What is a phagocyte? The role of phagocytes in the body's immune system
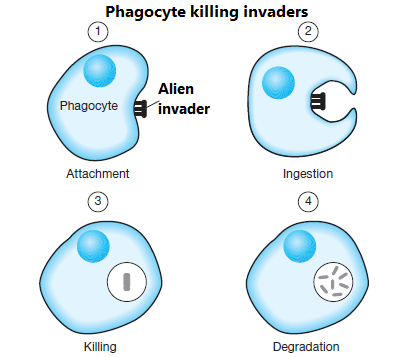
Large white blood cells that contribute to the body's defense system by consuming microorganisms, other cells, and foreign particles are called phagocytes.
The two leading phagocytic cells are neutrophils and macrophages. In response to bacterial infection in the body, neutrophils in the blood, and macrophages in certain tissues engulf the bacteria in the process of phagocytosis.
In addition to ingesting and digesting microbes, macrophages act as scavenger cells by ingesting old blood cells, dead tissue fragments, and cellular debris. Many macrophages reside in the spleen, lymph glands, tonsils, adenoids, and appendix and destroy microbes present in the lymph.
Each macrophage can ingest as many as 100 bacteria, sometimes larger ones such as fungi or malaria germs. Helps in wound healing. In contrast, neutrophils are active phagocytic white blood cells. They ingest foreign bacteria, viruses, or any microscopic protein particles. The ingested material is destroyed with the help of lysosomes containing active proteolytic enzymes inside the cell.
$PIZZA slices delivered:
@pixresteemer(3/5) tipped @jishan5