How does mutation occur by numerical change in chromosomes?
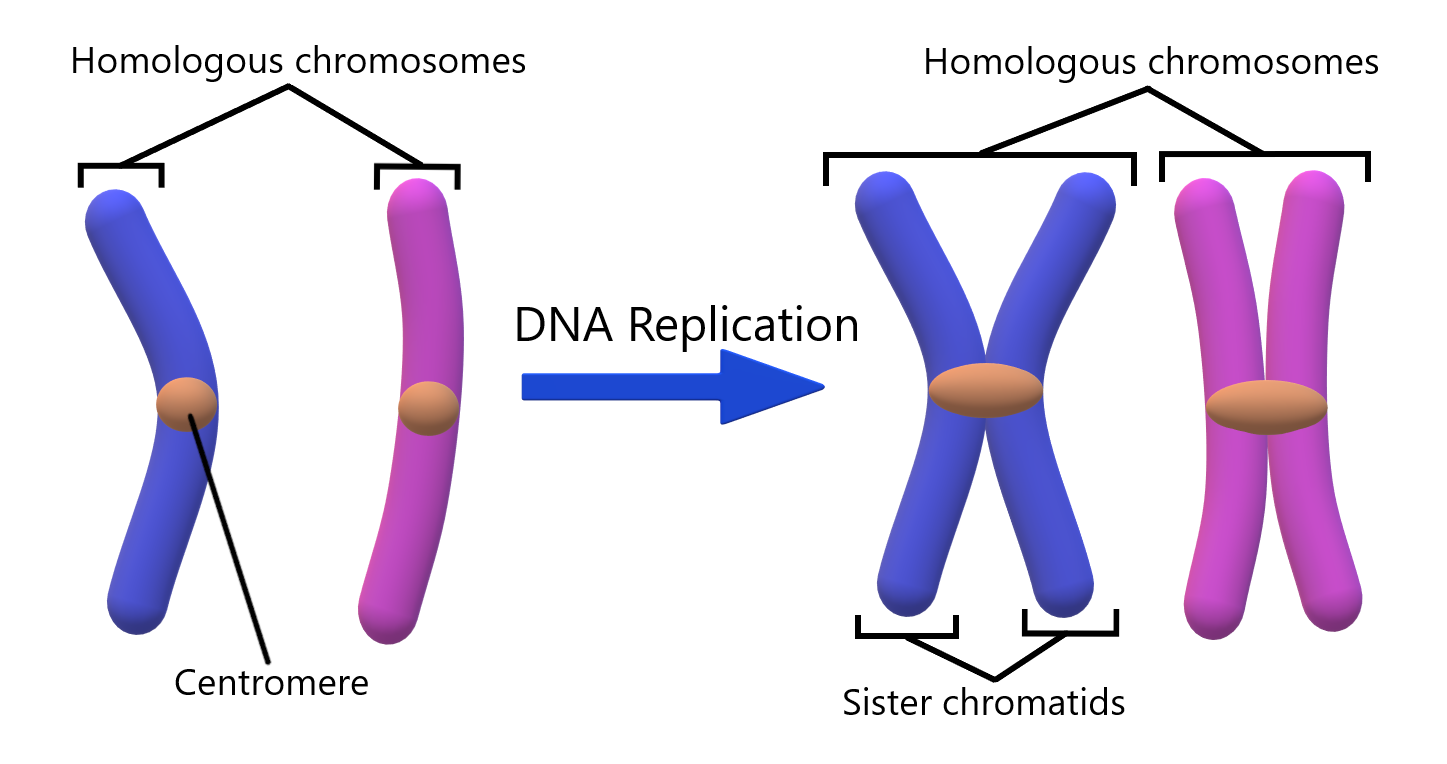
A set of different types of chromosomes in each cell of a species is called the genome. Higher plants usually have one genome in gametes and two genomes in somatic cells. But in some cases, there are exceptions to the ordinance.
This variation in the number of chromosomes in a body cell is called the numerical variation of chromosomes. Chromosome number changes are usually due to errors in meiosis but can also occur in mitosis. Mutations resulting from numerical changes in chromosomes are described below:
Chyuploidy: Euploid cells contain a complete set of chromosomes. Euproid species are diploid whereas euploid species are polyploid and contain three or four sets of chromosomes. For polyploidy, let X be the basic chromosome number.
Example: Triploid species, containing three complete chromosome sets 3X, triploid 4X. For diploid species, Xn is equivalent to n.n is the number of chromosomes in the gamete. Because every gamete possesses a single complete bunch of chromosomes. However, the identity X = n is not adequate for polyploid species.
For example, there are 42 chromosomes. As a consequence bread wheat is a hexaploid. Basic chromosome number, X = 7 and 6 X = 42 Again each triploid gamete contains half of the total chromosome number. Hence X = 21 x and n are not the same in bread wheat. Another type of eukaryote is polyploidy, which exists in monoploid (x) organisms, containing only one set of chromosomes.
Aneuploidy: Abnormalities in normally diploid species in which the resulting cells contain more or less than 2n chromosomes. Namely: 2n + 1, 2n – 1 etc. This condition is called euploidy.
While aneuploidy caused by the loss of one or more chromosomes is called hypoploidy and aneuploidy caused by the addition of one or more chromosomes is called hyperploidy.
Chromosome number from the diploid number If one chromosome is lost it is called monosomy (2n – 1) and if a pair of chromosomes is lost it is called nullisomy (2n-2).
Similarly, the addition of one chromosome to a diploid number is called trisomy and the addition of a pair is called tetrasomy. Again, when one chromosome is added in a monoploid organism, it is called (n + 1) disomy.
That's how mutation occur by numerical change in chromosomes