Immense function of the placenta(Building relationship between mother and child).
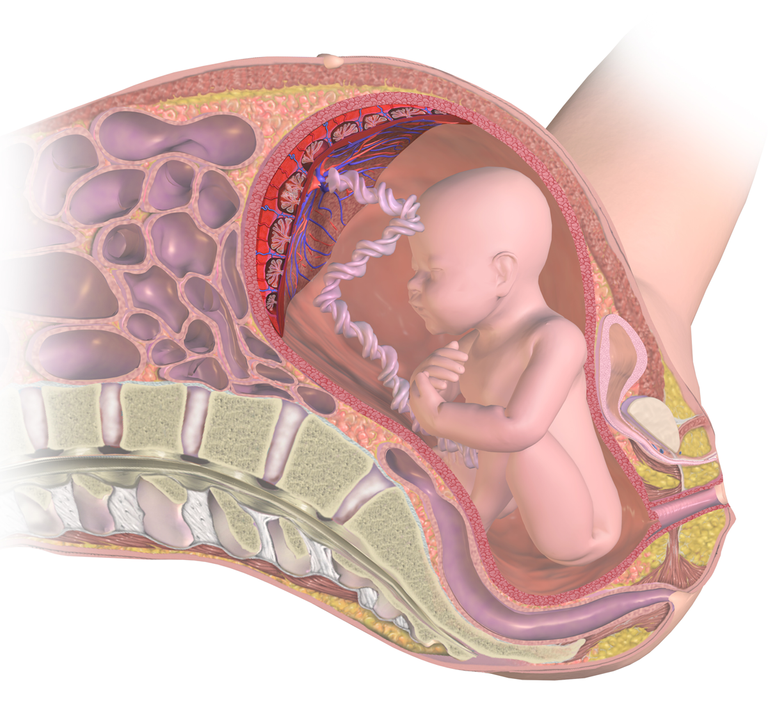
The placenta is an instrumental organ whose functions are short-lived, it actively connects the growing baby in the womb to the uterus during pregnancy. Shortly after pregnancy, the placenta develops and gets attached to the uterus wall, connecting the baby to the placenta is the umbilical cord. This makes the placenta as well as the umbilical cord, the baby's lifeline while it is in the uterus.
At the end of the first trimester, the placenta takes over the production of hormone, before this time, the corpus leteum is usually responsible for the handling of the hormone production. For most pregnant women, the first-trimester symptoms of fatigue and nausea will disappear the moment the placenta takes over completely usually in the second trimester.
The placenta can form anywhere in the uterus, some placenta positions are;
Anterior placenta: At this point, the placenta grows on the front wall of the uterus close to the abdomen.
Posterior placenta: The placenta grows at the back of the wall of the uterus.
Lateral placenta: At this point, the placenta grows on the right or left wall of your uterus.
Fundal placenta: The placenta in this case grows at the top of your uterus.
The functions of the placenta are enormous;
They produce hormones that help the baby grow well.
Helps to protect the baby in the womb.
They get rid of harmful waste and carbon dioxide from a growing baby.
Provides the baby with nutrients and oxygen.
It helps pass immunity from mother to child.
The placenta sometimes appears to move simply because the uterus expands the pregnancy as the fetus grows. Most placenta moves to the top or to the side of the uterus at 32 weeks of pregnancy, when delivery is close, the doctor advises in case there will be possible complications with the position of the placenta.
The placenta has two sides; one side is attached to the uterus and the other side is extremely close to the baby. The side that is attached to the uterine is deep reddish blue in color, while the other side facing the baby is gray.
Birthing the placenta is the third stage of delivery, if the baby is delivered vaginally the placenta will also come through that path. If the birth of the baby is through C-section, then the placenta will be removed from the uterus during the procedure as well.
Different factors can affect the health of the very important placenta during pregnancy;
Older people have more problems with the placenta compared to younger mothers.
High blood pressure can also affect the placenta greatly.
Being pregnant with more than one baby could increase issues with the placenta.
A break or leak in the amniotic sac before real labor begins, greatly increases the chances of placenta problems.
Conditions that impair the blood's ability to clot, or increase the chances of clotting would also increase the risk of placenta problems.
Women who smoke or use hard drugs during pregnancy have also been reported to stand a high chance of having placenta difficulties.
There is a higher chance of having a placenta problem when there has been a previous happening of such.
Abdominal trauma, such as a fall, sudden blow, or auto accident will cause such trauma which increases the chances of the placenta separating prematurely from the baby.
Initial uterine surgery: If there has been a previous surgery on the uterus, probably a surgery carried out to take out fibroids, the chances of having issues with the placenta are high.
Some forms of complication could arise with the placenta. After birth, a retained placenta is usually an issue, some of these conditions include;
Placenta previa, which occurs when the placenta totally or partially covers the cervix. This is more common in early pregnancy and may sometimes get resolved as the uterus grows, with its presence causing serious vaginal bleeding during pregnancy as well as during delivery.
Placenta accreta happens when part or all the placenta remains firmly attached to the uterus, while in normal terms, the placenta should detach from the uterine wall after childbirth. This condition is caused by the blood vessels and other placenta parts growing too deep into the wall of the uterine, this will lead to serious blood loss during pregnancy.
Retained placenta is another possible placenta complication, this one happens when the placenta is not delivered 30 minutes after childbirth. A retained placenta could be triggered because the placenta becomes trapped behind a partially closed cervix or because the placenta remains attached to the wall of the uterine. If the situation is left untreated, it could lead to serious infection and a life-threatening loss of blood.
If you at any point have the experience of severe back pain, abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, or uterine contractions, then pay a visit to your healthcare provider. Medications, alcohol, and substances can all transfer from the bloodstream to the baby to the placenta, so extra care needs to be taken to ascertain the protection of the mother, baby, and the placenta.
Reference.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/in-depth/placenta/art-20044425
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.