The Human Brain

At a weight of 3 pounds, the brain is arguably the most important organ in the human body. The brain has the responsibility of receiving information and interpreting it in addition it plays the role of building ideas and plans for execution. This is not to mention the endocrine function of the brain in addition to all these important features already mentioned.
The brain forms part of the central nervous system with the spinal cord running down its stem. It is formed by the cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem.
In this post, we want to take a look at the structural nature of this organ and describe its features.
The Brain
The brain structurally is made up of the cerebrum, the cerebellum and the brainstem.
The cerebrum- This is the largest part of the brain and has two lobes one on the right and the other on the left. It has the function of receiving impulses from the ears, eyes, tongue, olfactory nerve and skin. The cerebellum functions to form thoughts, and stimulate the muscles for movement in walking and actions like speech.
Cerebellum- Under the cerebrum the cerebellum has involuntary “machine-like” that do not require thought. Things like posture and balance.
Brainstem- The brain stem is the stock that holds the cerebrum and cerebellum in place and acts to relay never connection from these organs to and from the spinal cord. In addition to this, it performs automatic functions like in maintains breathing, heartbeat, digestion and other involuntary actions.
Halves of The Brain
The brain is divided among its organs into two halves. The cerebrum's halves communicate with each other through a bundle of fibres known as the corpus callosum. The hemispheres of the cerebellum have nerve fibres that twist to the opposite side so that the left brain controls the right brain and the right brain controls the left.
The right and left brains have different functions usually the right brain is more artistic and has more functions n creativity while the right brain is more analytical and calculative.
Lobes of The Brain
The cerebrum has large fissures that divide it into different lobes. The right and the left hemisphere are divided into 4 lobes these are the frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital lobes. Each of these lobes or part have its specific functions.
All these lobes work together to ensure the collective function of the brain.
Language
The left hemisphere for most people is the part of the brain that is involved with the understanding of language. This is typically called the dominant part of the brain. The right hemisphere is usually involved worth interpreting the visual information that is seen through the eyes.
In one in three people who use the left hand as their more dominant hand, the centre for speech is found on the right side of the brain. Tests may be needed to be sure of which hemisphere has the speech centre.
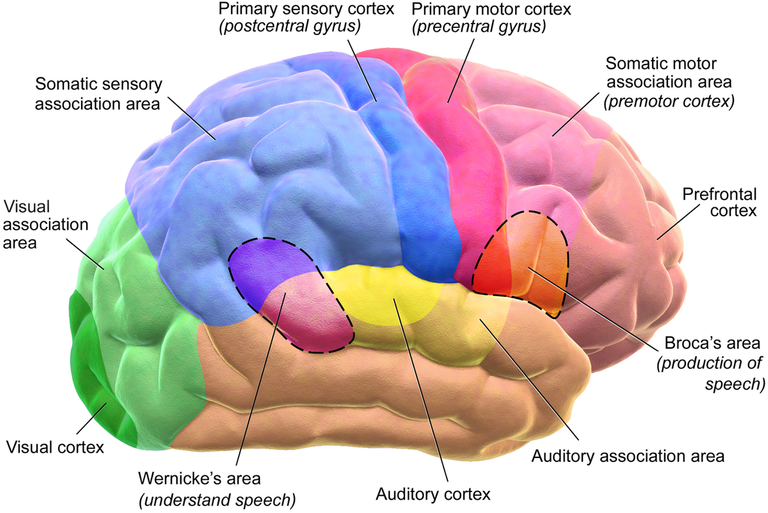
Broca’s area- This area is usually found in the left hemisphere of the brain. When there is an injury to this part of the brain, muscles responsible for speech are hard to move and speaking is difficult. This is called Broca’s Aphasia.
Wernicke's area- This is also found in the dominant hemisphere and injury to this area causes the person to say things that have no meaning. The person may say sentences that do not make any sense or they may make sounds that are not understandable.
Cerebral Cortex
The outer surface of the brain is made up of coils of nerve bodies that are coiled up into folds and ridges. The cerebral cortex has billions of nerve cells. The never cell bodies on the outer portion of the brain make up the grey matter and their continuations, their axons are the white matter.
The folds in the brain are known as the gyrus while the intersections between each fold are known as the sulcus. The folds and sulcus are very important in knowing the regions of the brain.
Deeper anatomy
The axons of the brain connect the different areas of the cortex. There is information being moved from one fold to the other on the brain or from lobe to lobe and then to the deeper brain anatomy
The thalamus is one of the structures that make up the deeper anatomy. It makes up the lower part of the third ventricle. Its function is mainly for automatic behaviour. It alerts the body when we are hungry or need water or need to sleep. It is the main organ in charge of the pituitary gland.
The pituitary gland is housed in a part of the skull known as the sella turcica. The pituitary stalk holds the pituitary to the brain. The pituitary gland is the master gland of the body.
The pineal is located posterior to the third ventricle it is the body's clock and it helps to regulate this activity.
The Thalamus is the main organ that takes and gives information to the cortex. It acts as a relay centre.
Other parts of the deep anatomy of the brain are the basal ganglia and the limbic system and they function mainly to aid the cerebral cortex to perform its function.
Conclusion
The brain is a magnificent organ that plays the main role of organizing the body's function. The brain has parts that perform different roles. In this post were able to talk about some features of the brain but there is more to the brain than this.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.
Thank you!!