The Role of the Immune System in Safeguarding Health
Yesterday, I woke up feeling a bit under the weather with a sore throat, runny nose, and cough. Despite not feeling my best, I pushed myself to carry on with my daily activities, trying not to appear weak. Little did I know that in the background, my immune system was working tirelessly to protect me and keep me healthy. This got me thinking about the incredible role our immune system plays in safeguarding our well-being from various health threats, ranging from simple flu to more complex conditions like cancer and pneumonia, or even the deadly Covid-19. Let's dive into the fascinating world of our immune system.
When people are asked to name the most crucial systems in our bodies, they often mention the Nervous System, Circulatory System, Respiratory System, and Digestive System, but they frequently overlook the immune system, which is equally vital. The immune system is a complex network of cells and proteins spread throughout our bodies, including macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, B cells, T cells, antibodies, complements, basophils, eosinophils, mast cells, and natural killer cells. These are just a few of the components that make up our intricate immune defense system.
A lot of us do not even understand our immune system works and that is why it is very difficult to understand the importance of vaccines. The immune system is an important part of our being alive, but it can also be the cause of our death either when they fail to function or are too active. The body is what is being defended by the immune system and this includes on top, under, and including the skin. So back to what the immune system does in the body. Generally, the immune system communicates, kill enemies, cause inflammation, activate other cells, produces antibiotics, kill infected cells, remember previously encountered antigens, and so on.
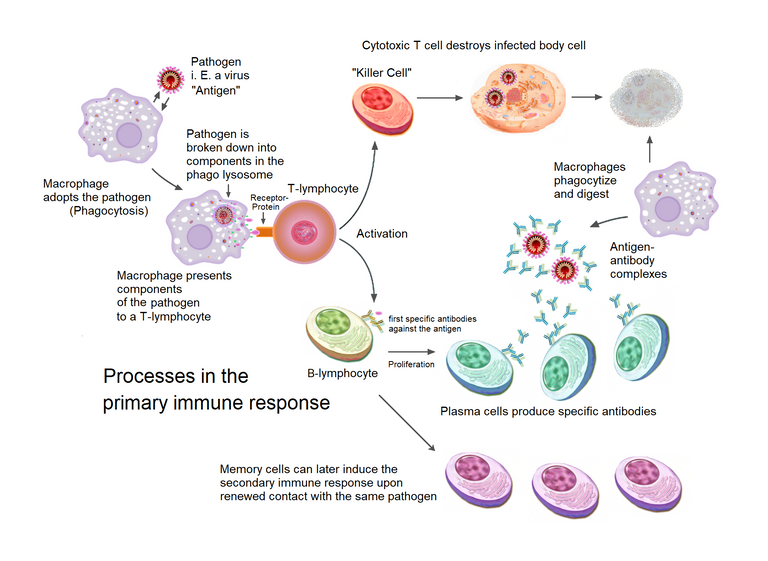
In the case of an infection from a cut, the first problem is the breaking of the skin and that is where bacteria are able to get into the body and start to reproduce. At the onset, the bacteria might not be identified but over time, they begin to damage the body. But as you would expect, the immune system swipes into action. Macrophages which are about 21 micrometer in diameter starts to engulf and trap the invading microorganism. After this is done, they begin to cause inflammation, after which they trigger other immune responses by releasing messager protein. Neutrophils rreaches this area and begin to release toxins to attack the invaders and after which they undergo self death to prevent them from destroying the body cells.
if the neutrophils are unable to eliminate the invading bacteria, dendritic cells step in and present the antigens to activate other cells that can fight the pathogens. In the case of a bacterial infection, the immune response moves to the lymph nodes, where Helper T-cells and Killer T-cells are activated to attack the invaders. Helper T-cells multiply to strengthen the attack and store a memory of the invader in the form of Memory T-cells. B-cells are also activated to produce antibodies like IgA, IgG, IgM, and IgE, while Memory B-cells are activated to recognize the invader in case of future encounters.
This is just a simplified explanation of a fraction of the immune system's incredible work. So, the next time you wake up with a sore throat or a minor infection that you might not consider significant, remember that your immune system is diligently working to keep you safe and healthy. It truly is a remarkable defender of our well-being.
Citation
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7148618/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279364/
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphys.2018.00113/full
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546670/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7840870/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2850372/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26827/

Immunology was one of the topics i found very interesting in the university, my anatomy lecturer kinda made if fun but his exams and questions were always too difficult so i lost interest along the way, but the idea of cells protect other cells and your system's integrity much like military and police protecting civilization is always a fascinating thing to learn
Immunology is very interesting, but one reason why a lot of us run away from it is our lecturers. Nigerian University lecturers usually make it almost impossible to like a course during exams because they want to show they are superior making us look like we didn't come for lectures 😂😂😂😂😂.
Yay! 🤗
Your content has been boosted with Ecency Points, by @busted1.
Use Ecency daily to boost your growth on platform!
Support Ecency
Vote for new Proposal
Delegate HP and earn more
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.