Why are workover operational activities performed on an petroleum well?
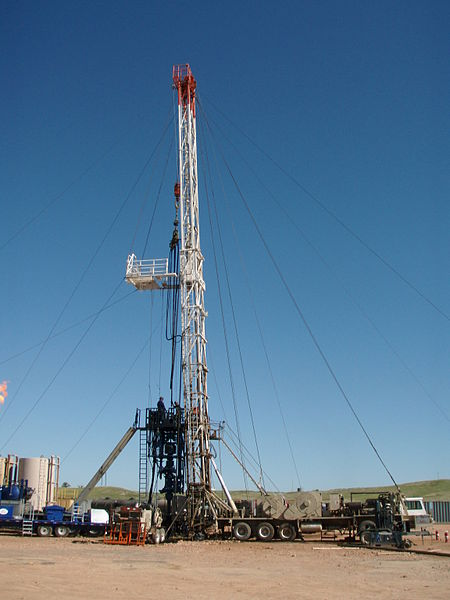

Before understanding the reasons why a producing oil well may need a workover during its life, we must also understand what a well workover is.
The word workover is designated to the operational activity that is used to refer to any type of intervention that we can perform to any oil well during the life of the well while it is in production, intervening a well to perform a workover implies that techniques can be applied to repair the well and solve the productivity problems that it has.
In a generalized way, a well workover should be seen as the cost of having to remove the production tubing in the well and replace the component that is preventing the correct production of the well and with this we can extend the life of the well.
Reasons why we should perform well workovers
Within petroleum engineering it is necessary to consider the optimization of workover jobs, since this type of work is the most complex, difficult and costly of investment, there are several reasons to perform a well workover, however a primary workover can be carried out as long as the well completion is inefficient due to some of its damaged equipment, among these damaged equipment are the production tubing, downhole components such as safety valves and electrosubmersible pumps as the one shown below:

If we consider for example that a well has lowered its production or if it is null, it is very likely that some downhole equipment is damaged, in the case of an electrosubmersible pump, the reconditioning of the well for this case is to reach the well and establish a camp, since it is a job that can last between 7 to 15 days at the most, The operators must be under the supervision of the rehabilitation operations engineer, under his command they must take control of the well, for this purpose water or brine must be injected to control the formation pressures of the well, once the well is under control, the production tubing is taken out and the electro-submersible pump power cable clichés are removed.
Once all the drill pipe is removed, the pump is disconnected and replaced by a new one, the production tubing string is lowered again with the new pump and sticking new clamps to the power cable until reaching the final depth.
This is a case explained in a generalized way in which a workover of an electro-submersible pump can be performed and the production of the well can be recovered.
Conclusion
It should be noted that the reasons for which a workover of oil wells must be performed is to activate a well so that its production is optimized according to the capacities it has at the time, it is also important to note that well workovers are extended to the fact of having to intervene a well for reasons that go beyond its productivity, such as environmental reasons, in which a well can be intervened to correct engineering details in the design of the completion of the well that prevents proper production and that is environmentally friendly.
References
A NEW MATHEMATICAL MODEL FOR THE WORKOVER RIG SCHEDULING PROBLEM

Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.