An expanded definition of reduction/Oxidation reactions

Introduction
In the previous article, we saw the first definition of redox reactions which involves the element oxygen. In that first definition, redox reactions involve the loss of oxygen and the gain of it too. The definition is not limited just to that element oxygen. It has been expanded to include another important element in chemistry and that is Hydrogen. So let us see this new dimension.

Redox defined in terms of Hydrogen
Hydrogen is an important element in chemical reactions. Just like oxygen, it is often involved in many reactions both in the laboratory and industrially. So in this definition, oxidation is defined as a reaction in which hydrogen is removed from a compound. The complementary or other half of the reaction is just the opposite. So reduction is defined as a reaction in which an atom gains hydrogen.
We are going to consider the following 3 reactions with regards to hydrogen and see how they satisfy this definition or redox reactions.
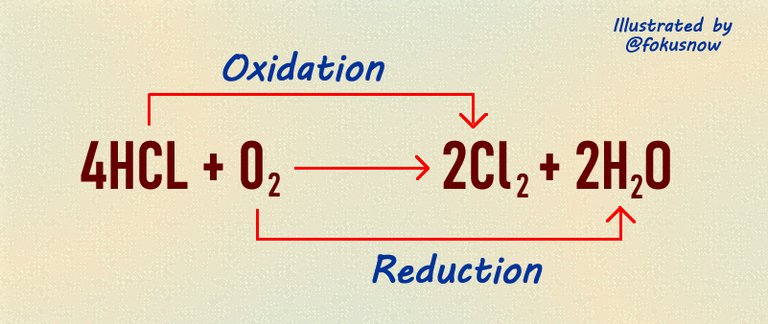
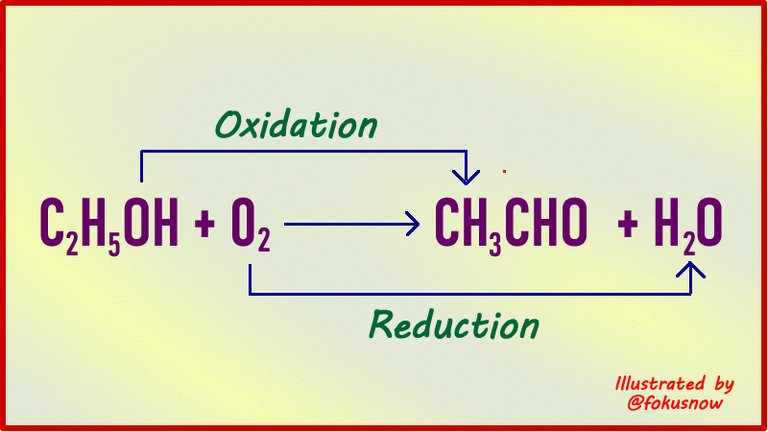
Let us think about this equation above which is a typical redox reaction. We will break it down into various parts.
Reactants: The reactants in this equation are hydrogen chloride and oxgygen.
Products: The products are chlorine and water.
Oxidation: In this reaction, the oxidation is that part which involves removal of hydrogen from a compound. If you observe carefully, there was hydrogen in hydrogen chloride before the reaction. But after the reaction, the hydrogen in hydrogen chloride is lost such that chlorine remains alone after the reaction.
Reduction: The remaining half of the equation which is reduction involves the addition of hydrogen to another atom. In the above equation, oxygen was a lone atom before the reaction. But after the reaction, it gained hydrogen from hydrogen chloride to form water.
Oxidizing agent: In the above equation, the atom that donated its hydrogen is know as the oxidizing agent. Thus, chlorine in the equation acts as the oxidizing agent.
Reducing agent: The reducing agent is the element that gained the oxygen donated. In this case, oxygen becomes the oxidizing agent.
Now we can look at another example of redox reaction in which the definition also centers on the element hydrogen.
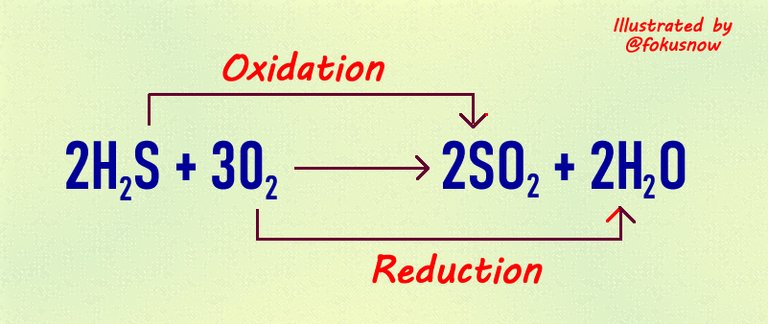
Now the above is a great example of a redox reaction. Again the definition is around movement of hydrogen in the reaction. Here is it:
Reactants: In this equation, hydrogen sulphide reacts with oxygen and both for the reactants.
Products: After the reaction, the products formed are sulphur(iv) oxide and water.
Oxidation: Take note that the hydrogen sulphide donated its hydrogen after the reaction. It was oxidized to sulphur (iv) oxide. In that way, the oxidation half of the reaction is very well established here.
Reduction: For the remaining half of the equation which is reduction, oxygen gained hydrogen after the reaction to form water. This half is the reduction reaction.
Oxidizing agent: The element which donated its hydrogen in thus reaction is sulphur. It is thus known as the oxidizing agent.
Reducing agent: The element that gained that donated hydrogen is oxygen. Thus oxygen is referred to as the reducing agent.
Here is the final example
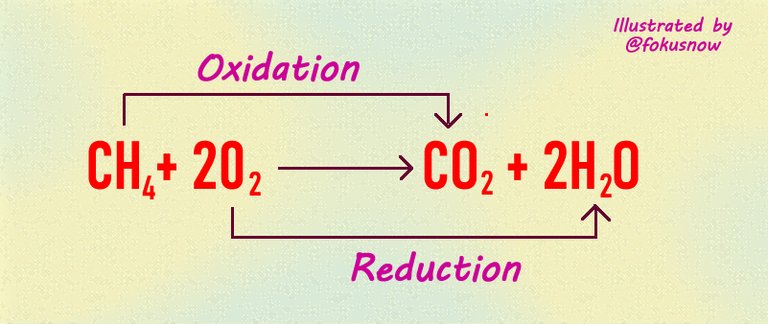
Reactants: In the above example, oxygen and methane form the reactants. They are on the left side of the equation.
Products: The products are carbon (iv) oxide and water.
Oxidation: The oxidation happens when methane looses its hydrogen. At the end of the reaction, it is oxidized to carbon dioxide. This is the oxidation half of this reaction.
Reduction: The reduction involves gaining the donated oxygen. In this reaction, oxygen gains the hydrogen donated by carbon to form water.
Oxidizing agent: Carbon, the element that lost its hydrogen after the reaction is known as the oxidizing agent.
Reducing agent: Oxygen which gained the donated hydrogen is considered the reducing agent.

Conclusion
In this presentation, we have seen yet another definition of redox reactions based on the element hydrogen. Loosing hydrogen in a reaction is considered as oxidation while reduction is gaining hydrogen. This is what we have seen with the 3 examples presented above.
There is yet another dimension to this redox reaction definition. That is what we will broadly discuss in the article with examples.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.