Working With Some Trigonometric Identities [Math]
Hi there. In this math post I cover the topic of trigonometric identities. This topic of trigonometric identities is purely an algebra topics. There is not much real life applications.
As there are some more formulas and identities out there I cannot put everything here. I showcase some of them here.
This post does assume that the reader is familiar with algebra topics such as factoring, multiplying & dividing fractions.
Reference: http://www.sosmath.com/trig/Trig5/trig5/trig5.html
Math text rendered with the use of LaTeX and QuickLaTeX.com

Common Formulas
We start with some common trigonometric formulas.
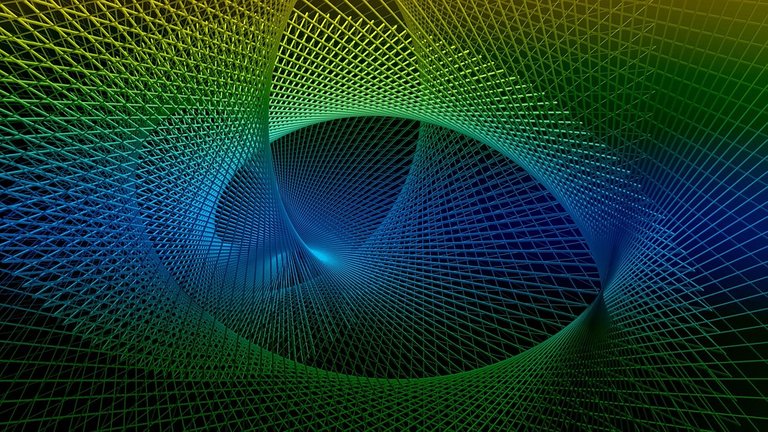
The tangent of an angle is the ratio of the sine of an angle divided by the cosine of an angle.
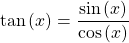
Reciprocal Identities
The reciprocal identities in trigonometry are based on sine, cosine and tangent functions.
One divided by the sine of the angle is the cosecant of an angle.
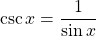
The reciprocal of the cosine of an angle is the secant of the same angle.
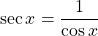
The reciprocal of the tangent of an angle is the cotangent of the same angle.

Pythagorean Identities
One of the most common and important formulas is this Pythagorean Identity.

Dividing everything in the above formula by the square of cosine gives this identity.
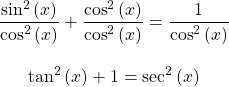
A less common identity (in my opinion) is this one.
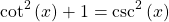
This is from dividing everything by the square of sine in 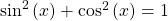 .
.

Some Examples
When it comes to these trigonometric identities, you want to show that one side is equal to the other side. Generally, you want to start with the harder side.
Example One
Show that cos(x) sec(x)}= 1.
This one is not difficult. Use the reciprocal formula for the secant of an angle.
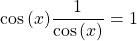
Example Two
Prove that 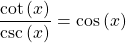 .
.
Use the reciprocal formulas for cotangent and cosecant. Afterwards work with the fractions.
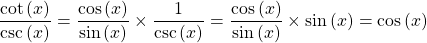
Example Three
Show that 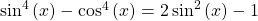 .
.
Start with the left side as it is factorable with the difference of squares factoring technique.
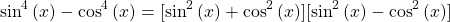
We have a factor that is the Pythagorean identity. Apply this identity 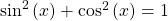 .
.
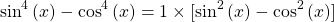
Rearranging the Pythagorean identity gives 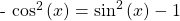 Substitute this accordingly.
Substitute this accordingly.
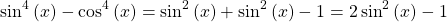
Example Four
Prove that 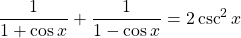
Work with the left side and add the fractions.
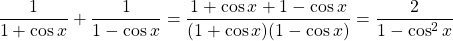
Note that 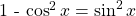 is from
is from 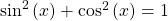 rearranged.
rearranged.


Double Angle Formulas
There are times where you deal with double of a given angle. These double angle formulas are helpful for calculating certain angles. I do not cover the examples here as I focus on the proofs here.
Double Angle Formulas For Sine, Cosine & Tangent
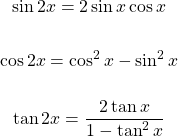
Example One
Show that 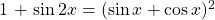 .
.
In this one you can start with either side. I am starting with the right side with expanding that binomial.
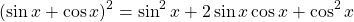
Use the Pythagorean identity to obtain the 1 and the 2 times the cosine and sine is sin(2x).
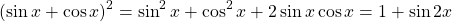
Example Two
Prove that 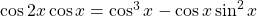 .
.
To start use the cosine double angle formula. Afterwards just use the distributive law.
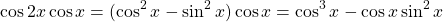
The examples shown here for the double angle formulas are on the easier side.

Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider supporting our funding proposal, approving our witness (@stem.witness) or delegating to the @stemsocial account (for some ROI).
Please consider using the STEMsocial app app and including @stemsocial as a beneficiary to get a stronger support.