Sacrificing a male laboratory rat, _Rattus norvegicus._
The medical profession has made it easy to carry out most medical practices on a living animal, an animal with similar characteristics to that of a human being (mammals). Most of the physiological aspects and experiments are usually carried out in this laboratory rat, whether the administration is high dose, middle dose, or low dose. To carry out this study, it involves various processes, like a close study of the effect of these extracts on the laboratory rat, where the results are recorded after due histological and biochemical experiments and analyses. One of the processes involved is tissue processing to harvest and study the changes experienced in target organs.
In the Lab, we made sure all the materials were available for the tissue processing. These materials are: a dissecting set, Absorbent cotton wool, 10% formal saline, hand gloves, a bash board, and dissecting pins.
Method used in the sacrifice
There are several ways of carrying out sacrifice, which involve Chloroform inhalation, diethyl ether inhalation, formalin inhalation, and cervical dislocation. It depends on what suits you or what really interests you. These methods are basically sedatives that instantly result in a rapid loss of consciousness. In the sacrifice, I went for chloroform inhalation, which is believed to be the common method for sacrifice.
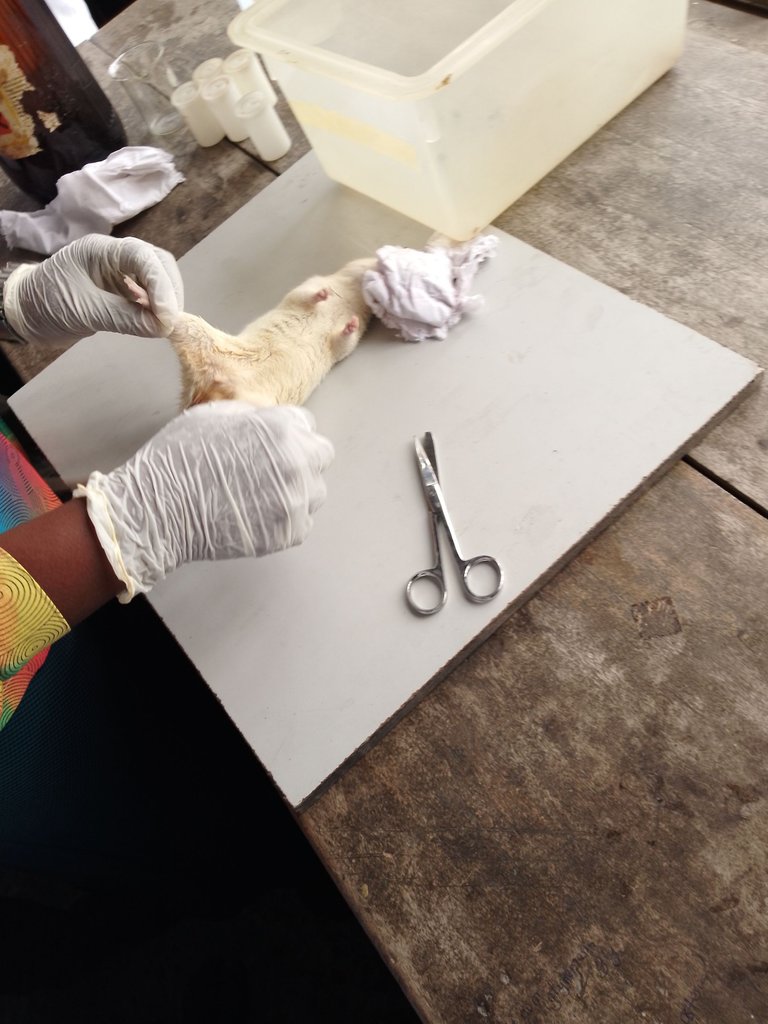
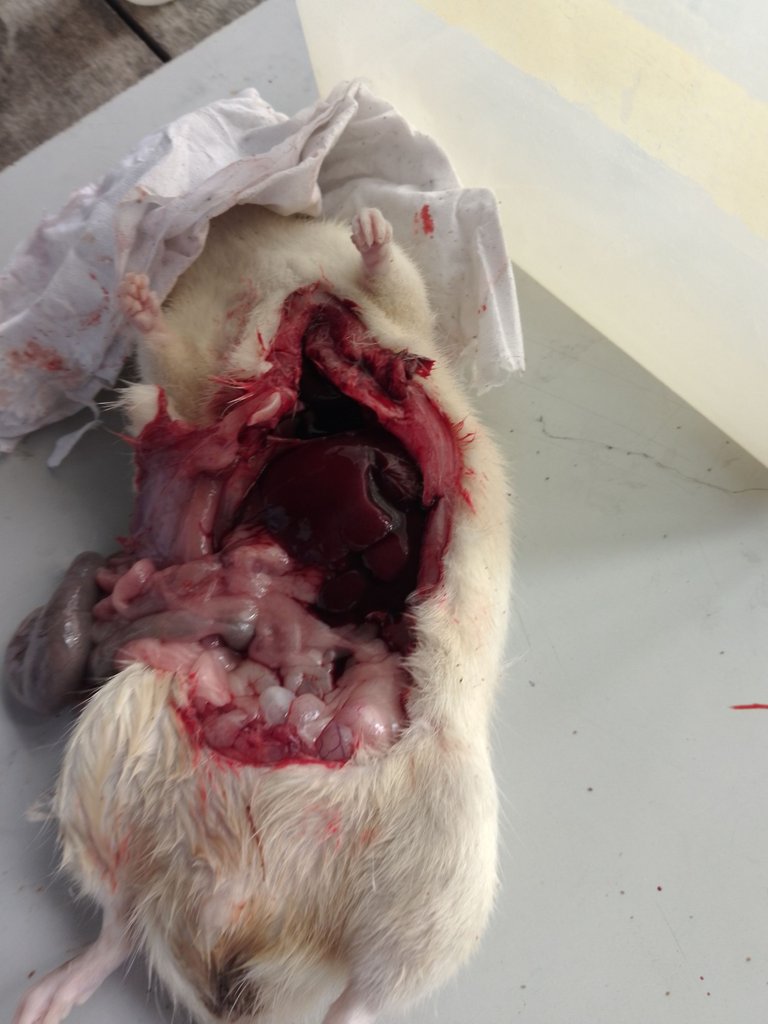
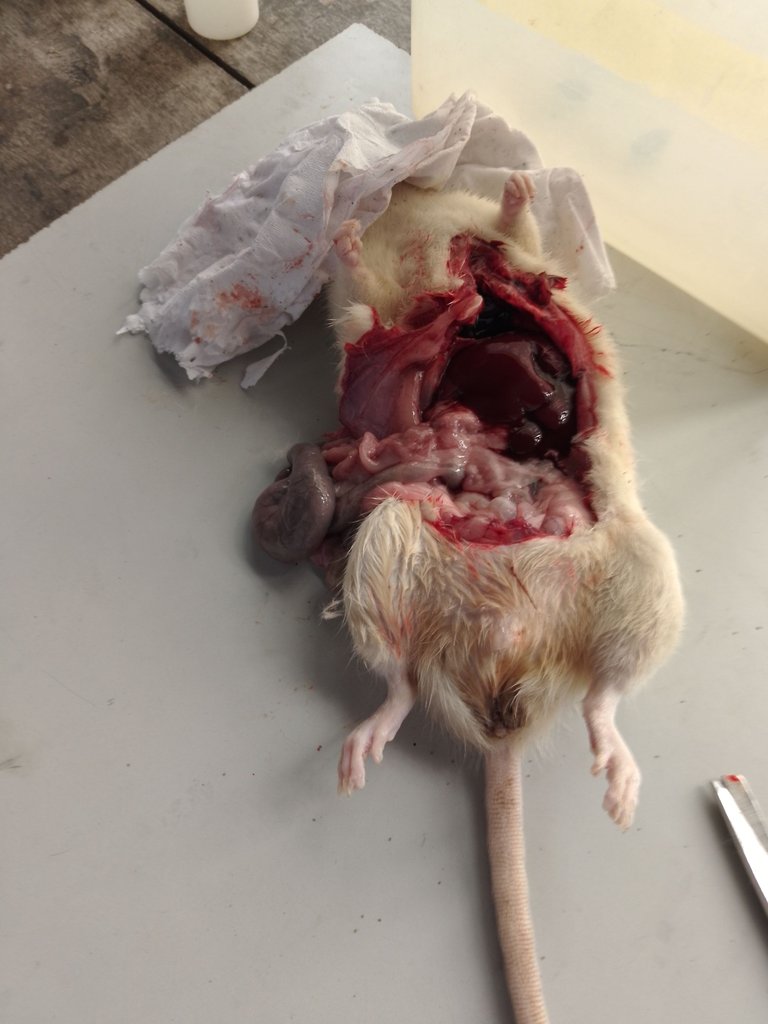

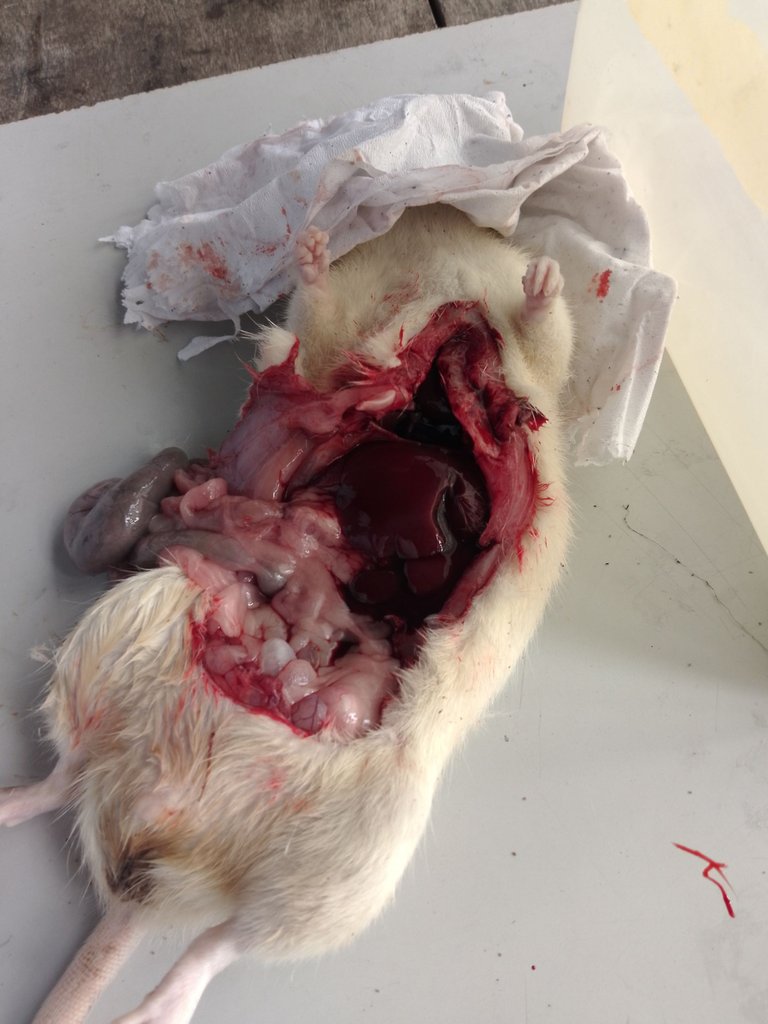
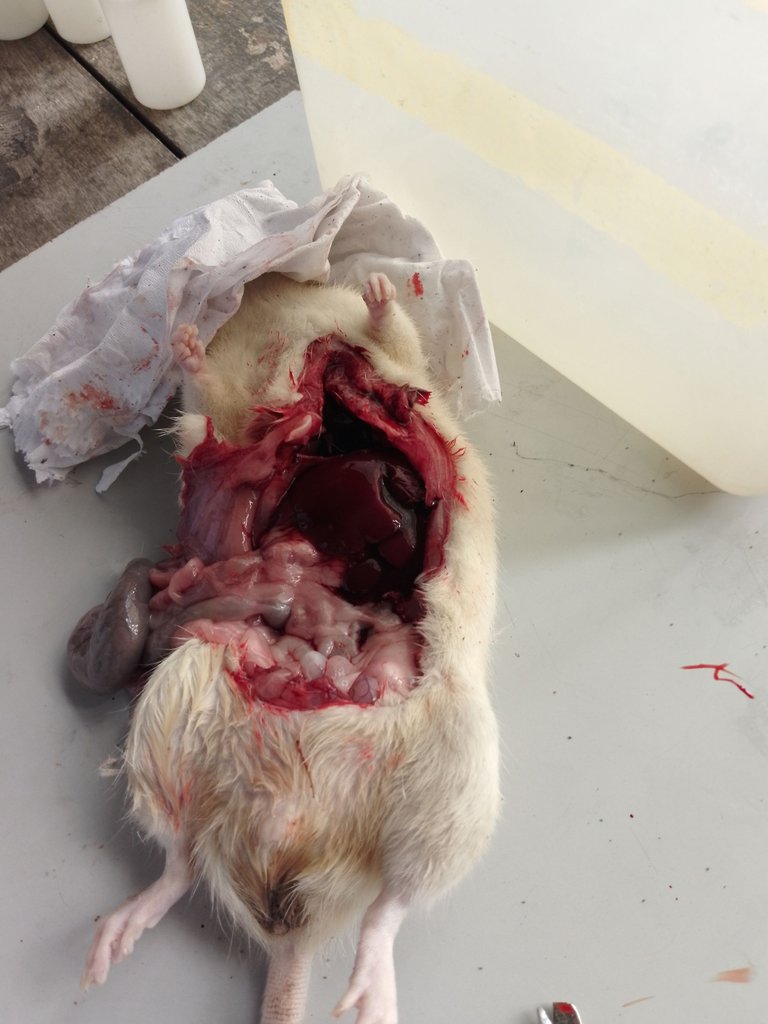
In carrying out sacrifice and harvesting, your mind must be directed towards the expected result, like the organ of study. Different organs have different approaches through which they are harvested based on their bodily activity.
Take, for example, the brain. The brain stops functioning seconds after sacrifice, which automatically alters the experiment you plan on carrying out. This means that for a positive result, a protective measure must be put in place to preserve the brain and its constituents. A common way of preserving it is through perfusion. Just like normal saline is given in the form of a drip to supplement the weak system, the same thing is applicable to perfusion.
What is perfusion?
Perfusion happens to be the passage of fluid or blood through the blood vessels, but in this case, perfusion is being carried out as a form of fixation through the use of either normal saline or phosphate buffered saline. After the perfusion is carried out, the animal can be sacrificed.
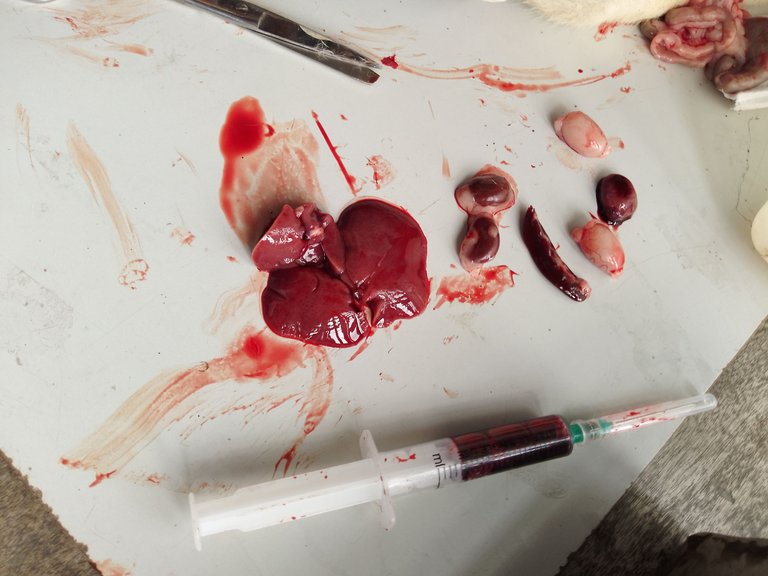
When harvesting other organs, they can be harvested without fixation. example, the liver, kidneys, testes, and the like. Depending on what component you are interested in, you will now determine if it should be frozen or fixed.
In harvesting, an incision is made in the abdomen through which the organs can be accessed.
From here other histological or histochemical procedures will be carried out.
Thank you for reading, let's share ideas.