An Overview of Rheumatology - Arthritis and Gout
@elity-sitio here again, and in today's post, I will be discussing Rheumatology in detail. Rheumatology is a branch of medicine or medical specialty that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatic diseases, which are conditions that affect the joints, muscles, and bones. The categories of the diseases can be autoimmune diseases, autoinflammatory diseases, crystalline arthritis, metabolic bone disease, pain syndrome, and vasculitides. These diseases can cause inflammation, pain, stiffness, and damage to the affected parts of the body. When you hear people say they have Rheumatism, it is a general name for any disease that is associated with pain and inflammation of joints, muscles, and connective tissues. The name Rheumatism is not a scientific name, they are referring to Rheumatoid arthritis. Examples of rheumatic diseases are rheumatoid arthritis, Paget disease, Osteoarthritis, gout, Pseudogout, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Sarcoidosis, Familial Mediterranean fever, and Still's Diseases. Unlike hematology, rheumatology has to do with the patient's history, physical examination, imaging, and lab. With all having to align together to reach a diagnosis.
The human immune system normally identifies the part of the body, its cell, tissues, organs, and other antibodies, and with autoimmunity, the immune system in the body starts to attack self-antigens which is normal, as the body has some antigen that could be tackled by itself but this becomes a thing of concern with autoimmune disease, as the immune system starts to attack itself, and see itself as antigens or pathogens. Normally, when a person gets exposed to certain bacteria or pathogens, not everyone will fall ill as a result of the pathogen, the body's autoimmune system will fight these antigens and some people will not come up exhibiting the symptoms of the pathogen but when there is a problem where the body starts to mistake itself and body as an antigen and attacks it, then it is an autoimmune disease. Similar to this is something that happens with mutation. In one way or the other, there are mutated genes in our body, but we possess tumor-suppressing systems with genes like P53 which destroy these types of cells. When the tumor-suppressing systems are unable to suppress these mutated genes and kill these cells, we start to see people who have growths in their cells, tissues, and organs which could be benign or cancerous.
Back to Rheumatology. Rheumatologic diseases can be divided into non-inflammatory diseases and inflammatory diseases. Non-Inflammatory Rheumatologic diseases include Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis, and Fibromyalgia, while inflammatory Rheumatologic diseases include Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Seronegative Spondyloarthritis, Gout. When we say Arthritis, it is the inflammation of joints or the structures surrounding joints, Enthesitis is the inflammation of the tendon, and ligaments (Entheses) where the bones are inserted, and enthesitis is common in reactive arthritis. When arthritis is mono (monoarthritis), it affects one joint, when it is oligo (Oligoarthritis), it affects 2 to 4 joints, and when it is poly (polyarthritis), it affects 5 or more joints. Arthritis might be accompanied by Arthralgia (which is a pain in the joint) and can be inflamed (inflammation signs include redness, hotness, swelling, pain, and loss of function).
While Rheumatological diseases can affect the joints and other specific areas, they can show extra-articular manifestations such as Rheumatoid Arthritis showing manifestations including Epideritis, carpal tunnel syndrome, and pericarditis. Sjogren syndrome shows extra-articular manifestation such as dry mouth and eye, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus shows extra-articular manifestation which includes Rash in the skin, renal insufficiency, and Reactive Arthritis shows extra-articular manifestation such as Urethritis and conjunctivitis.
When patients appear before a physician, it is important to identify the previous history of the patient which confirms if the patient had a previous occurrence or a medical condition in the past such as hypertension or diabetes. Confirm if the patients have an allergy to drugs or food, and ask if they have been hospitalized in the past or had a major surgery. Simple general questions such as family history, social history, sexual history, and other previous medical histories can be important when diagnosing. Rheumatology Patients can complain of joint pain, stiffness, lack of function, skin rash, lesions, swellings, sweating, eye issues, bowel irregularities, malignancy, and in rare cases bone fracture.
When patients complain of pain, it is important to see the site of pain, the onset, the course, the duration, the distribution of the pain, character, and severity, whether is it aggravated, and what relieves it, it is associated with any other medical symptoms. When the patients have joint pains, the same steps should be followed. The site of the pain should be confirmed, and so on. For Rheumatology, when there is pain in the joint predominantly, it is osteoarthritis, in the case where the stiffness is predominant, alongside swelling, and redness then it is inflammatory arthritis, in the case where the is loss of function in the joint.
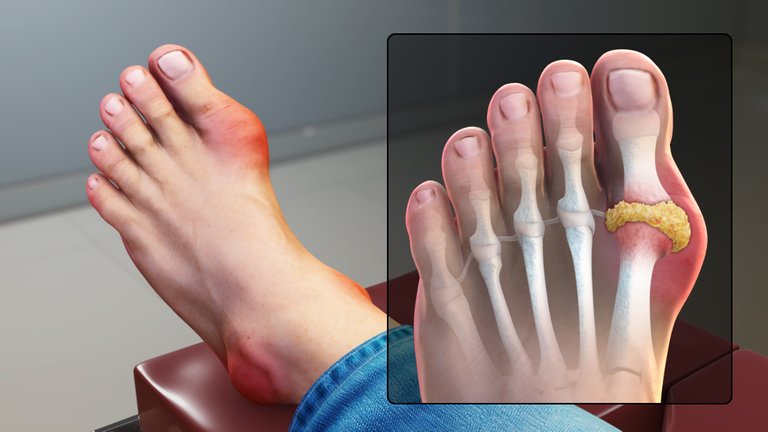
In the case where Monosodium urate crystals are deposited in the joint, it is referred to as Gout. Remember that Gout is an inflammatory Rheumatology disease. It occurs as a result of too much Uric acid in the blood (hyperuricemia) forming crystals in joints and kidneys. When this occurs repeatedly, it can lead to arthritis. Increased consumption of purine (such as shellfish, red meat, and organ meat) is a major cause of monosodium urate crystals. Gout usually affects the joint of the big toes first with severe pains in the toes at the hour of attack and hours after the attack, the attack can last for days. It can also affect other joints such as the knee, elbow, ankle, and wrist. Treatments include the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, colchicine, Xanthine oxidase inhibitors such as Allopurinol, probenecid, and modification of diet.
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/331715-overview?reg=1
https://www.rheumatology.org/I-Am-A/Patient-Caregiver/Health-Care-Team/What-is-a-Rheumatologist
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/rheumatology
https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/muscle-bone-and-joints/conditions/gout
https://patient.info/doctor/rheumatological-history-examination-and-investigations
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.
When this issue is not quickly treated, it can lead to the leg been amputated