Understanding heat as a form of energy and its effects.

Introduction
It is all too easy to see the effect of heat on natural activities around us. For example, when walking outdoors on a very sunny day, the heat from the sun can raise one's temperature and make them feel hot. When liquids are placed outdoors during a sunny day, the heat from the sun can change the temperature of the liquid and warm it. Whenever an object is heated, there is the transfer of energy which results in the temperature rise of that object.
Heat transfers energy also known as thermal energy when the electrically charged atoms of the heat source moves and collides with each other. They transfer to an object or body which has lower temperature and causes its temperature to rise.

Direction of flow of heat energy
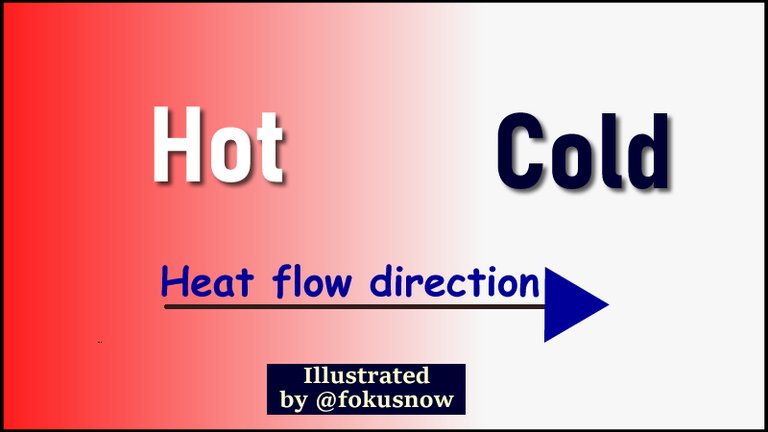
Heat energy usually flows from a region or object of higher temperature to one of lower temperature. This is because the electrically charged atoms of the heat source posses some kinetic energy, and hence move more vigorously than those of a lower temperature. A basic observation of the interaction between cold and warm objects explains this better.
If two objects of varying temperatures are placed in contact with each other, one can note the direction of flow of heat. Heat normally flows from the hotter object to the one that is colder, warming it as a result. The warmer object does not get colder. Instead, the colder object gets warmer. In essence, that explains the direction of flow of thermal energy. It flows from warmer temperatures to colder temperatures.
Temperature is a very important quantity which affects the nature of heat energy. Basically, the warmer a body is, the more heat energy it possesses. Automatically, heat flows to an object of lower temperature from one of higher temperature. The higher the temperature of a body the hotter it is, and the more thermal energy it possesses and vice versa.

Effects of heat on objects
Heat can cause various changes in the physical or chemical properties of objects. The rate and type of change usually is determined by the temperature of the heat and the type of material involved. Below are some major ways heat affects objects:
1. Change of State: One of the major effects of heat is the change of state of the object or body undergoing heat. The following are some of the ways objects change their state when heated:
Solid to Liquid: Heat can cause a solid object to change to a liquid state. This process is often called melting and can be seen in various forms. For example, when ice is heated, it can quickly turn into a liquid. Metals can be heated to a very high temperature to turn them into a liquid. Metals like zinc and iron and others. In fact, heating is one of the main ways to separate some metals from their ores in mining.
Liquid to Vapour: When a liquid is heated to a very high temperature, it can turn to vapour. This process is often referred to as vaporization. The liquid molecules of water turn into vapor molecules at a certain high temperature. That usually happens at boiling point.
2. Thermal expansion: Certain objects enlarge in size when heated to a certain temperature. That is usually the case of objects with an enclosed space or vacuum. Example of such objects include plastic, metal containers, etc. Thermal expansion causes an increase in the size of dimension of the object involved. If heating is continued and temperature is increased, the object might explode.
3. Physical change: Many objects can loose some or all of their physical properties when they are subjected to some degrees of heating. For example, magnets loose some of their magnetic powers when heated. Some elastic materials loose their ability to regain its original shape after they have been heated. Other physical properties that could be affected so much by heating includes the density of an object, electrical resistance, color, shape and other physical properties.
4. Thermionic emission: Heating cause cause certain materials to loose electrons in a process called thermionic emission. This happens when the sudden raise in temperature as a result of heating causes some of the electrons of the metal to overcome their binding energy that holds atoms together and become free, effectively leaving the surface of the metal.
In the world of physics, thermionic emission is used in many industrial processes such as in early vacuum tubes used for television and computers. Even today, it still has applications in the industry.
5. Chemical change: Heating can cause chemical change in metals and other objects. The raise in temperature can cause the breaking of chemical bonds that hold atoms together. When these bonds are broken, it can lead to the formation of new compounds or in the lost of some chemical properties of the object.
New molecules can be formed from heating of compounds. Also, certain compounds break down into simpler ones in a process known as thermal decomposition. This is another chemical change that could happen as a result of heating. This has an industrial application in the physic world such as in the industrial processing of petroleum.

Conclusion
Heating has so much value to cause changes in objects, make them have new properties or change their physical properties. Temperature is directly related to heating and usually affects the direction of flow of thermal energy.
In the next presentation, we will see specific details of the industrial application of heating in production.
Energy in physics was an interesting topic. Molecules can be melted through it's different of states.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.
Congratulations @fokusnow! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 7000 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPCheck out our last posts:
Understanding heat as a form of energy and its effects is crucial in various aspects of our lives. Heat, often seen as the transfer of thermal energy, plays a fundamental role in everyday activities. It can be harnessed for warmth and power, but excessive heat can also lead to discomfort and environmental issues. Industrial heat recovery systems, for instance, demonstrate how we can efficiently capture and repurpose excess heat from industrial processes, reducing energy wastage and environmental impact. Recognizing the multifaceted nature of heat empowers us to make informed choices that balance comfort, efficiency, and sustainability.