Exploring the Circulatory System of Scoliodon: A Vital Mechanism for Survival
Circulatory System of Scoliodon
Click on the image or click here to visit the image source : Skin and Respiratory System of Scoliodon
Scoliodon, commonly known as the spiny dogfish shark, is a fascinating aquatic creature that has captured the attention of marine biologists for decades. One of the key reasons for this fascination lies in the intricate workings of its circulatory system. The circulatory system of Scoliodon plays a vital role in its survival, enabling efficient oxygen transport, waste removal, and overall physiological functions. In this article, we will embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of Scoliodon's circulatory system, shedding light on its specialized features and highlighting its critical role in sustaining the shark's remarkable adaptability.
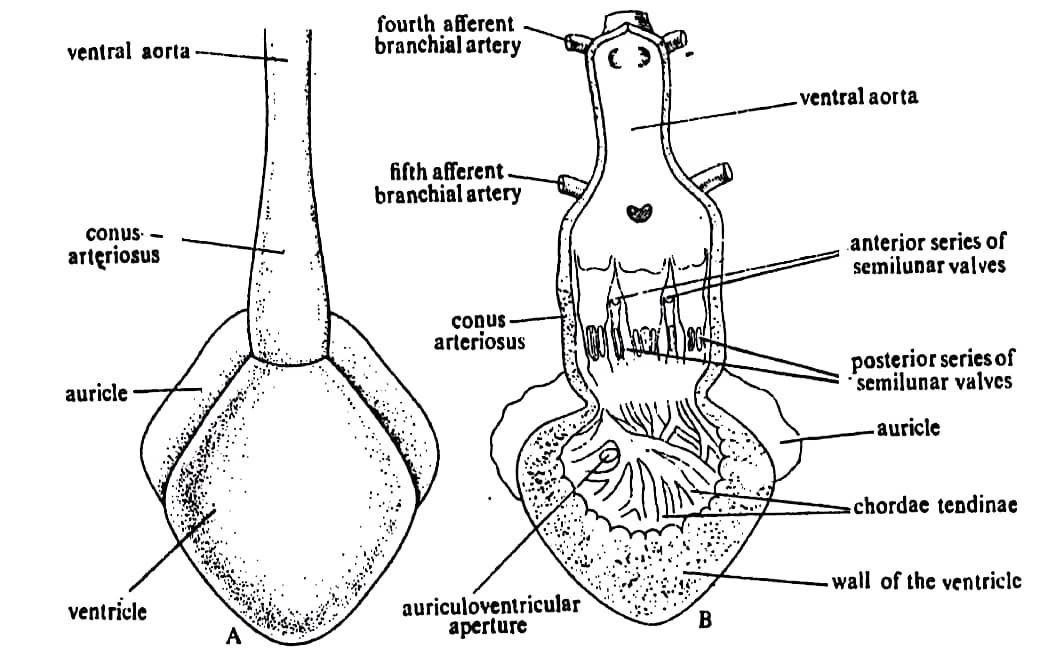
At the core of Scoliodon's circulatory system is its unique structure, known as the elasmobranch circulatory system. Unlike the familiar four-chambered heart of mammals, Scoliodon possesses a two-chambered heart, consisting of a single atrium and a single ventricle. This adaptation allows for a more streamlined circulation process, enabling efficient oxygenation and waste removal throughout the shark's body.
The circulatory process begins with the deoxygenated blood entering the heart through the sinus venosus. From there, it moves into the atrium and then into the ventricle. Here comes an interesting twist: Scoliodon has a specialized structure called the spiral valve within its ventricle. This valve serves to increase the surface area and prolong the time of contact between the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, ensuring a more effective oxygen transfer.
Once the ventricle contracts, the oxygenated blood is pumped out to the gills through a single large artery known as the afferent branchial artery. The gills play a crucial role in gas exchange, as they extract oxygen from the water and release carbon dioxide. In Scoliodon , the gill arches, equipped with numerous gill filaments, provide an extensive surface area for efficient oxygen uptake.
As the deoxygenated blood passes through the gills, it releases carbon dioxide and picks up fresh oxygen, becoming oxygenated once again. The oxygenated blood then enters the efferent branchial arteries and is distributed to the various tissues and organs of the shark's body.
Interestingly, Scoliodon exhibits a remarkable adaptation called regional heterothermy, where certain regions of its body maintain higher temperatures than others. This adaptation is supported by the circulatory system, as warm oxygenated blood is selectively directed to specific regions, such as the swimming muscles and brain, ensuring optimal functioning even in colder waters.
The circulatory system of Scoliodon is not only responsible for oxygen transport but also plays a crucial role in waste removal. Metabolic waste, such as carbon dioxide and urea, is carried away by the deoxygenated blood, which is then directed to the kidneys for filtration and removal of these waste products.
Furthermore, the circulatory system of Scoliodon also contributes to its impressive thermoregulation capabilities. By selectively redistributing warm oxygenated blood to different regions of its body, the shark can maintain an optimal body temperature, allowing it to thrive in various aquatic environments.
The circulatory system of Scoliodon is a marvel of adaptation and efficiency. Its specialized structure, two-chambered heart, spiral valve, and selective blood distribution mechanisms contribute to the shark's survival and adaptability in diverse aquatic habitats. By ensuring efficient oxygen transport, waste removal, and thermoregulation, this circulatory system enables Scoliodon to thrive as a successful predator in the vast oceans.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.
Congratulations @burn-it-down! You received a personal badge!
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
Check out our last posts:
Support the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!
There is reasonable evidence that this article is machine-generated. Posting such content is considered fraud. Fraud is discouraged by the community and may result in the account being Blacklisted.
Guide: Why and How People Abuse and Defraud
If you believe this comment is in error, please contact us in #appeals in Discord.