate treatment strategies to mitigate potential complications.
Arterial Occlusion
Arterial occlusion, caused by atherosclerosis or thrombosis, can disrupt blood flow in the arteries supplying the forearm and hand, leading to ischemia and tissue damage. Patients may present with symptoms such as pain, pallor, pulselessness, and paresthesia, indicating compromised blood supply to the affected regions. Prompt diagnosis and intervention, such as thrombolytic therapy or surgical revascularization, are essential to restore blood flow and prevent tissue necrosis.
Arterial Embolism
Arterial embolism, characterized by the lodging of an embolus in a blood vessel, can obstruct arterial flow in the forearm and hand, causing acute ischemia. Individuals may experience sudden onset of severe pain, coldness, and mottling of the affected limb, necessitating immediate medical attention. Treatment options, including catheter-directed thrombolysis or surgical embolectomy, aim to remove the embolus and restore adequate blood supply to prevent irreversible tissue damage.
Arterial Aneurysm
Arterial aneurysms, defined as localized dilations of blood vessels, can occur in the arteries supplying the forearm and hand, posing risks of rupture and hemorrhage. Patients with arterial aneurysms may present with a pulsatile mass, pain, and neurological deficits, necessitating careful monitoring and potential surgical intervention to prevent complications. Surgical techniques, such as aneurysm resection or endovascular repair, aim to address the aneurysm while preserving vascular function.
Arterial Trauma
Arterial trauma, resulting from penetrating injuries or fractures, can disrupt the arterial blood supply to the forearm and hand, leading to significant hemorrhage and potential ischemic complications. Immediate assessment, control of bleeding, and vascular repair are critical in managing arterial trauma to preserve limb function and prevent long-term sequelae. Surgical techniques, including vascular repair or reconstruction, may be employed to restore arterial flow and promote tissue viability.
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Thoracic outlet syndrome, a condition characterized by compression of the neurovascular structures passing through the thoracic outlet, can affect arterial blood flow to the forearm and hand. Patients may experience symptoms such as arm pain, paresthesia, and weakness, indicating compromised vascular supply due to compression. Treatment approaches, including physical therapy, postural corrections, and in some cases, surgical decompression, aim to alleviate symptoms and improve arterial flow to the affected regions.
By recognizing the clinical relevance of arterial pathologies that can affect the forearm and hand, healthcare professionals can intervene effectively to restore blood flow, prevent tissue damage, and improve patient outcomes. Through timely diagnosis, appropriate treatment strategies, and collaborative care, individuals affected by these arterial conditions can receive the necessary support to regain optimal vascular function and preserve the functionality of their forearm and hand.
In conclusion, the arterial blood supply of the forearm and hand represents a complex and essential vascular network that sustains the functionality and well-being of these anatomical regions.
From exploring the origins and courses of the major arteries supplying the forearm and hand to delving into the clinical manifestations of arterial pathologies and the advancements in surgical interventions, this comprehensive overview sheds light on the interplay between anatomy, pathology, and surgical care in optimizing vascular function and patient outcomes.
References
(1) Arterial Supply to the Upper Limb - Subclavian - TeachMeAnatomy. https://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/vessels/arteries/.
(2) Body Anatomy: Upper Extremity Vessels | The Hand Society. https://www.assh.org/handcare/safety/vessels.
(3) Ulnar artery: Branches, definition, clinical notes | Kenhub. https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/the-ulnar-artery.
(4) The Cardiovascular System of the Upper Limbs - Innerbody. https://www.innerbody.com/anatomy/cardiovascular/arm-hand.
(5) Upper limb: Arteries, veins and nerves | Kenhub. https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/neurovasculature-of-the-upper-limb.
(6) Peripheral artery disease (PAD) - Symptoms and causes. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-artery-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20350557.
(7) Arm Artery Disease | Society for Vascular Surgery. https://vascular.org/patients-and-referring-physicians/conditions/arm-artery-disease.
(8) Avoiding and Managing Forearm Hematomas - Cardiac Interventions Today. https://citoday.com/articles/2011-mar-apr/avoiding-and-managing-forearm-hematomas.
(9) Overview of upper extremity ischemia - UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-upper-extremity-ischemia


I am a complete beginner who resides in Africa's Western Hemisphere. My name is James, but you may reach out to me through the Facebook page [James Kossy] (https://www.facebook.com/christ.messenger.904) Physics, chemistry, and biology are the three topics that I find most enjoyable. My current studies are taking place at the university level, with the intention of becoming a recognized professional in physiotherapy. I am fascinated by all things technological, and I take pleasure in contributing to the fascinating technological advancements that are taking place throughout the world today. In my spare time, I'd like to learn more about programming and help others with any technical problems they may be having. 💞 ***🌹❤️ Thank you so much to everyone who has supported me thus far. ****💞 At the moment, I don't have the right words to say how much I appreciate all of your help. You never cease to astonish me with your generosity. For me, this has turned into a haven of enjoyment. Thanks to colleagues like you, this has all been possible. You've been a great support for me. Everything you have done for me and my family has been greatly appreciated, and I will always be grateful to you. 💕.
Posted Using InLeo Alpha
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.