Innovative Fire Starter Briquettes: A Sustainable Solution for Energy Production and Waste Management
Welcome back mga Ka-Research.
Let us explore the research paper of Sharmaine Roselle S. Sallan (@sharmavii)
Check the previous post of the research paper of the Grade 12 Sapphire.
Introduction:
The world is in dire need of sustainable energy sources as the demand for energy continues to rise, and non-renewable resources rapidly deplete. The environmental crisis caused by pollution and the depletion of natural resources calls for urgent action towards sustainable alternatives. The research entitled "Innovation on Eco-Waste: Developing All-Natural Fire
Starter Briquettes as an Alternative for Charcoal Lighter Fluids" offers a potential solution to reduce waste and minimize pollution through the production of all-natural fire starter briquettes. The study primarily focuses on utilizing agricultural waste to produce eco-friendly and cost-efficient fuel for everyday use.
Background:
Charcoal lighter fluids, commonly used to ignite charcoal, are derived from non-renewable fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. Moreover, the production process involves chemicals that are harmful to both human health and the environment. On the other hand, agricultural waste, such as sawdust, rice husks, and corn cobs, is a readily available resource that is often disposed of improperly, causing severe environmental and health concerns.
This research proposes a solution by utilizing agricultural waste to produce all-natural fire starter briquettes. The briquettes offer a cleaner, safer, and more sustainable alternative to charcoal lighter fluids. Furthermore, it provides an opportunity for waste-to-wealth conversion by transforming waste into a valuable product.
Methodology:
The research involves the collection, drying, and pulverization of agricultural waste materials. The powdered waste is then mixed with a binder, such as starch or molasses, and compressed into briquettes. The briquettes are then dried and tested for combustion efficiency, durability, and emission levels.
Results:
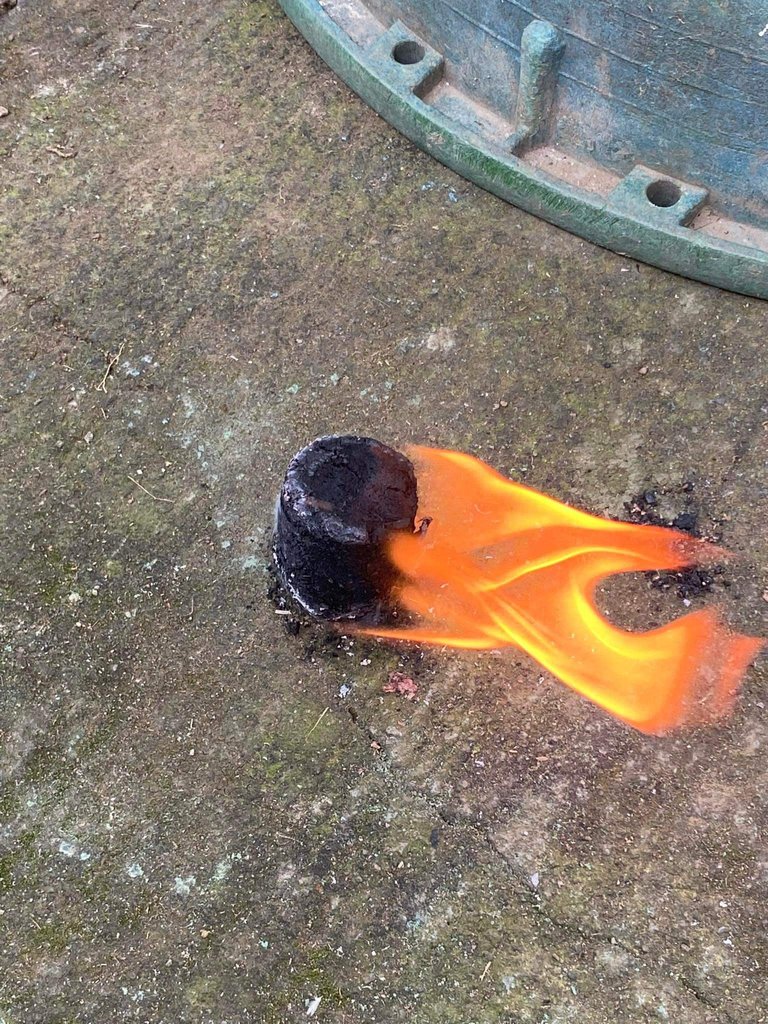
The study found that the all-natural fire starter briquettes have a higher combustion efficiency compared to traditional charcoal. The briquettes also produce lower emissions, reducing the negative impact on air quality and human health. Additionally, the briquettes are more durable than charcoal, maintaining their shape and integrity during handling and transportation. The use of agricultural waste also contributes to waste management, reducing the amount of waste disposed of in landfills and open fields.
Moreover, the production process of the all-natural fire starter briquettes is more cost-efficient than traditional charcoal production. The use of agricultural waste as a raw material significantly reduces the overall cost, making it a more affordable option for consumers. The production process also offers employment opportunities, contributing to socio-economic development.
Discussion:
The all-natural fire starter briquettes provide a promising alternative to charcoal lighter fluids. The use of agricultural waste as a raw material not only reduces waste but also contributes to sustainable energy production. Furthermore, the production process offers a cost-efficient and employment-generating solution to the energy crisis.
However, the study acknowledges the challenges in scaling up the production process. The mass production of the all-natural fire starter briquettes requires further research and development to ensure consistent quality and efficiency. Additionally, market acceptance and consumer behavior change are critical factors in promoting the adoption of this sustainable solution.
Conclusion:
The research on "Innovation on Eco-Waste: Developing All-Natural Fire Starter Briquettes as an Alternative for Charcoal Lighter Fluids" presents a promising solution towards sustainable energy production and waste management. The all-natural fire starter briquettes offer a cleaner, safer, and more cost-efficient alternative to traditional charcoal and charcoal lighter fluids. The study encourages further research and development to scale up the production process and promote market acceptance. The adoption of this sustainable solution can significantly contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and waste disposal concerns.
This research is a significant contribution to the growing body of literature on sustainable energy production and waste management. It highlights the potential of agricultural waste as a valuable resource and offers a promising solution to the energy crisis and pollution concerns. The all-natural fire starter briquettes present a sustainable and viable alternative to traditional charcoal and charcoal lighter fluids, providing significant benefits to both the environment and consumers.
The potential impact of this research is immense. It offers a solution to the energy crisis, air pollution, and waste disposal concerns while contributing to sustainable development and job creation. Further research and development in this area can lead to a more significant adoption of the all-natural fire starter briquettes, leading to a reduction in the use of charcoal lighter fluids and traditional charcoal. This, in turn, can lead to a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, contributing to the global efforts to mitigate climate change.
Moreover, the use of agricultural waste as a raw material for the production of the all-natural fire starter briquettes offers a solution to the waste management crisis. It provides a valuable use for agricultural waste, reducing the amount of waste disposed of in landfills and open fields, and contributing to waste reduction efforts.
The study also highlights the potential for job creation in the production of the all-natural fire starter briquettes. The production process offers employment opportunities, contributing to socio-economic development and poverty reduction.
In conclusion, the research on the development of all-natural fire starter briquettes presents a promising solution towards sustainable energy production and waste management. It offers a cleaner, safer, and more cost-efficient alternative to traditional charcoal and charcoal lighter fluids while contributing to sustainable development, job creation, and waste reduction efforts. The study encourages further research and development in this area to promote market acceptance and adoption of the all-natural fire starter briquettes. The potential impact of this research is immense, contributing to the global efforts to mitigate climate change, promote sustainable development, and reduce waste disposal concerns.
THANK YOU FOR READING
References:
1. Abubakar, S., & Imam, S. (2021). A review on the production and utilization of briquettes from agricultural waste. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 136, 110462.
2. Hossain, M. M., & Adelina, S. (2016). Sustainable production of briquettes from agricultural waste. International Journal of Renewable Energy and Water Resources, 4(3), 182-189.
3. Meng, J., Chen, H., & Zhang, S. (2018). Biomass briquettes: Status, challenges, and opportunities. Bioresource Technology, 259, 377-391.
4. Nyambuya, T. N. (2015). Towards sustainable waste management in Zimbabwe: An appraisal of the potential of biomass briquetting. Journal of Cleaner Production, 107, 630-638.
5. Oyedepo, S. O., & Fagbenle, R. O. (2016). Sustainable energy production from waste biomass: A review of biomass briquetting. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 65, 922-931.