Revealing the Rhythmic Symphony: A Guide to Heart Rate and Circulation Regulation
Created with Bing
Have you ever given thought to how your heart stays motivated to continuously pump blood throughout your body? This essential process is governed by a remarkable interplay of complex processes. Cardiac output is the fundamental factor in determining how well the heart and blood vessels work. In this piece, we set out on a quest to understand cardiac output and the interesting mechanisms that govern heart rate.
Simply explained, cardiac output measures how much blood the heart pumps in a given amount of time. It's the vital force that carries oxygen and nutrients to all of your cells and keeps you alive. When the body's needs change, the heart responds by increasing or decreasing its output, whether from the calm of rest or the thrill of exercise.
Stroke volume and heart rate are dissected for their contributions to cardiac output. Both stroke volume and heart rate are measures of how often the heart contracts and how much blood is expelled with each beat. Together, these two elements provide the basis for learning about the intriguing world of cardiac output and its control.
By the time you reach your destination, you'll have a newfound respect for the pulsating orchestra that keeps you alive. Let's fasten our seatbelts and set off on an exciting journey into the fascinating world of cardiac output and the control of heart rate.
What are the fundamentals?
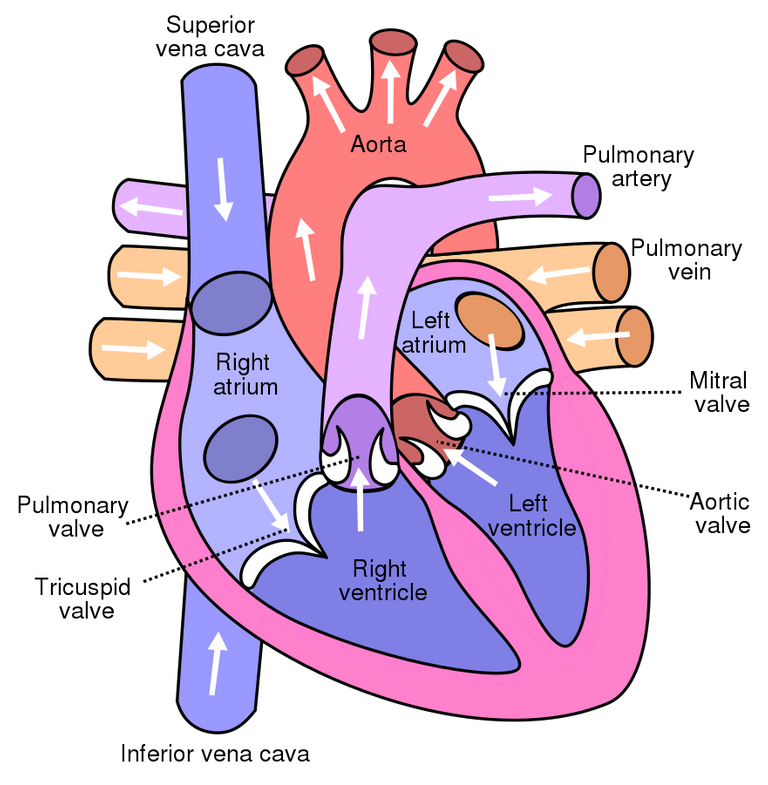
Understanding cardiac output is crucial to comprehending the role the heart plays in maintaining life and vitality. Heart rate multiplied by the distance blood travels in a minute is called cardiac output. It's analogous to a river's flow rate, except that the fluid being measured is blood, which sustains life.
Just exactly how does this enchanted procedure operate, then? Our hearts, the magnificent, hardworking pumps that they are, are the starting point. The heart squeezes blood out of the vessels with each beat, sending it on its way to all parts of the body.
Cardiac output is calculated by analyzing two key indicators: stroke volume and heart rate. When the heart contracts, it ejects a certain volume of blood, known as the stroke volume. It's the same as the amount of water a squirt gun would shoot out if you squeezed it. The number of times your heart beats in a minute is your heart rate.
Picture yourself using a garden hose to fill a swimming pool. You can fill that pool in no time at all if you raise both the volume of water flowing out of the hose with each squeeze (stroke volume) and the number of times you squeeze the hose per minute (heart rate). The same holds true for cardiac output; the higher it is, the more blood the heart pumps out with each beat and the faster it beats, on average, every minute.
Let's examine stroke volume in further detail now. Quite a few things may have an effect on it. Preload, or the quantity of blood that is pumped back to the heart, is one such factor. More blood entering the heart causes the muscle to expand slightly, which, like a rubber band being pushed back, aids in producing a more powerful contraction and hence a higher stroke volume.
Coolest of all, our bodies are intelligent enough to regulate our cardiac output in response to changing demands. In order to provide more blood, oxygen, and nutrients to our working muscles, our hearts speed up and our blood pumps out more blood every beat. To keep up with the demands of our busy lifestyle, it's like giving our circulatory system a turbo boost.
That wraps up the fundamentals of cardiac output. How much blood our hearts are able to pump per minute is determined by a number of factors, including stroke volume, heart rate, preload, and afterload. To keep our bodies supplied with nutrients and oxygen, our hearts function like the most advanced blood-pumping machines.
Let's talk about what makes up cardiac output.
As we've already established, cardiac output is the volume of blood pumped by the heart in one minute. But what precisely are the major factors that make up this crucial metric? Together, let's dissect this problem.
Stroke volume will be the first factor examined. The most important factor in cardiac output is stroke volume. It is a measure of how much blood is pumped out of the heart with each beat. It's analogous to how much water comes out of a tap when you open it. More blood is pumped out of the heart and into the body's blood vessels (cardiac output) when the stroke volume is larger.
But stroke volume is insufficient on its own. It is dynamically related to another major factor—heart rate. The frequency of our heartbeats is measured in beats per minute, or heart rate. It's analogous to how a song's tempo determines the tempo of the whole performance. When our heart rates rise, the number of times our hearts beat in a minute rises. As a result, the heart is able to pump more blood.
Let's discuss the relationship between stroke volume and heart rate right now. It's a delicate dance in which each partner makes little adjustments and compensations to keep the others in check. When situations or causes reduce stroke volume, our hearts respond by raising the heart rate to keep cardiac output constant. The heart may also increase stroke volume in response to a reduction in heart rate to maintain constant blood flow.
However, that's not all! There is more to heart function than just cardiac output. There are other external variables that might affect stroke volume. Preload, the amount of blood in the heart's chambers right before contraction, is an important consideration. It's analogous to filling a bucket to the point where you can safely dump it. Higher preloads provide the heart with more blood to pump, which may improve stroke volume and, in turn, cardiac output.
The afterload should also be taken into account. Afterload refers to the pressure the heart must overcome as it pumps blood into the body's arteries. Imagine the resistance that water encounters while trying to go through a small conduit. When arterial resistance is high, as in certain medical conditions, the heart has to work harder to pump blood out, which may reduce stroke volume and cardiac output. In contrast, if afterload is low, like when there is little resistance to blood flow, the heart is able to pump more blood with each beat, increasing stroke volume and cardiac output.
Our hearts are like fantastic conductors, orchestrating a symphony of parts to deliver blood and oxygen across the body. Volumes, rates, and resistances all work together in a complex ballet that keeps us alive.
Determine the potential influences on cardiac output by answering the following questions
Created with Bing
Imagine, then, that your heart is a pump, constantly distributing blood to all parts of your body. However, did you know that various variables affect the exact amount of blood your heart pumps each minute? Let's delve in and investigate these variables in depth.
The initial option is preload. When your heart contracts, the chambers fill with blood, a process known as preload. It's analogous to having gas in the tank but not starting the car. The heart expands a little bit more when there is more blood returning to it, maybe because of an enhanced venous return from the body. And what do you know? Increased cardiac output is the result of a larger stroke volume, which is achieved by stretching the heart.
However, that's not all! Afterload is another component that influences cardiac output. When your heart pumps blood into the arteries, it encounters a force known as afterload. It's like the resistance your heart must overcome every time it beats. It's possible that your stroke volume and cardiac output might decrease if the afterload was significant, as it would be in diseases like hypertension. However, if afterload is minimal, the heart has an easier time pumping blood out, leading to a greater stroke volume and a higher cardiac output.
The time has come to discuss contractility. The contractile strength of your heart is the measure of this power. The strength of your heart's muscles More powerful contractions of the heart muscle result in a greater stroke volume and a higher cardiac output. Hormones like adrenaline may promote cardiac function by increasing contractility during times of stress.
Also, remember to keep your heart rate in mind. The cardiac output is also affected by the heart rate. Increased cardiac output occurs when the heart pumps a greater volume of blood per unit of time. Exercising, experiencing stress, or feeling thrilled may all bring this on. When the heart rate reduces, as it does during rest and sleep, cardiac output falls as a direct result of the lower heart rate.
The dynamic adaptability of these elements to different contexts is intriguing to consider. In order to meet the increased demands for oxygen and nutrients that occur during exercise, the heart increases its cardiac output. Your body's ability to perform at its peak requires a wonderful balancing act.
With this newfound knowledge, we can appreciate the wonderful orchestra inside us—our hearts leading the symphony of life, ensuring our well-being, and keeping us in sync with the world around us. Wow, we've come a long way, but in a nutshell, Our hearts are like tireless actors.
References
American Heart Association: Heart Rate. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/consumer-healthcare/what-is-cardiac-arrest/heart-health-101#mainContent
Geaghan, J. P., & Keough, V. A. (2017). Stroke Volume. In StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482160/
Guyton, A. C. (1992). Textbook of medical physiology. W.B. Saunders Company.
Wiktorowicz, M. E., Sargent, A. K., Schumacker, P. T., & Bridges, C. R. (2017). Autonomic Control of Cardiac Output. Comprehensive Physiology, 7(2), 659-700. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c160038
Katz, A. M. (2011). Physiology of the Heart. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Opie, L. H., Braunwald, E. (2015). Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. Elsevier Health Sciences.
How does the Frank-Starling mechanism work? (2021). Retrieved from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/how-does-the-frank-starling-mechanism-work
What is Heart Failure? (2020, November 20). Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/heart-failure
Cardiac output during exercise: role of stroke volume and heart rate. (2019, September 25). Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6754465/
Harrell, K., & Kain, Z. (2017). Measurement of cardiac output. Anesthesiology Research and Practice, 2017, 1-10. doi: 10.1155/2017/6913912


Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.
Very good explanation and especially the example you give. Our heart is a complete orchestra.
Thank you for sharing it.