Neurology || Neuro Pathology of Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral Palsy! Cerebral Palsy!! Cerebral Palsy!!! You must have heard me say these words in my post. I mentioned it a lot in my numerous posts on the cranial nerves, as well as in my other neurology posts. Let's discuss cerebral palsy in this post. Please remember to upvote and follow me if you like this post.
Cerebral palsy (CP) is an upper motor neurological disorder or lesion that affects movement and muscle tone. It is caused by damage to the brain, either before, during, or after birth. Cerebral Palsy is non-progressive in nature over time(it doesn't get worse as a defect).
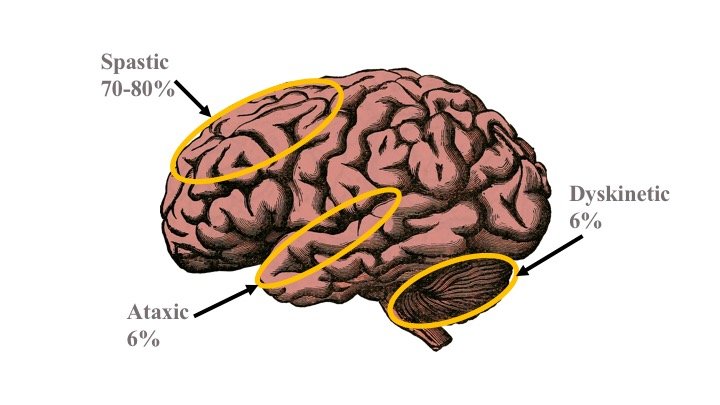
Epidermiology of Cerebral Palsy
It is believed to be the most common cause of disability in children, which affects their function and development. There is a worldwide report of Cerebral Palsy prevalence ranging from 1.5 to 4 children out of 1000 birth. In the United State in 2002, the rate of prevalence of Cerebral Palsy was 1.76 in 1,000 people..
Etiology of Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral palsy is multifactorial, as there are several causes of the disorder but most of the causes can be traced back to development before birth (prenatal development), or immediately after birth development (postnatal). Premature birth is a common cause of cerebral palsy. It is a result of improper development of the brain before the birth of the child. Premature birth can lead to Periventricular leukomalacia which affects the white matter of the brain as a result of inadequate supply of blood, leading to inadequate formation of these part of the brain causing them to die. Another cause of Cerebral Palsy associated with premature children is Isolated intraventricular hemorrhage where the capillaries near the cerebral ventricular system rupture causing blood to go into the cerebral ventricular system causing hydrocephalus. Both Periventricular leukomalacia and Isolated intraventricular hemorrhage lead to the lesion of the upper motor neuron causing cerebral palsy. ,,
Another cause of Cerebral palsy is Intrauterine infection in cases of toxoplasma gondii, Rubella, Cytomegalovirus, Herpes simplex virus and other viral infections. can lead to cerebral palsy.,,,,. In cases where there isn't enough blood flow and oxygen to the fetal brain during fetal growth, leading to hypoxic insult as a result of issues such as placental abruption, or placenta previa causing lack of blood and oxygen to the fetus can lead to Cerebral Palsy. This palsy as a result of placental abruption could also occur during the birthing process such as placental compression during childbirth, causing a lack of blood and oxygen to the fetus's brain could lead to cerebral palsy.,.
After birth, infants can still have cerebral palsy. This can be during the birthing process causing a intracerebral hemmorhage, or resulting from meningitis, or encephalitis or cases of acute ischemic stroke. Conditions such as Kernictarus (high level of bilirubin as a result of high hemolysis), when this causes the blood brain barrier, it would destroy certain structures of the brain including the basal ganglia, causing brain injury or lesion.,,.
Pathophysiology of Cerebral Palsy
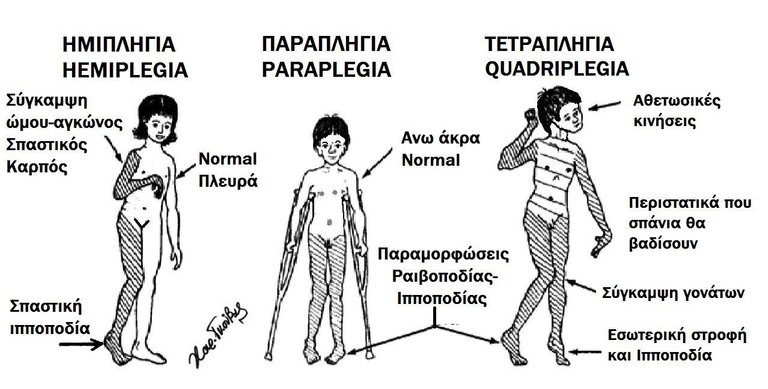
Spastic Cerebral Palsy has to do with the lesion of the upper motor neurons of the cortex. Upper motor neuron lesions would lead to hyperreflexia, clonus, spasticity, and weakness in tone.. Spastic Cerebral Palsy can be subdivided into Hemiplegic, diplegic and quadriplegic.. When there a lesion in the left side of the upper motor neuron, it will prevent the ability to stimulate the lower motor neurons, leading to the spaticity, hyperreflexia, in the contralateral side of the lesion.,,. With diplegic, it affects the medial surface of the upper motor neuron, thereby affecting the lower motor neurons in the brain cauing lower extremity palsy with little on upper extrimity palsy.with quadriplegic Spastic Cerebral Palsy, both upper and lower extremities are affected.
Dyskinetic Cerebral Palsy is an injury associated with the basal ganglia. Basal ganglia initiate movement, and prevent unwanted motor movement, so when there is a lesion in the Basal ganglia, the ability to prevent unwanted motor movement is lost. This will lead to unwanted motor movement which can be associated with disorders such as Chorea, and Dystonia (where there is a tensed rigidity, and sustained involuntary movement).,,
Ataxic Cerbral Palsy has to do with the lesion of the cerebellum, which functions in speech production, balance, posture and cordination. When there is an injury or palsy to the area of the cerebellum, speech production is difficult or impossible. Patients will develop hypotonia, ataxia, and since it plays a role in cordination and there is an abnomaility in such, and patient could develop Dysmetria.,,.
Complications of Cerebral Palsy
Since there is an abnormal development of the brain, it could lead to load of cognitive complications and abnormalities in the patient. Patients with Cerebral palsy might experience cognitive disabilities, seizure, strabismus and visual abnormalities, hearing impairment, scoliosis, pulling the femur causing hip dislocassion, speech difficulty, Dysphasia, difficulty swallowing, Sialorrhea, Aspiration pneumonia, hypoventilation syndrome, restrictive lung disease, and pain, weakness and joint contractures, as a result of spasticity.,,.
Treatment of Cerebral Palsy
Treatment of Cerebral palsy isn't definitive, rather treating the complications associated with it is very important. This complications can be managed via medicine or surgery, depending on the area affected by the palsy. When patients have pasticity, antispasmodics can be used.drugs such as Diazepam, baclofen, and tizanidine act on the central nervous system while drugs such as botulinum toxin injection and dentroline can be used.. Surgically, it can be managed with options such as tendon releases, placement of baclofen pump, hip derotation and rotation surgery, and surgically repairing the strabismus.,.
Image Reference
Image 1 || Wikimedia Commons || Cerebral Palsy Types
Image 2 || Wikimedia Commons || Cerebral palsy forms
Good information you share here. Unfortunately I have seen many cases of children with this condition and most of the time it is related to poor nutrition. Not precisely to infections although it could clearly cause it.
Nutritional deficiencies of important elements in the process of formation of the nervous system in the process of pregnancy is the main cause, at least according to my experience.
I suppose that the cause will vary depending on the geographical area, I would have to check statistics.
Yay! 🤗
Your content has been boosted with Ecency Points, by @electronico.
Use Ecency daily to boost your growth on platform!
Support Ecency
Vote for new Proposal
Delegate HP and earn more
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.
Very good information! thanks
!1UP
You have received a 1UP from @gwajnberg!
@stem-curator, @neoxag-curator
And they will bring !PIZZA 🍕.
Learn more about our delegation service to earn daily rewards. Join the Cartel on Discord.
I gifted $PIZZA slices here:
@curation-cartel(5/20) tipped @eni-ola (x1)
Learn more at https://hive.pizza!
Dear @eni-ola,
Our previous proposal expired end of December and the Hivebuzz project is not funded anymore. May we ask you to review and support our new proposal (https://peakd.com/me/proposals/248)?
Thank you for your help!
Great piece of article from you, neuroscience is really a great broad topic that one must be vigilant with. Also it’s very important to always check up especially in the early stages so as to have early treatment as the saying goes “prevention is better than cure”. Thanks for lecturing us on this, have a nice day.