Smooth Muscle Physiology (Calcium/Phosphatase)
We have been discussing Muscles and I have been able to look extensively into the skeletal muscles, but today, we will be doing something a little bit different and that is the smooth muscles. I will be looking at different types of smooth muscles, their contraction, and their relaxation. I will also be talking about the characteristics of smooth muscles and their control. While cardiac muscle is only located in the heart, skeletal muscles attached t bones, smooth muscles can be found in several part of the bone from the skin, to the tracts, hollow organs, vessels, and the eyes.
It should be known that smooth muscles are non-striated muscles. In the Skeletal muscle, there are different structures such as the myosin, the actin that makes up the sarcomere which creates the striped appearance but in the smooth muscles, there are protein myofilaments that are arranged in a different way and this could possibly be because it is uni-nucleated, unlike the skeletal muscles that are multinucleated. Surrounding the tissue of the smooth muscle is the Sarcolemma (plasma membrane). Inside the smooth muscle cells are dense bodies which are made up of a protein known as alpha actinin which is anchored to the plasma membrane. between two dense bodies is an intermediate filament which is composed of vimentin and desmin holding them together. The dense bodies have filaments in them known as the thin filament made up of actin (f) and tropomyosin. Interdigitating the thin filaments is the thick filament which is composed of myosin.Kenhub, Oxford Academic
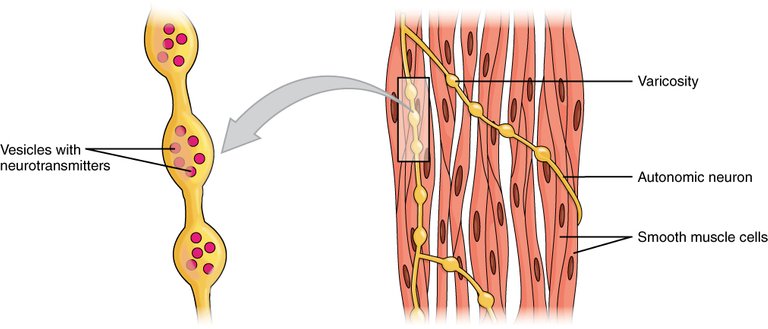
In smooth muscles, whenever the muscle contracts, it causes the dense body to shorten, causing the smooth muscle to squeeze itself. Smooth muscles are of two types, the unitary smooth muscle (visceral smooth muscle) and the multiunit smooth muscle. The Unitary smooth muscle is found in the GI tract and the Urogenital tract. These muscles are interconnected with one another through the Gap junction and it is inervatated by the autonomic nervous system via the parasympathetic or the sympathetic nervous system which integrates the the synaptic bulb, where there are bulbs known as Varicosity which are made up of various neurotransmitters which releases neuroepinephrine, which flows from one cell to another in the musclecausing a rhythmic and simultaneous contraction.physiology.org, ncbi, ncbi 2. .The multiunit Smooth Muscle is found in the Iris in the dilator and constrictor pupillae, the Bronchial smooth muscle, The Tunica Media in the large arteries, the Ciliary Muscle of the eyes, the arrector pili muscle. Thw multiunit Smooth muscle is made up of stimulatory neurons which are not connected together by Gap junction while having their nerve endings. their contraction are not rhythmic since they are structurally independent and are useful for fine control.pressbooks-dev, oregon state University,
In the smooth muscle cells are pacemaker cells which posseses leaky calcium channels which is always open for calcium to get into the cell slowly bringing in positive ions into the cell. The membrane potentials become more positive forming a slow wave and the channel forms a wave going down because potassium also getting out of the cells through the potassium channels which can be leaky causing the cell the cells to be negative bringing the membrane to rest. If the threshold potential is reached as a result of potasium loss, the voltage gatted channel becomes opened instead of leaky causing calcium to flood into the cells ausing the channel to become extremely positively charged. This can be triggered by protons acting on smooth muscle to contract or inhibit it to contract, hormones such as histimine, gastrin can also affect the smooth muscle causing positive or negative ions to flow in or out of the cells, the nervous system can also act on the smooth muscle with neurotransmitter such as acetylcholine which act on muscarinic type 3 receptors activating the G protein and phospholipase C which degrades PIP2 into two IP3 and DAG where the DAG activates protein kinase C. IP3 possesses special channels in Sarcoplasmic reticulum which store calcium ions. In the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum is the Calsequestrin which mediates the activity of the calcium channels in the Sarcoplasmic reticulum. physiology.org, ncbi, nmls,
In the digestive system, smooth muscle cells exist in two layers, the longitudinal layer, Oblique layer, and the circular layer. These muscles help in the digestion of food, and remember that it is involuntary.ncbi, Like I wrote above, smooth muscles contain both thin and thick muscle which is found in cardiac and skeletal muscle. The only branched muscle amongst all type of muscle is the cardiac mucle. ncbi, kenhub,
Image Reference
Going through the post, I was able to refresh my memory of what I have learnt back then in my biology classes- the thick/thin filaments, the syncytium muscle fibre, the sarcoplasmic reticulum storing Ca(II) ions, myofibrils arranged parallelly in the sarcoplasm. Would like to add that Smooth muscles are the only class that has fibres tapered at both ends giving the fusiform shape. Interesting right? Thanks for sharing :)
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.