Neuro Pathology - Pathophysiology of Acute Ischemic Stroke
As I continue on Neuro Pathology, let's discuss Acute Ischemic Stroke discussing the causes, Etiology, and pathophysiology first then I would discuss clinical features. I could continue with diagnosis and treatment but for now, let's break down the etiology and pathophysiology. The causes of Acute Ischemic Stroke can be as a result of Global Hypoperfusion, Thrombic causes, Arterial Embolic causes, Cardiac Embolus, Vasculitis, Paradoxical embolus
Global Hypoperfusion can be caused by certain conditions including Cardiac arrest, where there is no cardiac output, low mean arterial pressure, as well as no blood flowing to the cerebrum in the brain. When blood isn't reaching the cerebrum for a long time, it would lead to Ischemia and Infarction. Another cause for Global hypoperfusion in a person who has severe acute respiratory failure thereby causing low oxygen to the cerebrum and leading to Ischemia. Another cause would be the presence of fatty plaque in the internal carotid artery causing Stenosis there not allowing enough blood to flow through to the cerebrum, which would lead to ischemia. Another cause of Global Hypoperfusion is too low blood pressure as a result of using antihypertensive drugs or as a result of a condition, causing the pressure of blood to reduce and not be able to push blood to the brain. Shock is also not also excluded, as shocks such as septic shock, and cardiogenic shock thereby leading to low perfusion cause a drop in blood pressure and blood not going to the cerebrum of the brain. , , ,
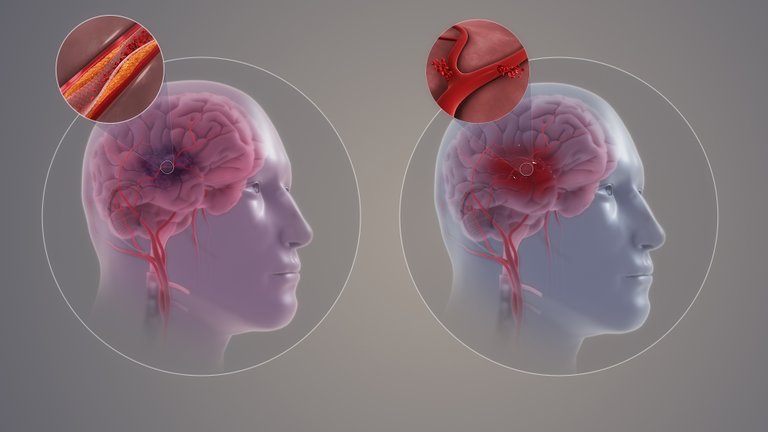
Acute Ischemic Stroke can occur as a result of thrombotic causes which are prone to occur in large vessels such as the internal carotid artery, middle cerebral artery (M1), Basilar artery, Vertebral artery, as well as in small vessels which include the LenticularStriate artery, and the pontine branches which can form thrombi. This thrombosis can be caused as a result of some risk factors which include hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, smoking, and obesity. Also, old age can be a risk factor for thrombosis in these vessels. The risk factors lead to plaque (atherosclerosis) accumulation in the vessels leading to stenosis and occlusion of the vessels which could reduce oxygen and blood flow to neurons. ,
Embolic causes are another cause of Acute Ischemic Stroke which can occur in the form of arterial to arterial emboli where a plaque in the wall of vessels is ruptured or broken where the plaque begins to move freely known as an embolus. This embolus can reach the internal Carotid artery, which would then lead to ischemia as a result of blood not being able to pass through the internal carotid artery because the embolus blocks the artery. This can be a result of an Aortic Arch Plaque, and Internal Carotid Artery plaque breaking free to block blood from reaching the brain neurons., , , ,

Paradoxical embolism is another cause that is a result of an atrial septal defect such as a patent foramen ovale, Atrial septal aneurysm, where a hole is formed between the right and left atrium between the fossa ovale, in the heart. This can lead to an embolus in the middle cerebral artery, and the posterior cerebral artery leading to an ischemia and a stroke., ,
Cardiac Embolism also involves the atria, the ventricle, and the valve. Cardiac Emboli would happen with a left atria thrombosis as a result of atrial fibrillation, mechanical valve, rheumatic heart disease, and infective endocarditis, which could lead to the formation of a clot in the left atrium. Left Ventricle Thrombus can also cause cardiac embolus. These thrombi can occur as a result of a left ventricular aneurysm, and arterial myocardial infarction could also lead to blood-forming. Heart failures can also cause thrombosis in the heart. These thrombus become detached and forms an embolus which then goes to the carotid structure where it gets stuck in cerebral vessels leading to ischemia.
It could also be caused by vasculitis which could be autoimmune, infectious, and a primary Central Nervous System vasculitis. This can lead to an attack of the cerebral vessels causing them to be inflamed and narrowing the vessel increasing the rate of clotting in the vessels which could lead to an ischemia and an infarction. Other cases such as dissection from a trauma in the coratid, a tear of the endothelial layer, and connective tissue diseases can cause a clot preventing the flow of blood and oxygen to the brain., ,
The vascular territories that receive the blocking, occlusion, or hitting determine the clinical manifestation. If the Anterior cerebrum artery is affected, it will to the ACA syndrome, and in similar ways, there will be the MCA syndrome if the Middle Cerebral artery is affected, PCA syndrome if the Posterior Cerebral artery is affected, and ICA syndrome if the inferior carotid artery is affected which could cause Carotid stump syndrome. The vertebral artery being affected can affect the medulla, the posterior part of the cerebrum.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.