Introduction To Anatomy - Making anatomy fun and easy for students
Hey everyone, so I'm starting with a good news!! And what is this news about? We just wrapped up our MBBS exam and I would love to be writing on one of my favourite subjects – Anatomy. I know a lot of students find this course to be a bit of a headache, especially for those who aren’t keen on big, picture-filled textbooks. I’ve heard my friends on campus grumble about how hefty the textbooks can be, and it’s totally understandable why some might struggle to enjoy the course.
But you know what? This tough nut can actually be cracked quite easily. So, I’m excited to share some tips with my friends and colleagues on how to ace this course through this platform. I’ll be diving into different anatomy topics starting today, and first up on the list is the introduction to anatomy where we’ll explore various ways of classifying it. Let’s make anatomy a little less intimidating and a lot more interesting!
Anatomy gives birth to a rich and engrossing history that dates back to ancient civilizations. The early study of anatomy was closely tied to religious hypotheses and superstitions, but it laid the foundation for modern improvements in medicine and science. Through the contributions of key historical figures like Vesalius, the study of anatomy has grown up to become a vital part of our understanding of the human body.
History has it that ancient Egyptians and ancient Greeks were among the first civilizations to inquire into the study of anatomy. The Egyptians embalmed their deceased and studied the internal organs, while the Greeks made noteworthy contributions to the field through the dissection of animals. However, it was not until the Renaissance era that the study of anatomy truly flourished.
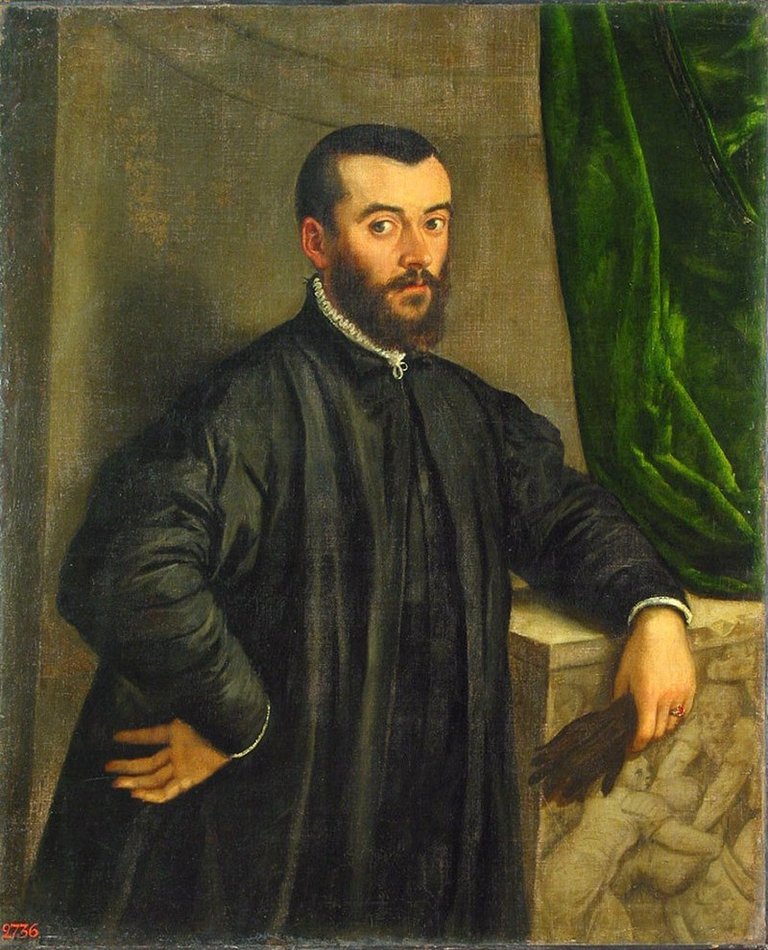

Andreas Vesalius, a Belgian anatomist, is often referred to as the father of modern anatomy. His groundbreaking work, "De Humani Corporis Fabrica," published in 1543, challenged many of the long-held beliefs about anatomy.
Vesalius emphasised the significance of dissecting human bodies to attain a true knowledge of anatomy, rather than depending only on ancient texts and animal dissections. His detailed observations and explicit descriptions revolutionised the study of human anatomy and laid down the groundwork for modern anatomical research.
Following Vesalius, other key figures made significant contributions to the study of anatomy. William Harvey's work on the circulatory system in the 17th century, and Marcello Malpighi's observations of microscopic anatomy in the 17th century further refined our knowledge of the human body. These frontiers paved the way for the development of modern medical practices and advancements in healthcare.
Now, let us know what anatomy is all about. Anatomy is portrayed as the scientific study of the structure of living organisms, including their internal systems and organs. It contains a wide range of branches, each with its own focus on specific areas of the body. Two major branches of anatomy are gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy.
Gross anatomy, also known as macroscopic anatomy, is the study of the visible structures of the body, such as bones, muscles, and organs. It involves the examination of organs and tissues without the aid of a microscope, and often involves dissection and observation of human cadavers and other large specimens. Gross anatomy provides a thorough awareness of the body's structure and role at a macroscopic level, serving as the basis for other branches of medicine and biology.
On the other hand, microscopic anatomy, also known as histology, concentrates on the analysis of cells and tissues at a microscopic level. It pertains to the use of a microscope to explore tiny structures such as cells, tissues, and organs at the cellular and molecular level.

Microscopic anatomy allows for a deeper familiarity of the functions and interactions of the body's smallest components, providing insights into the mechanisms of disease and the development of new medical treatments.
Anatomy encompasses the study of structures from cells to organs by providing a comprehensive insight of the body's organisation and function at different hierarchical levels. It starts with the study of cells, which are the basic building blocks of all living organisms. Cells come together to form tissues, which in turn make up organs. Knowledge of the structure and function of cells, tissues, and organs is basic for comprehension on how the body works as a whole. For example, the study of muscle tissue at a microscopic level provides insights into how muscles contract and generate movement, while the study of the heart at a macroscopic level helps in interpreting its structure and function in pumping blood throughout the body.
Having an understanding of basic anatomical terminology is important for anyone studying the human body.
Before we move on, let's know what the terminology stands for.
Terminology refers to the vocabulary or specific language used within a particular field or subject. In the context of anatomy, anatomical terminology contains the specialised words and phrases that are used to describe the structures, functions, and relationships of the human body.
Whether you are a student who wishes to pursue a career in healthcare or simply have a curious mind, having a grasp of these fundamental terms is necessary. In this section, we will introduce and explore these basic terms. I'll present some relatable examples and comparisons to ensure clarity to enable you to understand better.
First, let's start with the term "anatomy" itself. We have already defined what anatomy is all about. It examines the physical structure of the body, including the bones, muscles, organs, and systems. For example, when we say "the anatomy of the heart," we are referring to the physical makeup and arrangement of the heart's chambers, valves, and blood vessels.
Next, we have "physiology," which is the study of how the body works and functions. It focuses on the processes and functions of living organisms, such as digestion, circulation, respiration, and reproduction. To illustrate this, think about how digestion breaks down food into nutrients that the body can use for energy. This is a physiological process that involves the coordination of various organs and systems.
Moving on, we come to the concept of "anatomical position," which is the standard reference posture for describing the human body. In the anatomical position, the body is standing upright, facing forward, with arms at the sides and palms facing forward.
Image created using Copilot
This position provides a consistent point of reference for describing the location and orientation of body parts. For instance, when a doctor examines a patient, they often use the anatomical position to communicate the location of specific symptoms or injuries.
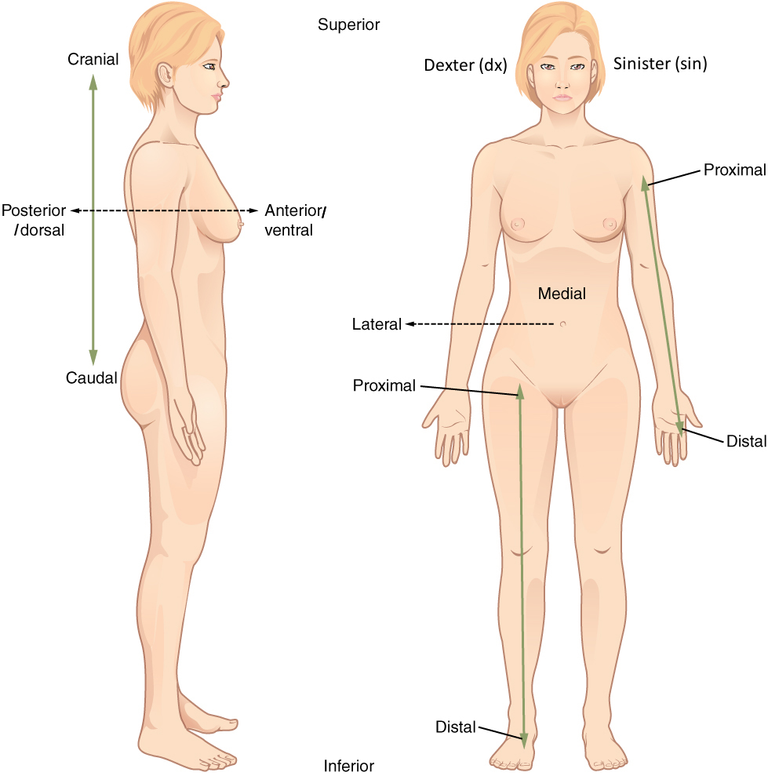
Furthermore, we have terms such as "proximal" and "distal" to describe the location of body parts in relation to the point of attachment. "Proximal" means closer to the point of attachment, while "distal" means farther away. A relatable example of this would be the relationship between the shoulder and the wrist. The shoulder is proximal to the wrist because it is closer to the point of attachment (the body), while the wrist is distal to the shoulder as it is farther away.
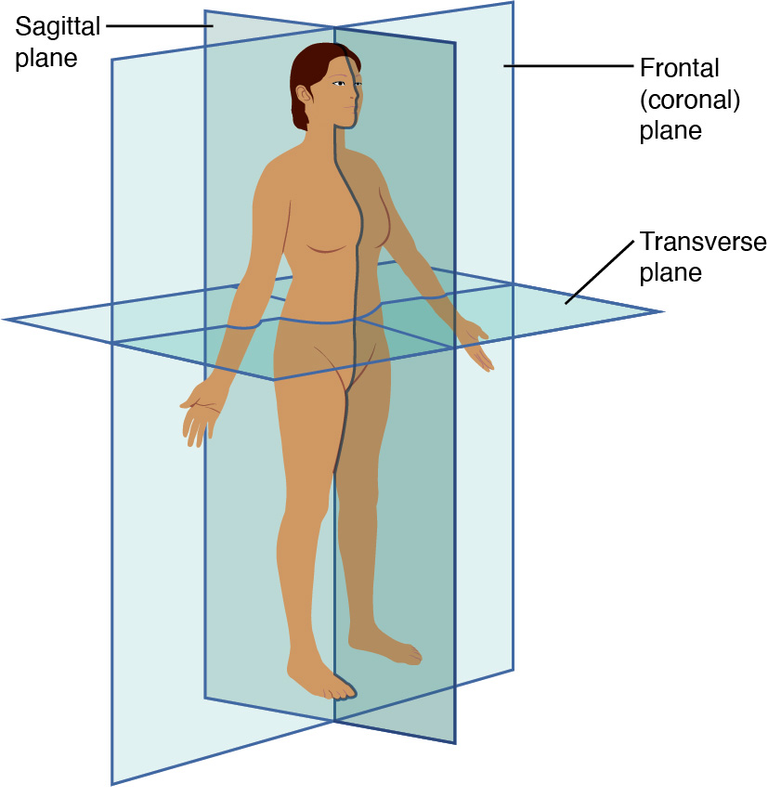
Finally, we cannot overlook the importance of body planes and sections, which are used to visualise and dissect the body for study and diagnosis. The three main planes are the sagittal plane (divides the body into left and right halves), the frontal or coronal plane (divides the body into front and back), and the transverse or horizontal plane (divides the body into top and bottom). Understanding these planes and sections facilitates communication between healthcare professionals and provides a framework for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
So mastering basic anatomical terminology is important for anyone interested in the study of the human body. If we familiarise ourselves with these fundamental terms and concepts, we can then gain a deeper understanding of the structure, function, and relationships within the body.
So that's all for today, on the next topic, we'll be looking at the various ways of classifying anatomy. Starting with the organs to the bigger systems of the body. Acknowledging all these will bend us to understand the role of many parts of our body. Trust me, you don't want to miss the next article!!
Let's make anatomy easy and interesting for students around the world 😀
References
- https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-6-anatomical-terminology#fig-ch01_06_02
- https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/education/the-human-anatomy
- https://www.britannica.com/science/anatomy
- Source.
- https://byjus.com/biology/anatomy-and-physiology/
- https://study.com/learn/lesson/anatomy-types-examples.html
- https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/education/the-human-anatomy
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anatomy


I am a complete beginner who resides in Africa's Western Hemisphere. My name is James, but you may reach out to me through the Facebook page [James Kossy] (https://www.facebook.com/christ.messenger.904) Physics, chemistry, and biology are the three topics that I find most enjoyable. My current studies are taking place at the university level, with the intention of becoming a recognized professional in physiotherapy. I am fascinated by all things technological, and I take pleasure in contributing to the fascinating technological advancements that are taking place throughout the world today. In my spare time, I'd like to learn more about programming and help others with any technical problems they may be having. 💞 ***🌹❤️ Thank you so much to everyone who has supported me thus far. ****💞 At the moment, I don't have the right words to say how much I appreciate all of your help. You never cease to astonish me with your generosity. For me, this has turned into a haven of enjoyment. Thanks to colleagues like you, this has all been possible. You've been a great support for me. Everything you have done for me and my family has been greatly appreciated, and I will always be grateful to you. 💕.
Posted Using InLeo Alpha
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.
Dear @jsalvage !
James!
You are strong enough to take an anatomy class!😃
I vomited after watching the human anatomy lecture.
Hehe, why did you watch it
James!
I once saw a human anatomy video on the Internet!
Hehe. Okay I can blame you for your feelings 😂... You can only be a medical student for you to pick interest in this stuff
James!
You are strong man!