The cell wall in plants
(Edited)
The cell wall is an essential structure for plants, providing support, protection and participating in various physiological processes. Unlike animal cells, plant cells are surrounded by this rigid wall that gives them shape and strength.
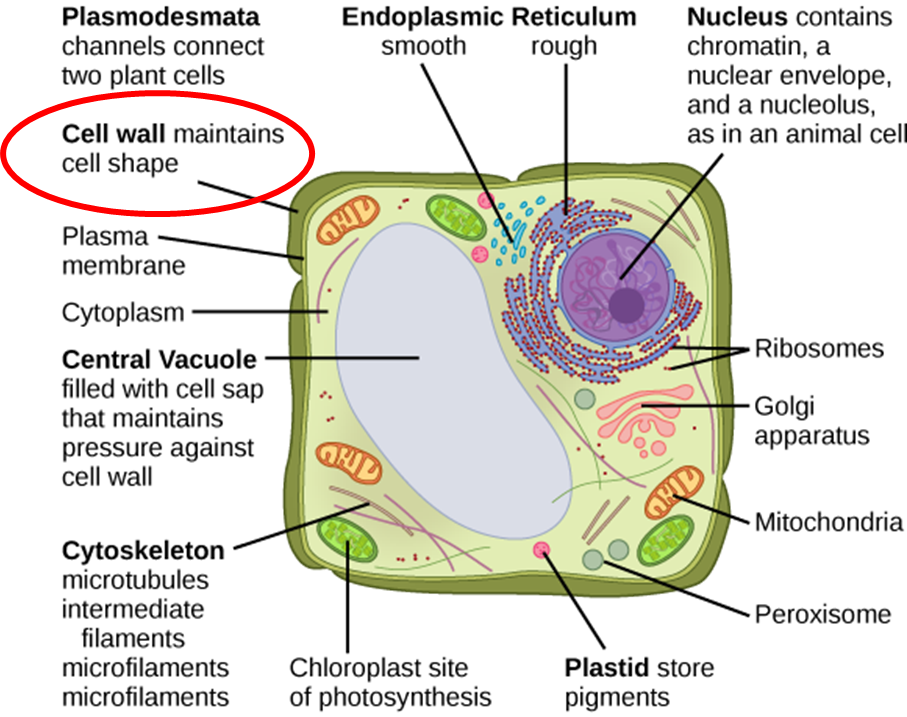
Among the main functions of the cell wall according to the mentioned to Mazparrote and Delescio (1998), are:
- Structural Support: the cell wall provides rigidity and shape to plant cells, which in turn allows the support of the entire plant.This rigidity is crucial so that plants can grow upright and maintain their shape.
- Protection: It acts as a physical barrier against pathogens such as fungi and bacteria, as well as against mechanical damage. The cell wall hinders the entry of these harmful agents into the cell.
Regulation of the passage of substances: Although it is a barrier, the cell wall also allows the passage of water, nutrients and other molecules necessary for the cell through pores. - Response to environmental stress: the cell wall can be modified in response to different types of stress, such as drought, salinity or pathogen attacks, strengthening the plant's resistance.
- Immunity: It plays a crucial role in the immunity of plants, it acts as a physical barrier that pathogens must overcome in order to colonize plant cells.
There is a pimary wall that is the first wall that forms around the cell, it is thin and flexible, allowing cell growth. A secondary wall is also formed between the primary wall and the plasma membrane once the cell has ceased its growth.It is thicker and stiffer than the primary wall, and its composition varies depending on the type of cell and its function.
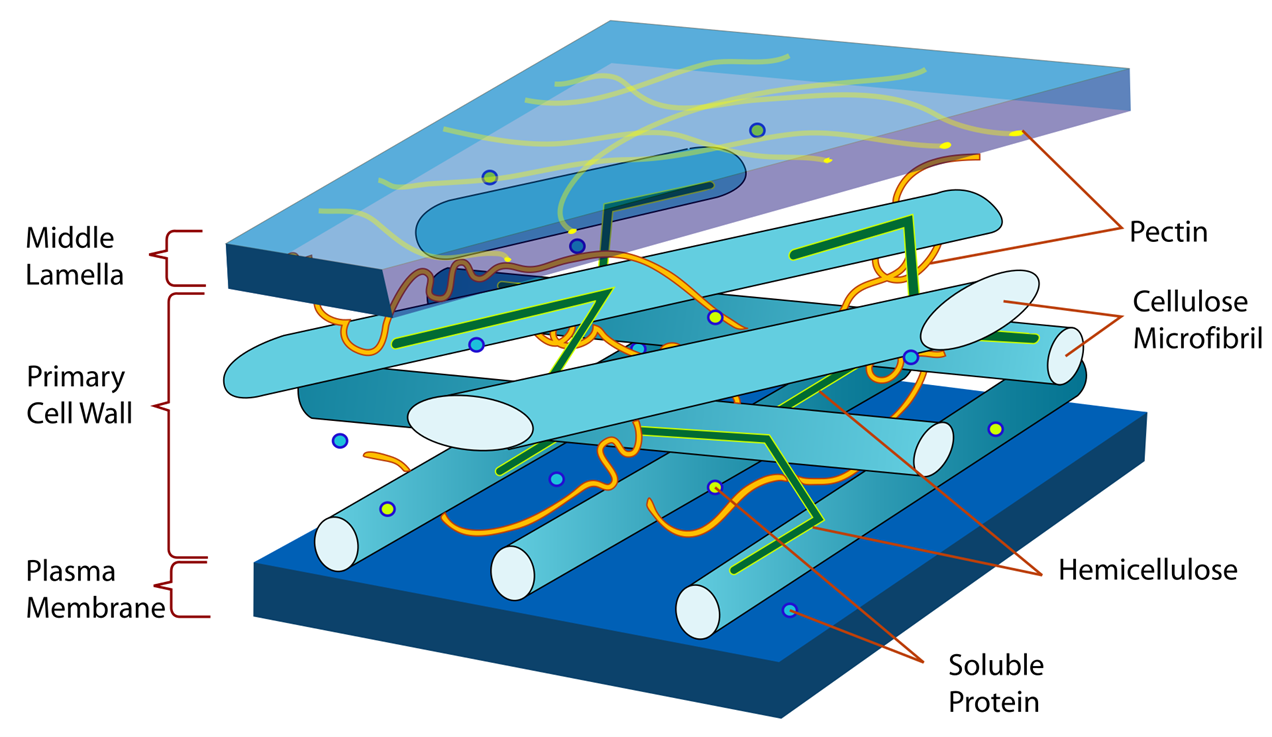
The cell wall is mainly composed of cellulose which is a polysaccharide that forms microfibrils that provide the main tensile force of the wall. Hemicellulose is another polysaccharide that interconnects cellulose microfibrils. Pectin, which is also a polysaccharide that provides flexibility and elasticity to the wall and Lignin: A complex polymer that is deposited on some cell walls, providing rigidity and resistance to compression, especially in woody tissues.
The study of the cell wall is fundamental in agriculture, as it allows us to better understand the resistance of plants to diseases and environmental stress. The development of varieties with more resistant cell walls can contribute to improving crop yields and reducing the use of pesticides. In the case of livestock farming, lignin is one of the components of the non-digestible cell wall in the stomach of the animal and makes the cell wall resistant to degradation, in that sense it is important to supply pastures that are not very mature because as the age of the pasture increases, more lignin accumulates.
Dear readers, the cell wall is a vital structure for plants, fulfilling essential functions for their survival and development, its complexity and dynamism make it an object of continuous study, with important implications in agriculture and biotechnology.
Thank you for reading our articles, until a next publication.
| Bibliographic references |
|---|
- Mazparrote, S. and Delascio, F. (1998). Botany. Biosphere Publishing House. Miranda, Venezuela.
- Fuentes, J. (1998).Agricultural botany. Mundi.press. Madrid, Spain.
Sources
- Photography and images: the images used in the article are in the public domain, information that can be verified in the link placed at the bottom of each image.
- Agrotecnia banner: made by the author @amestyj with own images
- Hive Banner: Designed by the author @amestyj with image owned by hive.



259
0
97.841 STEM
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.