Physics - Classical Mechanics - Measuring Pressure in Fluids
[Image1]
Introduction
Hey it's a me again @drifter1!
Today we continue with Physics, and more specifically the branch of "Classical Mechanics", in order to talk about Measuring Pressure in Fluids.
So, without further ado, let's get straight into it!
Pressure in Fluids
The concept of pressure is defined for both solids and fluids, but is more important when discussing fluids. The main reason being that fluids don't show any significant resistance to the force applied parallel to the surface of the fluid. The exerted force simply compresses or expands the fluid.
Variation with Depth
Considering a fluid of constant density, the pressure at the bottom of it is equal to the atmospheric pressure plus the pressure of the fluid itself due to its weight. The weight is simply equal to it's mass times the acceleration due to gravity.
The weight (force) of the fluid is thus:
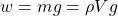
In the case of a cylinder fluid container (with a volume V equal to the area A times height h) we have:
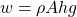
So, the pressure at the bottom (basically any depth h) is given by:
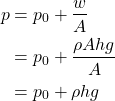
Note: Don't confuse pressure p with density ρ
Absolute and Gauge Pressure
When measuring pressure because the atmospheric pressure patm doesn't change much it makes sense to not include it in the calculations. Measuring equipment thus calculates something known as gauge pressure, pg. The total pressure is referred to as absolute pressure, pabs.
Their relationship is as follows:
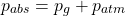
Measuring Pressure
Pressure is measured using various devices. Basically any property that changes in a fluid can be used in order to construct a pressure gauge.

[Image 2]
A manometer gauges based on the pressure caused by the weight of the fluid. Its quite common for only one side of the U-shaped tube to be open to the atmosphere. Of course, the device supposes that the fluid density is constant and thus simply calculates the value p = hρg.
The change of atmospheric pressure is commonly reported in weather forecasts as barometric pressure. The fluid used in a barometer is often mercury, and so as the atmospheric pressure varies, the mercury rises or falls. Because the atmospheric pressure also varies with altitude such an barometer can also be used as an altitude meter (altimeter).
Example
When an open U-tube is filled with two liquids, the difference in height can tell us about the density of the liquids.
The pressures of the liquids are equal and related follows:
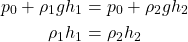
When the density is equal then the individual heights will of course also be equal. Otherwise:

RESOURCES:
References
- https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-osuniversityphysics/chapter/14-1-fluids-density-and-pressure/
- https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-osuniversityphysics/chapter/14-2-measuring-pressure/
- https://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics/fluids/density-and-pressure/a/pressure-article
Images
- https://pxhere.com/en/photo/1045542
- https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:A_fluid_tube_manometer.svg
Mathematical equations used in this article, where made using quicklatex.
Visualizations were made using draw.io.
Previous articles of the series
Rectlinear motion
- Velocity and acceleration in a rectlinear motion -> velocity, acceleration and averages of those
- Rectlinear motion with constant acceleration and free falling -> const acceleration motion and free fall
- Rectlinear motion with variable acceleration and velocity relativity -> integrations to calculate pos and velocity, relative velocity
- Rectlinear motion exercises -> examples and tasks in rectlinear motion
Plane motion
- Position, velocity and acceleration vectors in a plane motion -> position, velocity and acceleration in plane motion
- Projectile motion as a plane motion -> missile/bullet motion as a plane motion
- Smooth Circular motion -> smooth circular motion theory
- Plane motion exercises -> examples and tasks in plane motions
Newton's laws and Applications
- Force and Newton's first law -> force, 1st law
- Mass and Newton's second law -> mass, 2nd law
- Newton's 3rd law and mass vs weight -> mass vs weight, 3rd law, friction
- Applying Newton's Laws -> free-body diagram, point equilibrium and 2nd law applications
- Contact forces and friction -> contact force, friction
- Dynamics of Circular motion -> circular motion dynamics, applications
- Object equilibrium and 2nd law application examples -> examples of object equilibrium and 2nd law applications
- Contact force and friction examples -> exercises in force and friction
- Circular dynamic and vertical circle motion examples -> exercises in circular dynamics
- Advanced Newton law examples -> advanced (more difficult) exercises
Work and Energy
- Work and Kinetic Energy -> Definition of Work, Work by a constant and variable Force, Work and Kinetic Energy, Power, Exercises
- Conservative and Non-Conservative Forces -> Conservation of Energy, Conservative and Non-Conservative Forces and Fields, Calculations and Exercises
- Potential and Mechanical Energy -> Gravitational and Elastic Potential Energy, Conservation of Mechanical Energy, Problem Solving Strategy & Tips
- Force and Potential Energy -> Force as Energy Derivative (1-dim) and Gradient (3-dim)
- Potential Energy Diagrams -> Energy Diagram Interpretation, Steps and Example
- Internal Energy and Work -> Internal Energy, Internal Work
Momentum and Impulse
- Conservation of Momentum -> Momentum, Conservation of Momentum
- Elastic and Inelastic Collisions -> Collision, Elastic Collision, Inelastic Collision
- Collision Examples -> Various Elastic and Inelastic Collision Examples
- Impulse -> Impulse with Example
- Motion of the Center of Mass -> Center of Mass, Motion analysis with examples
- Explaining the Physics behind Rocket Propulsion -> Required Background, Rocket Propulsion Analysis
Angular Motion
- Angular motion basics -> Angular position, velocity and acceleration
- Rotation with constant angular acceleration -> Constant angular acceleration, Example
- Rotational Kinetic Energy & Moment of Inertia -> Rotational kinetic energy, Moment of Inertia
- Parallel Axis Theorem -> Parallel axis theorem with example
- Torque and Angular Acceleration -> Torque, Relation to Angular Acceleration, Example
- Rotation about a moving axis (Rolling motion) -> Fixed and moving axis rotation
- Work and Power in Angular Motion -> Work, Work-Energy Theorem, Power
- Angular Momentum -> Angular Momentum and its conservation
- Explaining the Physics behind Mechanical Gyroscopes -> What they are, History, How they work (Precession, Mathematical Analysis) Difference to Accelerometers
- Exercises around Angular motion -> Angular motion examples
Equilibrium and Elasticity
- Rigid Body Equilibrium -> Equilibrium Conditions of Rigid Bodies, Center of Gravity, Solving Equilibrium Problems
- Force Couple System -> Force Couple System, Example
- Tensile Stress and Strain -> Tensile Stress, Tensile Strain, Young's Modulus, Poisson's Ratio
- Volumetric Stress and Strain -> Volumetric Stress, Volumetric Strain, Bulk's Modulus of Elasticity, Compressibility
- Cross-Sectional Stress and Strain -> Shear Stress, Shear Strain, Shear Modulus
- Elasticity and Plasticity of Common Materials -> Elasticity, Plasticity, Stress-Strain Diagram, Fracture, Common Materials
- Rigid Body Equilibrium Exercises -> Center of Gravity Calculation, Equilibrium Problems
- Exercises on Elasticity and Plasticity -> Young Modulus, Bulk Modulus and Shear Modulus Examples
Gravity
- Newton's Law of Gravitation -> Newton's Law of Gravity, Gravitational Constant G
- Weight: The Force of Gravity -> Weight, Gravitational Acceleration, Gravity on Earth and Planets of the Solar System
- Gravitational Fields -> Gravitational Field Mathematics and Visualization
- Gravitational Potential Energy -> Gravitational Potential Energy, Potential and Escape Velocity
- Exercises around Newtonian Gravity (part 1) -> Examples on the Universal Law of Gravitation
- Exercises around Newtonian Gravity (part2) -> Examples on Gravitational Fields and Potential Energy
- Explaining the Physics behind Satellite Motion -> The Circular Motion of Satellites
- Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion -> Kepler's Story, Elliptical Orbits, Kepler's Laws
- Spherical Mass Distributions -> Spherical Mass Distribution, Gravity Outside and Within a Spherical Shell, Simple Examples
- Earth's Rotation and its Effect on Gravity -> Gravity on Earth, Apparent Weight
- Black Holes and Schwarzschild Radius -> Black Holes (Creation, Types, How To "See" Them), Schwarzschild Radius
Periodic Motion
- Periodic Motion Fundamentals -> Fundamentals (Period, Frequency, Angular Frequency, Return Force, Acceleration, Velocity, Amplitude), Simple Harmonic Motion, Example
- Energy in Simple Harmonic Motion -> Forms of Energy in SHM (Potential, Kinetic, Total and Maximum Energy, Maximum Velocity), Simple Example
- Simple Harmonic Motion Equations -> SHM Equations (Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration, Phase Angle, Amplitude)
- Simple Harmonic Motion and Reference Circle -> SHM and Smooth Circular Motion, Reference Circle
- Simple Harmonic Motion Exercises -> 2 Complete Examples on Simple Harmonic Motion
- Simple Pendulum -> Simple Pendulum (Return Force, Small Angle Approximations, More Accurate Period, Gravity Approximation)
- Physical Pendulum -> Physical Pendulum (Return Torque, Small Angle Approximations, Estimating Moment of Inertia)
- Exercises around Pendulums -> Complete Examples on the 2 types of Pendulums (Simple, Physical)
- Damped Oscillation -> Damping Force, Total Force and Differential Equation, Motion Equations, Special Cases
- Forced Oscillation and Resonance -> Forced Oscillation (Differential Equation, Amplitude, Resonance)
- Exercises around Damped and Forced Oscillation -> Complete Examples on Damped Oscillation and Forced Oscillation
- Chaos and Chaotic Oscillation -> Chaos, Unpredictability and Randomness, Chaotic Oscillation
Fluid Mechanics
- Density and Pressure -> Fluids and Fluid Mechanics, Density, Specific Gravity, Pressure
Final words | Next up
And this is actually it for today's post!
Next time we will talk about Pascal's principle and its use in Hydraulic Systems...
See ya!

Keep on drifting!
Posted with STEMGeeks
Electronic-terrorism, voice to skull and neuro monitoring on Hive and Steem. You can ignore this, but your going to wish you didnt soon. This is happening whether you believe it or not. https://ecency.com/fyrstikken/@fairandbalanced/i-am-the-only-motherfucker-on-the-internet-pointing-to-a-direct-source-for-voice-to-skull-electronic-terrorism
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.