Anestesia General Inhalatoria / General Inhalation Anaesthesia
Anestesia General Inhalatoria🏥
General Inhalation Anaesthesia🏥
Hey amigos lectores, espero estés bien! En esta oportunidad continuaremos con anestesia, como lo dije en el otro post antigua maquina de anestesia. en este capitulo hablaremos los efectos de la anestesia, el proceso anestésico y los tipos de anestesia.
Hey fellow readers, I hope you are well! This time we will continue with anaesthesia, as I said in the other post old anaesthesia machine. In this chapter we will talk about the effects of anaesthesia, the anaesthetic process and the types of anaesthesia.

La anestesia general es el resultado de la inhalación de un fármaco (gas o vapor), cuyo objetivo es producir una disminución del nivel de conciencia. Entre estos fármacos están el óxido nitroso (gas), el halotano, el isoflurano o el sevoflurano (vapores), que actúan a nivel cerebral
General anaesthesia results from the inhalation of a drug (gas or vapour), the purpose of which is to produce a decrease in the level of consciousness. These drugs include nitrous oxide (gas), halothane, isoflurane or sevoflurane (vapours), which act on the brain.
Dicho de otra manera es un coma inducido médicamente con pérdida de reflejos protectores, como resultado de la administración de uno o más agentes anestésicos generales. Se lleva a cabo para permitir procedimientos médicos que de otro modo serían intolerablemente dolorosos para el paciente; o donde la naturaleza del procedimiento en sí mismo impide que el paciente esté despierto.
Put another way it is a medically induced coma with loss of protective reflexes, as a result of the administration of one or more general anaesthetic agents. It is performed to allow medical procedures that would otherwise be intolerably painful for the patient; or where the nature of the procedure itself prevents the patient from being awake.
La Anestesia general se enmarca en tres efectos que esto ocasiona en el cuerpo:
General anaesthesia is framed by three effects on the body:
- 1.Analgesia: Desaparición, natural o provocada, de cualquier sensación de dolor.
- 1.Analgesia: The disappearance, natural or provoked, of any sensation of pain.
- 2.Hipnosis o inconsciencia: perdida del conocimiento y por ende la capacidad de percibir de lo que lo rodea.
- 2.Hypnosis or unconsciousness: loss of consciousness and therefore the ability to perceive one's surroundings.
- 3.Relajación Muscular: momento en que finaliza la contracción muscular.
- 3.Muscle relaxation: the moment when muscle contraction ends.

Fases de la Anestesia
Phases of Anaesthesia
La anestesia tiene una serie de fases bien definidas y marcadas en el curso de su ejecución, que son las siguientes:
Anaesthesia has a series of well-defined and marked phases in the course of its execution, which are as follows:
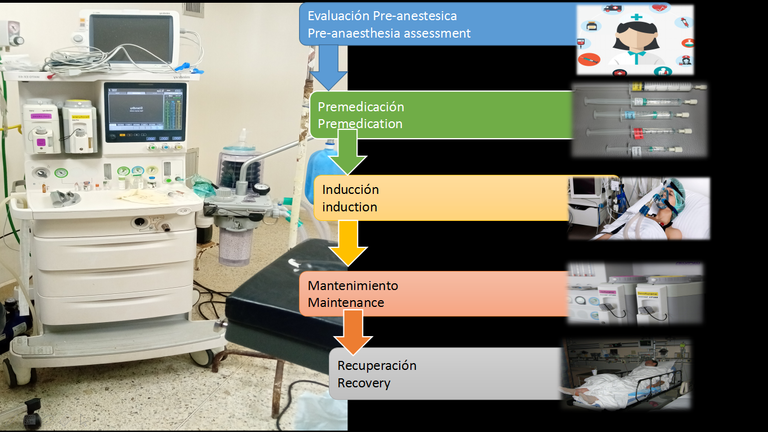
- A. Fase de evaluación pre-anestésica : Antes de un procedimiento planificado, el anestesiólogo revisa los registros médicos y/o entrevista al paciente para determinar la mejor combinación de medicamentos y dosis y el grado en que se requerirá un monitoreo para garantizar un procedimiento seguro y efectivo. Los factores clave en esta evaluación son la edad del paciente, el índice de masa corporal, el historial médico y quirúrgico, los medicamentos actuales y el tiempo de ayuno.
- A. Pre-anaesthetic assessment phase: Prior to a planned procedure, the anaesthesiologist reviews medical records and/or interviews the patient to determine the best combination of medications and doses and the extent to which monitoring will be required to ensure a safe and effective procedure. Key factors in this assessment are the patient's age, body mass index, medical and surgical history, current medications and fasting time.
- B. Premedicación: Consiste en la aplicación de fármacos que relajan al paciente para permitir la colocación adecuada de las vías intravenosas, monitores, mascarillas, etc...
- B. Premedication: Consists of the application of drugs that relax the patient in order to allow the proper placement of intravenous lines, monitors, masks, etc...
- C. Inducción: en esta fase el paciente pasa de un estado consciente o ligeramente sedado, a un estado de hipnosis. La inducción se realiza por vía intravenosa. En este momento se deben utilizar sedantes, bloqueantes neuromusculares y analgésicos.
- C. Induction: In this phase, the patient goes from a conscious or lightly sedated state to a state of hypnosis. Induction is performed intravenously. Sedatives, neuromuscular blockers and analgesics should be used at this time.
- D. Mantenimiento: en esta fase se mantiene al paciente en un nivel constante de la anestesia durante la totalidad del acto quirúrgico. El mantenimiento se hace con sedantes, relajantes musculares y analgésicos.
- D. Maintenance: In this phase, the patient is kept at a constant level of anaesthesia during the entire surgical procedure. Maintenance is done with sedatives, muscle relaxants and analgesics.
- E. Recuperación: cuando la anestesia desaparece el funcionamiento del cuerpo va volviendo a la normalidad de una manera progresiva.
- E. Recovery: when the anaesthesia wears off, the body's functioning gradually returns to normal.

Transferencia Anestesica
Anaesthetic Transfer
Se preguntaran como ocurre este proceso en el cuerpo, pues les voy a mostrar este gráfico para que se puedan ir apoyando en la explicación.
You may wonder how this process occurs in the body, so I am going to show you this graph so that you can support yourselves in the explanation.
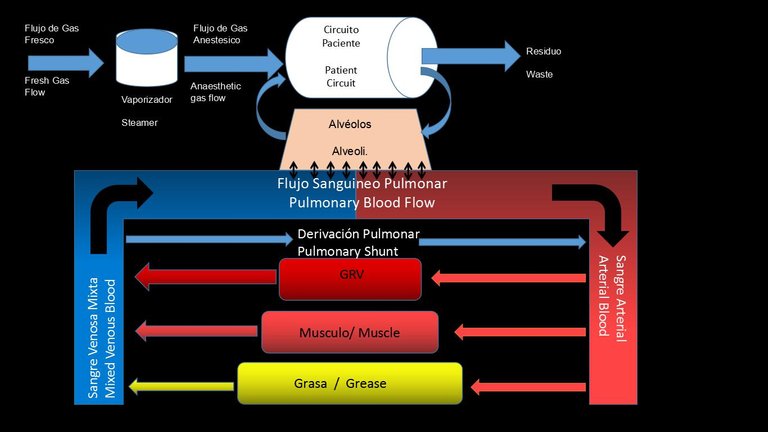
Una serie de gradientes de presión comenzando por el vaporizador de la maquina de anestesia, continuando por el circuito del respirador, el arbol alveolar, sangre, y tejidos musculares aseguran el movimiento del gas.
A series of pressure gradients starting from the anaesthesia machine's vaporiser, continuing through the ventilator circuit, the alveolar tree, blood, and muscle tissues ensure the movement of the gas.
Es importante saber, que la presión parcial anestésica en el sistema nervioso sube rápidamente porque tiene un mayor flujo de sangre, mientras que en los músculos y grasa suben y bajan mucho más lentamente, porque los compartimientos de musculo y grasa representan volúmenes efectivos mucho mayores y tienen menor flujo sanguíneo que el grupo rico en vasos.
Importantly, the anaesthetic partial pressure in the nervous system rises rapidly because it has a higher blood flow, whereas in the muscle and fat compartments it rises and falls much more slowly, because the muscle and fat compartments represent much larger effective volumes and have lower blood flow than the vessel-rich group.
Así como tambien que la presión parcial en grasa continua aumentando después de que se detiene la administración de anestésico, siempre que la presión parcial en el gas alveolar y en la sangre arterial sean mayor que la del compartimiento graso.
As well as the partial pressure in fat continues to increase after anaesthetic administration is stopped, as long as the partial pressure in the alveolar gas and arterial blood is higher than that in the fatty compartment.
Como se traduce esto en un lenguaje mas coloquial, bueno que en la grasa el gas anestésico permanece menor tiempo porque no contiene un alto flujo sanguíneo, mientras que en la sangre y músculos si, lo que permita que el proceso de sedación sea mas rápido.
How this translates into more colloquial language, well, in fat the anaesthetic gas stays for a shorter time because it does not contain a high blood flow, whereas in blood and muscle it does, which allows the sedation process to be quicker.
Agentes Anestésicos
Anaesthetic Agents
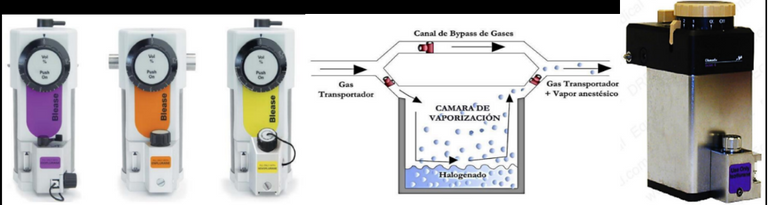
Estos son los responsables de la sedación y cada uno tiene un efecto diferente en el cuerpo, el especialista elegirá con cual trabajar según sea la necesidad de la cirugía, cabe mencionar que actualmente los mas usados son el Isuflurano Y el Sevorano
These are responsible for sedation and each one has a different effect on the body, the specialist will choose which one to work with according to the need of the surgery, it is worth mentioning that currently the most used are Isuflurane and Sevorane.
- Metoxiflurano: el mas potente y lento de los alogenados, disminuye la contractibilidad cardíaca. puede producir insuficiencia renal de alto gasto resistente a la vasopresina.
- Methoxyflurane: the most potent and slowest of the allogenics, decreases cardiac contractility. may produce vasopressin-resistant high output renal failure.
- Isoflurano: deprime levemente la función cardíaca por preservación de los reflejos carotideos. Tiene escaso efecto cerebrales, llegando a proteger el encéfalo de los episodios de isquemia cerebral. Poca afección hepática y renal. Es un gas muy utilizado hoy en día
- Isoflurane: slightly depresses cardiac function by preserving carotid reflexes. It has little effect on the brain, even protecting the brain from episodes of cerebral ischaemia. Little hepatic and renal involvement. It is a gas widely used nowadays.
- Desflurano: 17 veces mas potente que el oxido nitroso, irrita las vias aéreas. Puede reducir la producción intracraneal con la hiperventilación. Es un protector cerebral.
- Desflurane: 17 times more potent than nitrous oxide, irritates airways. Can reduce intracranial output with hyperventilation. It is a brain protector.
- Sevorano: es más potente que el desflurano y de una potencia menor que el Enflurano, altera poco la contractibilidad miocardio.
- Sevorane: more potent than desflurane and less potent than Enflurane, it has little effect on myocardial contractility.
- Enflurano: deprime la contractidad miocardica. Aumenta la secreción de liquido cefalorraquídeo. Puede originar convulsiones a concentraciones elevadas e hipocapnia.
- Enflurane: depresses myocardial contractility. Increases cerebrospinal fluid secretion. May cause seizures at high concentrations and hypocapnia.

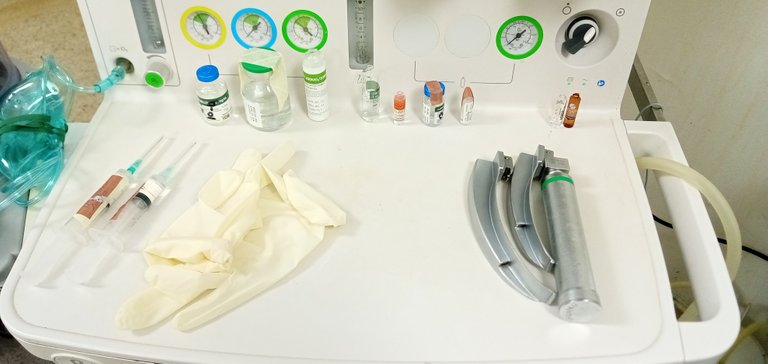
Administración de la Anestesia
Administration of Anaesthesia
La anestesia general por inhalación se realiza a través de una mascarilla o tubo respiratorio, si se realiza a través de una mascarilla el paciente no necesitará apoyo artificial para respirar; en cambio si la anestesia se realiza por intubación significa que durante la cirugía el paciente necesita apoyo artificial para poder continuar con su ciclo respiratorio.
General anaesthesia by inhalation is done through a mask or breathing tube, if it is done through a mask the patient will not require artificial support for breathing; on the other hand if the anaesthesia is done by intubation it means that during the surgery the patient needs artificial support to be able to continue with his or her breathing cycle.
Conocer la anestesia es muy importante, ya que es una de las cuestiones que más nos preocupan a la hora de ir a una operación. Entender más sobre la anestesia nos ayudará a reducir nuestros temores.
Knowing about anaesthesia is very important as it is one of the issues we are most concerned about when going into surgery. Understanding more about anaesthesia will help us to reduce our fears.
En otra ocación seguiremos hablando de la anestesia, ya que es un tema muy largo y da mucha tela que cortar, espero que les haya gustado esta información y sea útil, no olvidés votar, compartir y seguirme para estar al tanto de más información sobre el sistema sanitario.
On another occasion we will continue talking about anaesthesia, as it is a very long topic and there is a lot to discuss, I hope you liked this information and that it is useful, don't forget to vote, share and follow me to be aware of more information about the health system.

Este post es 100% original.
Todo el Contenido de este post es de mi autoria.
This post is 100% original.
All the content of this post is of my authorship.
https://twitter.com/josdad_01/status/1457134420285169664
The rewards earned on this comment will go directly to the person sharing the post on Twitter as long as they are registered with @poshtoken. Sign up at https://hiveposh.com.
Buen post amigo! Información valiosa y muy importante, saludos 😁
Muchas gracias 🤗, y también debo agradecer por dedicar tu tiempo a leer mi post.
Buenas, Su post ha sido propuesto para ser votado a lo largo del día por el witness @cervantes. Un saludo.